Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Waja F3
Uploaded by
Nanteni Ganesan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views80 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views80 pagesWaja F3
Uploaded by
Nanteni GanesanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 80
Learning Objective: 1.
1 Analysing the human breathing mechanism
__
6
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the structure of the human respiratory system
Identify the structure of the lung
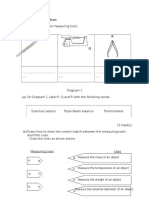
1. Label the diagram below to identify the structure of the human respiratory system
using the words given.
2. Label the diagram below to identify the structure of the lungs using the words given.
1 / 0
a!
"""""""""""""""""""
c!
"""""""""""""""""""
b!
"""""""""""""""""""
#rachea $ronchus %ungs
#rachea Alveolus $ronchiole
a!
"""""""""""""""""""
b!
"""""""""""""""""""
c!
"""""""""""""""""""
Learning Objective: 1.1 Analysing the human breathing mechanism
__
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the process of inhalation and e'halation
(elate changes of air pressure in thoracic cavity to inhalation and e'halation
&escribe the breathing mechanism
1. Underline the correct answer in the statements below to describe the process of
inhalation and e'halation.
a. Inhalation is the process in which air is forced )in / out of! the lungs.
b. *'halation is the process in which air is forced )in / out of! the lungs.
2. Underline the correct answer to relate the changes of air pressure in thoracic cavity
during inhalation and e'halation.
a. &uring inhalation+ air pressure in the lungs is )less / greater! than the air pressure
outside the body.
b. &uring e'halation+ air pressure in the lungs is )less / greater! than the air pressure
outside the body.
,. #he diagram below show the breathing mechanism during inhalation and e'halation.
Underline the correct answer in the statements below to describe the breathing
mechanism during inhalation and e'halation.
During inhalation-
a. #he rib cage moves upwards and )inwards / outwards!.
b. #he diaphragm contracts and moves )upwards / downwards!.
During exhalation-
a. #he rib cage moves downwards and )inwards / outwards!.
b. #he diaphragm rela'es and moves )upwards / downwards!.
2 / 0
Learning Objective- 1.2 .nderstanding transport of o'ygen in the human body
__
/
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the diffusion of o'ygen from the alveoli into the blood capillaries
&escribe the transport of o'ygen by blood
&escribe the diffusion of o'ygen from blood capillaries into the cells
#he diagram below shows the diffusion of o'ygen from alveolus into a blood
capillary.
1. Underline the correct answers for the following 0uestions to describe the diffusion of
o'ygen from the alveoli into the blood capillaries.
a. In the lungs+ o'ygen diffuses from the )alveoli / blood capillaries! into
the )alveoli / blood capillaries!.
b. An alveolus has )thin / thic1! walls and a moist inner surface.
c. Inhaled air in the alveoli has a )higher / lower! concentration of o'ygen gas
compared to the blood in the capillaries.
2. Complete the statement below to describe the transport of o'ygen by blood.
2'ygen combines with the haemoglobin in the red blood cells to form
"""""""""""""""""""""""""""and is transported from the lungs to our body cells.
,. Underline the correct answers for the following 0uestions to describe the diffusion of
o'ygen from blood capillaries into the cells.
a. $lood containing o'yhaemoglobin in the blood capillaries has a )higher / lower!
concentration of o'ygen.
b. 2ur body cells are constantly using up o'ygen for respiration and thus have a
)higher / lower! concentration of o'ygen.
c. #his difference in o'ygen concentration between the blood capillaries and the cells
results in the diffusion of o'ygen from the )cells / blood capillaries! into the
)cells / blood capillaries!.
, / 0
Learning Objective: 2.1 .nderstanding the transport system in humans
__
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the circulatory system as a system of tubes with a pump and valves that
ensure one3way flow of blood.
4tate the function of the heart.
Identify the structure of the human heart.
1. Complete the statement below to describe the circulatory system in human using the
words given.
#he """""""""""""""""" in the human body flows in a one3way direction.
#he """""""""""""""""" pumps the blood through tubes called blood vessels.
#he """"""""""""""""""" ensure the blood flows in one direction.
2. Complete the following statement to state the function of the heart.
#he hearts is a muscular organ that """"""""""""" blood to all parts of the body.
,. Label the diagram below to show the structure of human heart using the words
given.
5 / 0
blood valves heart
c.
a.
d.
b.
%eft ventricle 6ena cava 7ulmonary vein #ricuspid valve
Learning Objective: 2.1 .nderstanding the transport system in humans
__
10
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
8ompare and contrast the structure of arteries+ veins and capillaries+
(elate the characteristics of the blood vessels to their functions+
1. #he diagram below shows a cross section of a vein+ capillary and artery.
Underline the correct answers below to compare and contrast the structure of
arteries+ veins and capillaries.
Types of blood
vessel
Characteristics
Thickness of all !i"e of lumen
#resence of
valves
6ein )thic1 / thin! )small / big! )yes / no!
8apillary 2ne cell thic1 6ery small )yes / no!
Artery )thic1 / thin! )small / big! )yes / no!
2. Dra lines to match the characteristics of the blood vessels with their functions.
Characteristics $unctions
6alves along the blood vessels
#o withstand high pressure of the
blood flowing through
#hic1 muscular wall #o prevent bac1flow of the blood
2ne3cell thic1 wall
#o allow e'change of materials
with the surrounding tissue
9 / 0
%ower parts of the
body
.pper parts
of the body
(ight %ung %eft %ung
:eart
Learning Objective: 2.1 .nderstanding the transport system in humans
__
6
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
8ompare and contrast o'ygenated and deo'ygenated blood.
Illustrate the path of blood flow in the circulatory system.
1. Complete the table below to compare and contrast between o'ygenated and
de3o'ygenated blood.
Oxygenated %lood De&oxygenated %lood
(ich in """"""""""""""""""""""".
8ontents (ich in carbon dio'ide.
$right """"""""""" in colour.
8olour &ar1/7urplish red in colour.
.sually flows out from the heart.
&irection
of flow
.sually flows """""""""" the heart.
;lows out from the lungs through the
pulmonary vein.
$lood
vessel
;lows to the lungs through the
""""""""""""""""""""".
2. #he diagram below shows the path of blood flow in the human circulatory system.
Complete the statements below to illustrate the path of blood flow.
#he flow of blood can be divided into two paths. In one path+ de3o'ygenated blood
flows between the heart and the """""""""""""and in another path+ o'ygenated
blood flows between the """"""""""""""" and the rest of the body. #his complete
circulation is called the double circulatory system.
6 / 0
Learning Objective: 2.1 .nderstanding the transport system in humans
__
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the role of the blood circulatory system in the transport of substances.
*'plain the importance of maintaining a healthy heart.
1. Complete the statement below to describe the role of the blood circulatory system in
the transport of substances using the words given.
#he main function of the circulatory system is to transport substances li1e
"""""""""""""""""""" and """"""""""""""""""" to cells and carries
"""""""""""""""""""""" and """"""""""""""""""""""""" away from the cells.
2. Complete the statements below to e'plain the importance of maintaining a healthy
heart using the words given.
a. #he heart is a vital organ in the """""""""""""""""""" system of the body.
b. <e can avoid heart disease by not """""""""""""""" cigarettes.
c. :ave a healthy diet that is low in cholesterol and """""""""""""""".
d. <e must also reduce salt and """"""""""""""""""""" regularly.
= / 0
waste products o'ygen carbon dio'ide nutrients
smo1ing transport fats e'ercise
Learning Objective: 2.1 Analysing the human blood
__
1
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
4tate the constituents of blood and their functions
4tate the blood groups
>atch the blood group of the donor to that of the recipient
?ustify the importance of blood donation
&escribe how donated blood is stored and handled
1. Dra lines to match the blood constituents with their functions.
%lood Constituent $unctions
(ed blood cells #ransport needed substances
<hite blood cells ;ight off diseases
7lasma :elp the blood to clot
7latelets #ransport o'ygen
2. Complete the statement below to state the blood groups.
:uman blood can be classified into four groups@ """""""+ """"""+ """""" and A$.
,. Complete the table to match the blood group of the donor to that of the recipient.
Donors 'ecipients
A$
A
$
2 2
5. Tick ()* the correct statement below to Austify the importance of blood donation.
a. $lood is re0uired for surgery. ) !
b. $lood is re0uired to treat patients with leu1aemia. ) !
c. $lood is re0uires to treat patients with haemophilia. ) !
d. $lood cannot be manufactured synthetically. ) !
9. Complete the statements below to describe how donated blood is stored and
handled using the phrases given.
a. """""""""""""""""""is important to ensure that the blood is not contaminated
b. $efore any """"""""""""""""""""" is done+ the blood is tested for compatibility.
c. $lood are stored in """"""""""""""""" and can last for about 50 days.
d. """""""""""""""""""""are stored as whole blood or separated as plasma+ red
blood cells or platelets.
/ 0
blood transfusion &onated blood blood ban1 $lood screening
Learning Objective: 2., Analysing the transport system in plants
__
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe how wilting occurs
&escribe what transpiration is
&escribe the function of stomata
1. Complete the statements below to describe how wilting occurs using the words given.
a. <ilting occur when plants loses more """"""""""""""" than it can absorbs.
b. #he cells of the plant lose their turgidity and become soft or """""""""""".
2. Complete the statement below to describe what transpiration is using the words
given.
#ranspiration is the process in which plants lose """""""""""""" by evaporation
through small openings on the leaves or """"""""""""""""".
,. Complete the statements below to describe the function of stomata using the words
given.
a. #he stomata of plants are usually open during the day to enable the e'change of
"""""""""""""""""""""""""" and """"""""""""""""" to ta1e place mainly for
photosynthesis.
b. #he stomata are closed on a hot day to """""""""""""" the loss of water by
""""""""""""""""""""""".
/ / 0
o'ygen reduce transpiration carbon dio'ide
water flaccid
stomata water
Learning Objective: 2., Analysing the transport system in plants
__
10
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the factors affecting the rate of transpiration
&escribe how the factors affect the rate of transpiration
&escribe the roles of transpiration
1. Complete the diagram below to identify the factors affecting the rate of transpiration.
2. Underline the correct answer below to describe how the factors affect the rate of
transpiration.
)a! 7lants transpire )faster+ slower! in the presence of light than in the dar1.
)b! #ranspiration is faster at a )higher+ lower! temperature.
)c! :igh humidity causes a )faster+ slower! rate of transpiration.
)d! #he more windy the surroundings+ the )higher+ lower! the rate of transpiration.
,. Complete the statements below to describe the roles of transpiration using the words
given.
)a! #ranspiration gets rid of e'cess """""""""""""""""from the plants.
)b! #ranspiration cools the plants by removing """""""""""
)c! #ranspiration helps to draw up water and """""""""""""""" from the soil.
10 / 0
;actors of #ranspiration
b. c. d. a. <ind
heat mineral salts water
Learning Objective: 2., Analysing the transport system in plants
__
11
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the locations of 'ylem and phloem
&escribe the functions of 'ylem and phloem
1. #he diagram below shows the cross section of a leaf+ stem and root of a plant.
Identify the xylem and phloem.
2. Dra lines to match 'ylem and phloem with the correct functions.
11 / 0
# -""""""""""""""""""
+ -""""""""""""""""""
' -""""""""""""""""""
! -""""""""""""""""""
T -""""""""""""""""""
U -""""""""""""""""""
Xylem
7hloem
#ransports food from the leaves
4ituated in the inner part of plant stem cell
#ransports water
4ituated in the outer part of plant stem cell
#ransports minerals
Learning Objective: ,.1 .nderstanding human e'cretion
__
10
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
*'plain what e'cretion is.
Identify the e'cretory organs in humans.
4tate the e'cretory products of each e'cretory organ.
*'plain the importance of e'cretion.
1. Complete the following statement to e'plain what e'cretion is.
*'cretion is the process of removing """"""""""" products from our body.
2. Label the e'cretory organs #, + and ' in humans in the diagram below.
,. Complete the table to show the e'cretory products of the following e'cretory organs.
-xcretory organs -xcretory products
Bidney and s1in
*'cess water+ mineral salts and """"""""""""
%ungs
*'cess water and """""""""""""""""".
5. Tick (* the correct statements which e'plain the importance of e'cretion.
)a! *'cretion helps to remove to'ic substances from our body.
)b! <e will fall sic1 or even die if the e'cretory products are not
removed from the body.
)c! *'cretion helps to increase our body temperature.
)d! *'cretion 1eeps us healthy.
12 / 0
(
7
C
Aorta
6ena cava
Bidney
a.
c.
b.
Learning Objective- ,.2 Analysing the urinary system in human
__
=
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the locations of 1idneys and other parts of the urinary system.
&escribe the shape of the 1idney.
Identify the structures of the 1idney.
1. Label the parts of the urinary system with the words given.
2. Complete the following statement to describe the shape of the 1idney.
#he 1idneys are """""""""""" shaped
,. Label the structures of the 1idney with the words given.
1, / 0
.rethra .reter .rinary bladder
8orte' >edulla 7elvis
.reter
(enal vein
(enal artery
c.
b.
a.
Learning Objective- ,.2 Analysing the urinary system in human
__
=
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes-
&escribe the functions of the 1idney.
*'plain the importance of maintaining healthy 1idneys.
1. Complete the following statements to describe the functions of the 1idney using
words given.
a. #he 1idney filters blood and removes urea+ e'cess mineral salts and water in the
form of """""""""""""
b. #he 1idney maintains the """"""""""""""balance in the body.
c. #he 1idney ensures that the """"""""""""" pressure is at a normal level.
d. #he 1idney reabsorbs """"""""""""" into the bloodstream.
2. Complete the passage below to e'plain the importance of maintaining healthy
1idneys using words given.
Bidney """"""""""""""" is a condition in which the 1idney cannot carry out
their normal functions. As a result+ waste products are accumulated and will
cause""""""""""""""" to our body. Bidney failure can be treated through
"""""""""""""""".
15 / 0
blood water urine glucose
dialysis harm failure
Learning Objective: ,., Analysing e'cretion in plants
__
9
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the ways plants eliminate their e'cretory products.
Identify the e'cretory products of plants.
1. Tick (* the correct ways in which plants eliminate their e'cretory products.
)a! 7hotosynthesis ) !
)b! <ilting ) !
)c! #ranspiration ) !
2. Complete the table below to show the e'cretory products of plants using the words
given.
-xcretory method -xcretory products
(espiration
"""""""""""""""""" and water
4hading of leaves+ flowers and
bar1 """""""""""""""""" wastes
19 / 0
8arbon dio'ide Ditrogenous
Learning Objective- 5.1 .nderstanding se'ual and ase'ual reproduction
__
=
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes-
4tate the importance of reproduction.
4tate the types of reproduction.
4tate what fertilisation is.
&escribe internal and e'ternal fertilisation.
1. Underline the correct answers to state the importance of reproduction.
(eproduction is the process in which living things produce new individuals or
)spring / offspring! and ensures the )continuity / e'tinction! of the species.
2. Underline the correct answers to state the types of reproduction.
#he two types of reproduction are 4e'ual reproduction and )Ase'ual / $ise'ual!
ase'ual reproduction and involves )one / two! organism or parent.
,. Complete the statements below to state what fertiliEation is.
;ertilisation is the process in which a sperm or male gamete fuses with an
""""""""""""" or female gamete to form a Eygote.
5. Underline the correct answer to describe internal and e'ternal fertilisation.
a. *'ternal fertilisation ta1es place )inside / outside! the body of a female.
b. Internal fertilisation ta1es place )inside / outside! the body of a female.
16 / 0
!exual reproduction .sexual reproduction
!imilarities
7roduces new organisms for continuity of species
Individuals
Fametes
;ertiliEation
Dumber of
2ffspring
Learning Objective: 5.1 .nderstanding se'ual and ase'ual reproduction
__
X100 = %
Learning Outcome:
8ompare and contrast se'ual and ase'ual reproduction.
1. Underline the correct answers below to compare and contrast se'ual and ase'ual
reproduction
1= / 0
Differences
)2ne individual / #wo individuals!
)>ale G ;emale / Do gametes needed!
)Deeded / Dot needed!
)%imited / Dot limited!
)2ne individual / #wo individuals!
)>ale G ;emale / Do gametes needed!
)Deeded / Dot needed!
)%imited / Dot limited!
Finger Amoeba >ucor 4tarfish :ydra
Heast ;erns 7aramecium Frass
Learning Objective: 5.1 .nderstanding se'ual and ase'ual reproduction
__
9
X100 = %
Learning Outcome:
8lassify animals and plants according to their ways of reproduction.
1. #he diagram below shows e'amples of living organisms.
Classify these animals and plants ase'ually.
1 / 0
4pore ;ormation (eAuvenation $inary fission
1. Amoeba
2."""""""""""""
1. >ucor
2. """"""""""""""""
1. 4tarfish
$udding
1. :ydra
2."""""""""""""""
6egetative reproduction
1.""""""""""""""""
2.""""""""""""""""
"
Ase'ual reproduction
#o carry sperms from the testes.
#o produce male gametes
7enis
#o produce a mil1y fluid that protects the sperm
#estes
4perm duct
7rostate Fland
#o transfer sperms into female reproductive
organ
4crotum
a!
b!
c!
Learning Objective- 5.2 Analysing the male reproductive system
__
10
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the parts of the male reproductive system.
&escribe the functions of the different parts of the male reproductive system.
4tate the role of sperm in reproduction.
&escribe the changes in male during puberty.
1. #he diagram shows the male reproductive system.
Label the following parts using words below.
2. Dra lines to match the following parts of the male reproductive with the correct
functions.
,. Underline the correct words the statement below to show role of sperm in
reproduction.
4perms produced in the testes can swim about in the female se' organ to
)ovulate / fertilise! the egg cell or ovum.
5. Complete the following statements to describe the change in male during puberty
using the word below.
1/ / 0
#estes 7enis 4perm duct
hair sperms increases
2vary 8ervi' .terus
Learning Objective- 5., Analysing the female reproductive system
__
=
X100 = %
After puberty between the age of 12 and 15+ the body of a boy """""""""""""" and
grows """"""""""""""" on the face+ armpits and around the pubic region. #he
reproductive system matures and begins to produce """"""""""""""
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the parts of the female reproductive system.
&escribe the functions of the different parts of the female reproductive system.
4tate the role of an ovum in reproduction.
1. #he diagram shows the female reproductive system.
Label the following parts using the words given.
2. Dra lines to match the parts of the female reproductive with the correct functions.
,. Complete the statement below which states the role of an ovum.
#he role of the ovum is to be """""""""""""""""" by a sperm to form a Eygote.
20 / 0
#o allow the baby to go out during birth.
#o 1eep and protect the developing
embryo.
#o produce egg cells )ova!
2vary
#o direct an ovum from an ovary to the
uterus
.terus
8ervi'
;allopian
tube
b.
c.
a.
Learning Objective- 5., Analysing the female reproductive system
__
1,
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes-
&escribe the changes in female during puberty.
8ompare and contrast male and female gametes in term of siEe+ numbers and
mobility.
1. Complete the following statements to describe the changes in female during puberty
using the word given.
After puberty between the age of 10 and 12+ the body siEe of a girl """"""""""""""
and grows """"""""""""""" on armpits and around the pubic region.
:er """"""""""""""""" begins to develop and becomes bigger. #he ovary
begins to release a mature egg or """""""""""""" every 2 days. 4he will
have her """"""""""""""""""""" at a regular interval about 2 days.
2. Underline the correct answers below to compare and contrast a male gamete and a
female gamete.
21 / 0
breasts increases hair ovum menstruation
&ifferences
)#estes / 2vary!
)4mallest cell / %argest cell!
)2ne / >illions!
)8an swim / 8annot move!
4perm cell 2vum cell
)#estes / 2vary!
)4mallest cell / %argest cell!
)2ne / >illions!
)8an swim / 8annot move!
2rgan
4iEe
Dumber
>obility
Learning Objective- 5.5 Analysing the menstrual cycle
__
10
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the meaning of menstruation.
&escribe the menstrual cycle.
&escribe the changes in the uterus wall during menstrual cycle.
(elate the fertile phase of the menstrual cycle to fertiliEation.
1. Complete the statement below to describe the meaning of menstruation using the words
given.
>enstruation is the """""""""""""""" through the cervi' and """"""""""""""of
the female and the menstrual discharge contains""""""""""""""+ dead ovum and
layer of tissue from the """"""""""""""""""""""""".
2. #he diagram below shows the menstrual cycle.
Complete the following statement to describe the menstrual cycle based on the
diagram above.
a. >enstruation starts on the """""""""""" day.
b. #he menstrual cycle consist of """""""""""""""days.
c. A mature egg or ovum will be released on the """"""""""""" day.
Complete the following statement in 0uestions , and 5 using the words given.
,. &uring menstruation+ the walls of the uterus will """""""""""""""""""". If
fertilisation ta1es place+ the wall of the uterus will continue to
""""""""""""""""""".
22 / 0
vagina blood discharge blood uterus wall
.terus wall brea1s down
.terus wall begins to thic1en
A mature ovum is released
If fertilisation ta1es
place+ the uterus wall
will continue to thic1en
$rea1 down thic1ens ;ertilisation
Learning objective- 5.9 Analysing fertiliEation and pregnancy
__
6
X100 = %
5. """"""""""""""""""""" will occur if a single sperm is able to swim into the uterus
during the fertile phase of the menstrual cycle and fuses with a mature ovum.
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe fertilisation in human
Identify the location of implantation of embryo
&escribe the development of a Eygote into an embryo and subse0uently into a foetus
until birth.
1. Complete the statement below to describe fertilisation in human using the words
given.
;ertilisation is the fusion between the """""""""""" and the """""""""""""
which ta1es place in the """""""""""""""""""""" to produce a Eygote.
2. >ar1 with / the location of implantation of the embryo in the figure below.
,. Complete the chart below on the se0uence of development until a baby is born using
the words given.
2, / 0
sperm fusion ;allopian tube ovum
2vum ;ertilisation *mbryo
Learning Objective- 5.6 .nderstanding the importance of pre3natal care
__
=
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
(elate the importance of ta1ing nutritious food to the health of both mother and
foetus during pregnancy.
*'plain the importance of avoiding the inta1e of substances that are harmful to the
foetus
1. Dra lines to match the type of food with its function to relate the importance of
ta1ing nutritious food to the health of both mother and foetus during pregnancy.
$ood $unction
6itamins a! 7revention of constipation in mother
;ibre b! ;or formation of haemoglobin in the
red blood cells.
7rotein c! #o build body tissues and growth.
8alcium and
7hosphorus
d! #o strengthen bones and teeth of
foetus and prevent tooth decay in the
mother
Iron e! #o strengthen the immune system
2. Complete the table below to e'plain the importance of avoiding the inta1e of
substances that are harmful to the foetus using the words given.
small baby mental retardation heart damage abnormal baby
.lcohol Drugs !moking
3 $rain damage 3 >iscarriage
25 / 0
Learning Objective- 5.= *valuating the importance of research in human reproduction
__
9
X100 = %
__
,
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
4tate the meaning of sterility.
&escribe ways to overcome sterility.
1. Underline the correct answer in the statement below to describe the meaning of
sterility.
4terility is the )inability / ability! to reproduce.
2. Complete the table below to match sterility with the correct ways to overcome
sterility using the information given.
0ays to overcome sterility
!terility
#a1ing nutritious food
4urgery
:ormone treatment
In vitro fertiliEation
29 / 0
a. #o increase sperm or egg production.
b. :elp to prevent sterility.
c. 8orrect the problems such as bloc1ed ;allopian tubes or bloc1ed sperm ducts.
d. :elp infertile couples conceive which fertiliEation occurs in the culture dishes.
%earning 2bAective- 5.= *valuating the importance of research in human reproduction
Learning Objective- 5.= *valuating the importance of research in human reproduction
__
X100 = %
Learning Outcome:
&escribe the methods of birth control
1. Dra lines to match the following methods of birth control with the correct
description.
1ethod -xamples Description
8hemicals
$irth control pills a. Involves refraining from
copulation during the fertile
phase.
4permicides b. >ade of artificial hormones to
prevent ovulation and the
release of ovum.
4urgical
6asectomy c. A device inserted into the
uterus to prevent implantation
%igation
d. 8ontain chemicals to 1ill
sperm.
$arrier /
>echanical
8ondom
e. 7revent ovulation and the
release of ovum.
I.8&
f. 4perm ducts are cut and
legated.
&iaphragm
g. ;allopian tubes are cut and
ligated.
(hythm method
h. #hin rubber cap fitted at the
cervi'
Learning Outcomes:
7resent argument against the abuse of birth control and its effects on the community.
*'plain the importance of research on human reproduction
26 / 0
Learning Objective: 5. Analysing the se'ual reproduction system of flowering plants
__
10
X100 = %
1. Complete the chart below using the list given.
2. 0rite #rue )#! or ;alse );! the importance of research on human reproduction.
a! 8an control an ever increasing world population. ) !
b! >arried couples cannot plan their number of children. ) !
c! #o find new and better methods of birth control. ) !
d! 4olve the problems of couples who do not have children. ) !
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the different parts of a flower.
Identify the male and female reproductive parts of a flower.
Identify the male and female gametes
2= / 0
-ffect of birth
control on the
community
2ood effect %ad effect
-
- - -
a! encourage free se'
b! prevent unwanted pregnancies
c! helps a family to limit the number of
children
d! can lead to a grey population
Learning Objective- 5./ Analysing pollination
__
=
X100 = %
&escribe the functions of the male and female reproductive parts of a flower in se'ual
reproduction.
1. Label the different parts of a flower using the words given.
2. #he diagram below shows the male and the female reproductive parts of a flower.
Underline the correct answer for the following statements.
a. #he )stamen / pistil! is the male reproductive part of a flower.
b. #he )stamen / pistil! is the female reproductive part of a flower.
,. Dra lines to match the reproductive parts of a flower with the correct statement
below.
5. Underline the correct answer for the following statements.
a. #he male reproductive parts of a flower consist of the )anther / ovary! which
produces pollen grains containing the male gametes.
b. #he female reproductive parts of a flower consist of the )anther / ovary! which
produces the ovule containing the female gametes.
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe what pollination is.
(elate the characteristics of flower to their agents of pollination.
4tate the types of pollination.
1. #he diagram below shows the process of pollination.
2 / 0
petal ovary anther stigma
b)
a)
c) d)
anther
filamen
t
stamen
stigma
style
ovary
ovule
pistil
Stamen
Pistil
Produces pollen grains which contain the
male gametes.
Produces ovules which contain the egg cells
or the female gametes.
Insect-pollinated flowers
and
ird-pollinated flowers
!lowers are small" dull coloured without
any smell or nectar. Pollen grains are
smooth with long filaments and hang out of
the flower.
#ind-pollinated flowers
!lowers are large and brightly coloured.
Produces a lot of sweet scented nectar.
Pollen grains are large and stic$y or spi$y
#ater-pollinated flowers
!lowers are found in plants that gorw near
water with pollen grains that can float on
the surface of water.
Learning Objective: 5./ Analysing pollination
__
11
X100 = %
Complete the sentence below to describe what pollination is.
7ollination is the transfer of pollen grains from """"""""""""" to """"""""""""".
2. Dra lines to match the characteristics of flower to their agents of pollination
,. Label the diagram below with the correct type of pollination using the words given.
Learning Outcomes:
8ompare and contrast self3pollination and cross3pollination.
*'plain the advantages of cross3pollination.
1. a. Complete the table below to compare and contrast self3pollination and cross3
pollination.
2/ / 0
Self-pollination %ross-pollination
4imilarities
Learning Objective: 5./ Analysing pollination
__
,
X100 = %
b. Underline the correct answers below.
2. #he following shows the advantages of cross3pollination.
Underline the correct answer for some of these advantages.
a. :as the characteristics of both the parent plants.
b. 7roduces )better / bad! fruits and seeds.
c. 7roduces )higher / lower! yield.
d. )%ess / more! resistant to diseases.
e. >ore adaptable to the environment.
Learning Outcome:
*'plain with e'amples the advantages of cross3pollination in agriculture.
1. Complete the table below to e'plain the advantages of cross3pollination in
agriculture using the information below.
,0 / 0
!elf&pollination
Cross&pollination
$oth processes involves the transfer of the pollen grains from
an """"""""""""""" to a """"""""""""""
&ifferences
a. )4ame / &ifferent! plants
b. )2ne / >any !
c. )Deeded / Dot needed!
a. )4ame / &ifferent! plants
b. )2ne / >any!
c. )Deeded / Dot needed!
;lowers fromII.
Dumber of plants
involved
Agents of pollination
Learning Objective: 5.10 .nderstanding the development of fruits and seeds in plants
__
=
X100 = %
Uses .dvantages
a! ;or e'amples paddy plants that have shorter
stal1s and upright leaves are easier to harvest.
b! 7roduces variety of paddy that ta1es shorter
time to mature such as >ahsuri and >alinAa.
c! #o increase yield of crops Dew varieties of paddy such as Badaria+
4e1embang and 4etanAung can increase the
yield of paddy in >alaysia from 1 ton/hectare to
5 tons/hectare.
d! >A(&I has produced a variety of paddy that is
resistant to red disease caused by a virus
carried by insects.
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the location where fertiliEation occur in flower
&escribe fertiliEation in plants.
&escribe the formation of fruit and seeds.
1. #he diagram below shows what happened after pollination.
,1 / 0
#o obtain crops with better characteristics
#o obtain crops that mature earlier
#o obtain crops that are resistant to pests and diseases
4eed ;ruit *mbryo
Learning Objective 5.11 4ynthesising the concept of germination of seeds
__
6
X100 = %
At which location /+ 3 or 4 does fertiliEation occur / ta1e place in flowerJ
%ocation of fertilisation- """"""""""""""""""
2. Complete the se0uence below to describe the process fertilisation in plants using the
information below.
,. !tate the changes to the following parts of flower after fertilisation using the words
below.
#arts of floer Changes
2vary
Kygote
2vule
7etals / sepals / stigma / stamen &rop off
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the structure of a seed.
*'plain the functions of the different parts of a seed.
1. Label the diagram below to identify the structure of a seed using the words given.
,2 / 0
A. 7ollen grain germinates.
$. Pollen tube grows down the style.
8. A male gamete fuses with the female gamete and a Eygote is
formed.
&. Pollen tube grows out from the pollen grains.
*. Pollen tube reaches the ovary and a male gamete enters the
ovule.
;. As pollen tube grows+ male gametes are developed.
. F C
plumule radicle testa
a)
b)
c)
%earning 2bAective: 5677 !ynthesising the concept of germination of seeds
__
2
X100 = %
2. Dra lines to match the different parts of a seed with the correct function.
%earning 2utcome-
&escribe the physical changes of seedling during germination
1. #he following information shows the physical changes of seedling during
germination.
.
,, / 0
*mbryo
(adicle
8otyledon
>icropyle
:ilum
#esta
4tores and provides food for the embryo.
&evelops into a new shoot.
&evelops into a root.
Attaches the seed to the fruit.
Allows air and water to enter.
7rotects the seed.
#esta brea1s.
7lumule emerges from the cotyledons and grows upwards to form two leaves.
(adicle emerges from the testa and grows downwards into the soil and lateral
roots grow from it.
8otyledons shrin1 and drop off.
Learning Objective- 5.12 Application of vegetative reproduction in flowering plants
__
1,
X100 = %
Complete the se0uence below using the above information to describe the physical
changes of seedling during germination in the correct order.
Learning Outcomes:
*'plain with e'amples the meaning of vegetative reproduction.
4tate the parts of the plants that can reproduce vegetatively.
8lassify flowering plants according to the parts that can reproduce vegetatively.
&escribe the application of research carried out on vegetative reproduction in
agriculture.
1. Complete the statement below to e'plain the meaning of vegetative
reproduction.
,5 / 0
#esta brea1s
a.
b.
8otyledons shrin1 and drop off.
$ryophyllum
4weet potato
#apioca
Ham
Finger
Frass $anana
6egetative parts of the
plant
Froup 1
Dame of the plants
6egetative parts of the
plant
Froup 2
Dame of the plants
6egetative parts of the
plant
Froup ,
Dame of the plants
$anana
Learning Objective- 5.12 Application of vegetative reproduction in flowering plants
__
9
X100 = %
#he ability of some plants to produce new plants without producing fruits and
""""""""""""""""" is 1nown as vegetative reproduction.
2. Complete the statement below to state the parts of the plants that can reproduce
vegetatively
Dew plants grow from the vegetative parts of the parent plants such as the roots+
""""""""""""""""" or """"""""""""""""""".
,. Classify the following plants into three groups based on the vegetative parts of each
plant.
Learning Outcomes:
8lassify flowering plants according to the parts that can reproduce vegetatively.
&escribe the application of research carried out on vegetative reproduction in
agriculture.
1. Dra lines to match the following plants with the correct modified stems that
reproduce vegetatively.
-xamples of plant 1odified stems
,9 / 0
Finger
Frass
Learning Objective- 9.1 Analysing the pattern of human growth
__
=
X100 = %
(hiEomes
$ulbs
#ubers
4uc1ers
(unners
86 Dra lines to match the application of plant tissue culture in agriculture with the
correct description.
.pplications Description
8loning
.seful in the cultivation of plants li1e
orchids.
7ropagation of plant
.sed to produce plants that are
tolerant to pests and disease
7roduction of pest and
disease resistant plants.
An unlimited number of plants that are
genetically similar can be produced
within a short period of time
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe what growth is+
Identify the characteristics used to measure growth rate+
1. Underline the correct answer below to describe what growth is.
Frowth is the process in which our body )increases / decreases! in siEe+ number in
cells and weight+ and changes its shape and functions.
,6 / 0
7otato
2nion
Learning Objective- 9.1 Analysing the pattern of human growth
__
5
X100 = %
2. Complete the statement below to identify the characteristics used to measure
growth rate.
Frowth can be determined by measuring the physical characteristics of a person
such as """""""""""""""""" and """"""""""""""""" over a period of time.
,. #he diagram below shows the human growth curve.
.nser the following 0uestions based on the information in the diagram above+
a. At which stage is growth the fastest / rapid growthJ
""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
b. At which stage is growth the slowest / slow growthJ
""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
c. At which stage growth is negative / negative growthJ
""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
d. At which stage is growth minimal / minimal growthJ
""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
Learning Outcome:
Analyse the growth curve for male and female+
1. #he diagram below shows the growth curve of human males and females.
,= / 0
Learning Objective- 9.1 Analysing the pattern of human growth
__
10
X100 = %
0rite )#rue! or );alse! for the following statement based on the information in the
diagram above
!tatement True ) $alse
a. #he growth for boys and girls are at the same rate until
they reached the age of 5 years old.
b. Firls grow faster than boys after the age of 15.
c. $oys grow faster than girls between the ages of 12 and 15
d. $oys grow faster than girls between the ages of 5 and 12
Learning Outcomes:
8ompare and contrast between the growth rate in male and female.
&escribe the effects of nutrition on the growth in children.
1. #he diagram below shows the growth curve of human males and females.
.
, / 0
Learning Objective: 1.1 Analysing the various minerals found in the *arth crust
__
16
X100 = %
Compare and contrast between the growth rate in male and female below.
#he differences in growth rate between the ages of-
2. Dra lines to match the following nutrients with their effects on the growth of children
if they lac1 these nutrients in their diet.
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe what a mineral is.
*'plain through e'amples that minerals e'ist in the form of natural elements or
natural compounds+
Identify the elements in natural compounds+
1. Complete the statement below to define what minerals are using the words
given.
,/ / 0
Iodine
Iron
Bwashior1or
Anaemia
Foiter
(ic1et
7rotein
6itamin &
4imilarities
1ale $emale
$oth grow at a same rate after birth until the age of-
___________
);aster / 4lower!
);aster / 4lower!
);aster / 4lower!
);aster / 4lower!
);aster / 4lower!
);aster / 4lower!
5 and 12
12 and 15
15 and 20
inorganic solid elements compounds.
Learning Objective: 1.1 Analysing the various minerals found in the *arth crust
__
X100 = %
>inerals are """"""""""""""""""""" found in the *arthLs crust in the form of
natural """""""""""""""""" or natural """"""""""""""""""".
2. 2roup the minerals below into natural elements or natural compounds-
,. Complete the following to identify the elements in a natural compound.
a. >etal o'ide M >etal N """""""""""""""""""""""""
b. >etal carbonate M >etal N """""""""""""""" N """""""""""""""
c. >etal sulphide M >etal N """""""""""""""""
d. 4ilicate M >etal N """""""""""""""" N 2'ygen
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the properties of minerals.
<rite e0uations in words to show the effect of heat on the minerals.
1. Complete the statements below to describe the properties of minerals using the
words given.
50 / 0
Datural elements Datural compounds
9atural 1inerals
8alcium carbonate+ magnesium sulphide+ silver+ mercury+
4ilicon dio'ide+ platinum+ aluminium silicate+
gold
dissolve heated carbon dio'ide sulphur dio'ide
o'ides
Learning Objective: 1.2 .nderstanding the reactions between metals and non3metals
__
19
X100 = %
a. >ost minerals are hard and cannot """"""""""""""" in water.
b. >ost metal """""""""""""""""" are very stable compounds.
c. #hey do not brea1 down when """""""""""""""""""""".
d. >etal carbonates brea1 down to give metal o'ides and """"""""""""""""".
e. >etal sulphides brea1 down to give metal o'ides and """"""""""""""""".
2. Complete the word e0uations below to show the effects of heat on minerals using the
words given.
a. 8opper carbonate """"""""""""""""" : carbon dio'ide
b. Iron sulphide """"""""""""""""" : sulphur dio'ide
c. %ead carbonate """""""""""""""""" : carbon dio'ide
Learning Outcomes:
4tate e'amples of metals and non3metals
&escribe the reactions between metals and non3metals
<rite e0uation in words for the reaction between metals and non3metals
4tate that metals react with non3metals at different rate
1. Complete the table below to group metals and non3metals using the words given.
51 / 0
copper o'ide iron o'ide lead o'ide
>ercury 4ulphur 7latinum &iamond Fold 8arbon
4ilver Fraphite Iron
Learning Objective: 1., .nderstanding silicon compounds
__
=
X100 = %
2. #he table below shows the rate of reaction between metals and non metal.
'eaction 'ate of reaction
>agnesium N o'ygen >agnesium o'ide 6ery ;ast
Aluminium N o'ygen Aluminium o'ide
Kinc N o'ygen Kinc o'ide
$ased on the result above+ underline the correct answer to describe the reactions
between metals and non3metals.
&ifferent metals react at )different rates / same rates! with non metals.
,. Complete the word e0uation below to show the reaction between metals and non3
metals.
a. Iron N 2'ygen M """""""""""""""""""""""""""
b. >agnesium N 4ulphur M """""""""""""""""""""""""""
5. Underline the correct answer below show the reaction between metals and non
metals. &ifferent metals will reacts with non3metal at )the same rate / different rate!.
Learning Outcomes:
4tate the different forms of silicon compounds
4tate the e'ample of silica
4tate the e'ample of silicate
(elate the properties of silicon compounds to their stability
*'plain through e'amples the uses of silicon compounds in our daily life
1. 9ame the two types of silicon compound.
52 / 0
1etals 9on 1etals
!ilicon
compoun
d
4ilica
!ilica
;lint
!ilicate
Asbestos
Learning Objective: 1.5 Analysing calcium compounds
__
12
X100 = %
2. 9ame two e'amples of silica.
,. 9ame two e'amples of silicate.
5. #he table below shows the properties of silicon compounds.
$ased on the properties of silicon compounds in the table-
Underline the correct answer to relate the properties of silicon compounds to their
stability.
4ilica and silicate are )stable / unstable! compounds.
9. Complete the statements below to e'plain through e'amples the uses of silicon
compounds in our daily life using the words given.
a. """""""""""""""""" is used to ma1e glass obAect li1e test tubes.
b. 8lay is used to ma1e """"""""""""""""""" obAects such as flower pots.
c. """""""""""""""""" is used to ma1e watches and prisms.
Learning Outcomes:
4tate the elements in calcium carbonate.
Identify the various forms of calcium carbonate.
&escribe the properties of calcium carbonate.
<rite e0uations in words for the reactions of calcium carbonates.
1. Tick ()* the correct elements in calcium carbonate.
5, / 0
Insoluble in water
&o not decompose on heating
&o not react with acids
4and ceramics CuartE
Learning Objective: 1.5 Analysing calcium compounds
__
6
X100 = %
O P 8alcium O P 4odium O P 8arbon O P 2'ygen O P :ydrogen
2. Tick ()* the forms in which calcium carbonate can e'ists.
O P coral reef O P marble O P eggshell O P limestone
,. Tick ()* the correct properties of calcium carbonate.
O P &issolves in water O P (eacts with acids
O P &oes not dissolves in water O P &oes not reacts with acids
O P Dot decomposed by heat O P &ecomposes on heating
5. Complete the word e0uations below to show the reactions of calcium carbonates.
Learning Outcomes:
(elate the properties of calcium compounds to their uses.
&escribe the formation of calcium o'ide and calcium hydro'ide
1. Dra lines to match the calcium compounds with its uses.
55 / 0
8alcium
carbonate
4alt
8arbon
dio'ide
<ater
a.
heat
8alcium
carbonate
8arbon dio'ide
b.
Calcium carbonate
)$rea1s down when heated to
form calcium o'ide and
carbon dio'ide!
Calcium oxide
)8alcium o'ide is a base!
Calcium hydroxide
)8alcium hydro'ide is a strong
base!
Calcium hydroxide solution
)(eacts readily with carbon
dio'ide!
#reating acid burns
#esting the presence of carbon
dio'ide
#anning of leather to remove
hair from hides
>a1ing of whitewash+ mortar
and plaster
>a1ing 0uic1lime
>a1ing glass and cement
Deutralising acidic soils
Learning Objective: 1.9 Analysing natural fuel resources and their importance
__
9
X100 = %
2. Complete the diagram below to describe the formation of calcium o'ide and calcium
hydro'ide using the words given.
Learning Outcomes:
%ist the natural fuel resources
*'plain the formation of natural fuel resources
1. Complete the diagram below to list the natural fuel resources.
59 / 0
8alcium carbonate
)%imestone/marble!
:eated
Adds a little water
&issolves in water
)4la1ed lime!
)Cuic1lime!
)%imewater!
8alcium hydro'ide 8alcium o'ide 8alcium hydro'ide solution
Datural gas
Learning Objective: 1.9 Analysing natural fuel resources and their importance
__
5
X100 = %
Datural fuel resource ;ossil fuels
2. #he diagram below shows the natural processes of petroleum and natural gas.
# + '
.rrange the formation of petroleum and natural gas in se0uence.
Learning Outcome:
&escribe the fractional distillation of petroleum
1. Complete the diagram below with the correct products in a fractional distillation of
petroleum using the words given.
56 / 0
7etrol Berosene &iesel $itumen
Q ,0R8
50R8 3 =9R8
=9R8 3 190R8
190R8 3 2,0R8
S,90R8
2,0R8 3 290R8
290R8 3 ,00R8
,00R8 3 ,90R8
a. 7etroleum gas
b.
c. Daphtha
d.
e.
h.
f. %ubricating 2il
g. ;uel 2il
:ot
crude oil
Learning Objective: 1.9 Analysing natural fuel resources and their importance
__
X100 = %
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the characteristics of the various fractions from the fractional distillation of
petroleum
&escribe the uses of the various fractions from the fractional distillation of petroleum
1. Underline the correct answer in the table below to describe the characteristics of the
petroleum products #, + and '.
5= / 0
Learning Objective: 1.1 .nderstanding electrostatic
__
X100 = %
!tages #roducts Colour
.mount of soot
produce
7
)Fas / 7etrol!
8olourless Do soot
C
Berosene
)slightly yellow / yellow! )less / more!
(
%ubricating oil
)slightly yellow / yellow! )less / more!
2. Dra lines to match the uses of the various fractions from the fractional distillation of
petroleum.
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe what electrostatics is
4tate the types of static electrical charges
4tate the properties of static electrical charges
1. Underline the correct answer below to describe what electrostatics is.
)*lectrostatic / *lectricity! is the study of static electrical charges.
5 / 0
7etroleum gas
;uel for coo1ing gas
7etrol
;uel for cars and motorcycles
Daphtha
(aw materials for plastics
Berosene
Aircraft fuel and lamp $itumen
(oad surfacing
Learning Objective: 1.1 .nderstanding electrostatic
__
X100 = %
2. Underline the correct answer below to state the types of static electrical charges
a. 2bAects with the same type of charges )repel / attract! each other.
b. 2bAects with different types of charges )attract / repel! each other.
,. Underline the correct answer below to state the properties of static electrical
charges.
a. A positively3charged obAect has more )protons / electrons! than
)protons / electrons!.
b. A negatively3charged obAect has more )protons / electrons! than
)protons / electrons!.
c. A )positively charge / neutral! obAect has the same number of protons and
electrons.
Learning Outcome:
&escribe ways to detect static electrical charges.
1. a. Underline the correct answer below to describe ways to detect static electrical
charges.
#he gold leaf of an )electroscope / microscope! will )diverge / collapse! when a
charged obAect is brought near the metal plate.
5/ / 0
Learning Objective: 1.1 .nderstanding electrostatic
__
=
X100 = %
b. Tick the correct bo'es below to show what happens to the gold leaf of an
electroscope in the following situations.
a. .ncharged electroscope
-ffect on gold leaf
&iverges
Do change
b. 7ositively3charged electroscope
-ffect on gold leaf
&iverges
Do change
c. Degative3charged electroscope
-ffect on gold leaf
&iverges
Do change
d. .ncharged electroscope and
uncharged rod
-ffect on gold leaf
&iverges
Do change
e. .ncharged electroscope and positively3
charged rod
-ffect on gold leaf
&iverges
Do change
f. .ncharged electroscope and
negatively3charged rod
-ffect on gold leaf
&iverges
Do change
Learning Outcomes:
*'plain everyday phenomena caused by static electrical charges
4tate the safety measure to be ta1en when dealing with static electricity
1. Underline the correct answer below to e'plain some e'amples of everyday
phenomena caused by static electrical charges.
90 / 0
>etal plate of
electroscope
>etal plate of
electroscope
>etal plate of
electroscope
>etal plate of
electroscope
(od
>etal plate of
electroscope
>etal plate of
electroscope
Learning Objective: 1.2 .nderstanding electricity
__
=
X100 = %
a. %ightning occurs when the )electrons / protons! that collect at the bottom of the
cloud move to the )positively / neutral! charged areas of nearby clouds.
b. %ightning also occurs when spar1s )Aump / stay stationary! between the clouds and
the *arthLs surface.
2. Underline the correct answer below to state the safety measure to be ta1en when
dealing with static electricity.
a. #all buildings usually have )lightning conductors / lightning insulators! installed to
prevent damage during lightning stri1e.
b. A lightning conductors consists of a thic1 )copper /plastic! strip which is connected
to a piece of copper buried in the ground.
c. <hen lightning stri1es a tall building directly+ the )electrons / protons! will flow
down to the ground through the )lightning conductors / lightning insulators!
Learning Outcomes:
Five e'amples of sources of electrical energy used in everyday life.
4tate what electricity is
4tate what is voltage and resistance
&escribe the directions of current and electron flow in an electric circuit
91 / 0
Learning Objective: 1., Applying #he .nderstanding 2f >easuring *lectricity
__
9
X100 = %
1. #he diagram below show two sources of electrical energy.
9ame these sources of electrical energy using the words given.
2. Underline the correct answer in the statement below to state what electricity is.
*lectricity energy is the flow of electrical charges or )electrons / neutrons! in one
direction.
,. Underline the correct answer in the statement below to state what is voltage and
resistance.
a. 6oltage is the energy re0uired to move electrical charges or )electrons / neutrons!
from one point to another.
b. (esistance of a conductor )opposes / does not oppose! the flow of electrical
charges through it.
5. Label the diagram to show the directions of current and electron flow in an
electric circuit using the words below.
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the instrument for measuring current
Identify the instrument for measuring voltage
4tate the unit for current
4tate the unit for voltage
4tate the unit for resistance
92 / 0
a.
b.
%ead3acid accumulator &ry cells
*lectron flow 8urrent flow
b.
a.
Learning Objective: 1., Applying #he .nderstanding 2f >easuring *lectricity
__
6
X100 = %
1. #he diagram below shows an instrument and the circuit symbol to measure current.
9ame this instrument- """""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
2. #he diagram below shows an instrument and the circuit symbol to measure voltage.
9ame this instrument- """""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
Underline the correct answer in 0uestion , and 5 below.
,. #he unit for measuring current is )volt / ampere!.
5. #he unit for measuring voltage is )volt / ampere!.
9. #he diagram below shows a resistor in a circuit.
9ame the unit for measuring resistance- """"""""""""""""""""" or T
Learning Outcomes:
>easure current in an electric circuit+
>easure voltage in an electric circuit.
1. #he diagram below shows the reading of 0.=2A on an ammeter.
9, / 0
Learning Objective: 1.5 4ynthesising the relationship between current+ voltage and
resistance
__
6
X100 = %
>easure the current from the ammeters below.
2. #he diagram below shows the reading of 5.96 on a voltmeter.
>easure the voltage from the voltmeters below.
Learning Outcomes:
8arry out the e'periment to study the relationship between resistance and current.
&escribe the effects of the change in resistance on current.
95 / 0
a! 8urrent M """""" A b! 8urrent M """""" A c! 8urrent M """""" A
a! 6oltage M """""" 6 b! 6oltage M """""" 6 c! 6oltage M """""" 6
Learning Objective: 1.5 4ynthesising the relationship between current+ voltage and
resistance
__
2
X100 = %
1. #he table below shows the result of an e'periment to determine the effects of the
changes in resistance on current.
.nser
the following
0uestions based on
the results
above.
a. 0hat is the ammeter reading when the resistance is at 1 ;J
"
b. 0hat is the ammeter reading when the resistance is at 10 ;J
"
c. 0hat is the brightness of the bulb when the resistance is at 10 ;J
"
d. Underline the correct answer based on the result above.
i. As the resistance in the circuit increases+ the brightness of the bulb
)increases / decreases!
ii. As the resistance in the circuit increases+ the ammeter reading becomes
)smaller / larger!
2. Underline the correct answer below to show the effects of the change in resistance
on current in the e'periment above.
#he current that flows in a circuit )increases / decrease! when the resistance in the
circuit is increased.
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the effect of the change in voltage on current.
4tate 2hmLs %aw.
1. #he table below shows the result of an e'periment to determine the effects of the
changes in voltage on current.
99 / 0
'esistance (;* .mmeter reading (.* %rightness of bulb
1 ; 9.00 . 6ery bright
2 ; 2.90 . $right
9 ; 1.00 . &im
10 ; 0.90 . 6ery &im
Learning Objective: 1.9 4ynthesising the concept of parallel and series circuit
__
6
X100 = %
Underline the correct answer below to show the relationship between the voltage and
the current in this e'periment.
As the voltage increases+ the current flowing through a conductor
)increases / decreases!
2. Underline the correct answer in the statement below that represents 2hmLs %aw.
8urrent flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage if the
resistance )(! is )constant / not constant!.
Learning Outcome:
Identify the components of an electric circuit and their symbols.
1. Label the diagram below to identify the components of an electric circuit and their
symbols using the words given.
96 / 0
9umber of dry cells <oltmeter reading (<* .mmeter reading (.*
<
)
I
= '
1 1.0 0.9 2
2 2.0 1.0 2
, ,.0 1.9 2
5 5.0 2.0 2
$ulb 6oltmeter 4witch *arth 8onnection
&ry cell Ammeter
Learning Objective: 1.9 4ynthesising the concept of parallel and series circuit
__
9
X100 = %
1. 2." ,."
;use
5. 9." 6."
(esistor Falvanometer
=. ." /."
(esistor (heostat
10. 11." 12."
(heostat
Learning Outcome:
&raw a diagram of a complete electric circuit
1. Dra a complete circuit+ using the following components in the diagram below.
9= / 0
switch bulb voltmeter ammeter dry cell
Learning Objective: 1.9 4ynthesising the concept of parallel and series circuit
__
12
X100 = % Learning Outcomes:
$uilt a series circuit
$uilt a parallel circuit
8ompare and contrast the arrangement of components in a series circuit and a
parallel circuit.
1. Dra a series circuit on the dotted line using all the components below.
9 / 0
dry cell
switch
bulb ammeter
voltmeter
switch bulb ammeter dry cell bulb
Learning Objective: 1.6 Analysing current+ voltage and resistance in a series circuit
__
,
X100 = %
2. Dra a parallel circuit on the dotted line using all the components below.
,. 8ompare and contrast the arrangement of components in a series circuit and a
parallel circuit.
Underline the correct answer below.
Difference
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the current flowing through the components in a series circuit.
&escribe the voltages across the components in series circuit
&escribe the resistance in a series circuit
1. #he diagram below shows the amount of current flowing through the components in a
series circuit.
9/ / 0
switch bulb ammeter dry cell bulb
4eries circuit 7arallel circuit !imilarities
#he dry cells supplies the current
#he switch controls the flow of current
2ne the )same / two or more!
path
2n the )same /two or more!
path
Arrangement of
components
Learning Objective: 1.6 Analysing current+ voltage and resistance in a series circuit
__
6
X100 = %
$ased on the diagram+ underline the correct answer in the statement below.
#he amount of current flowing in a series circuit is the )same / different! at any point.
2. #he diagram below shows the voltages across the components in series circuit
$ased on the diagram+ underline the correct answer in the statement below.
#he total voltage that flows across the components in a series circuit
)e0uals /does not e0ual! to the voltage of the battery.
,. #he table below show the result of an e'periment.
%ulbs in a series circuit %rightness
6ery bright
&im
6ery dim
$ased on the result above+ underline the correct answer to describe resistance in a
series circuit.
#he more resistance added in a series circuit+ the amount of current flowing will
)decrease / increase! because resistance opposes the flow of current.
Learning Outcome:
*'plain the advantage and the disadvantage of series circuit.
1. <rite #rue )T! or ;alse )$! for the following advantages and disadvantages of a
series circuit.
a. 2nly one is needed to control all electric appliances in a series circuit.
b. #he current in a series circuit will increase if the number of dry cells
connected in series is increased.
60 / 0
Learning Objective: 1.= Analysing current+ voltage and resistance in a parallel circuit
__
5
X100 = %
c. If one bulb blows+ the other bulbs will light up in the series circuit.
d. #he voltage supplied by dry cells is shared e0ually among all the bulbs
in the series circuit.
e. If more bulbs are added in a series circuit+ the voltage across each bulb
will decrease.
f. If more bulbs are added in a series circuit+ the brightness of
the bulbs will decrease
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe the current flowing through the components in a parallel circuit
&escribe the voltage across the component in a parallel circuit
&escribe the resistance in a parallel circuit
1. #he diagram below shows the amount of current flowing through the components in a
parallel circuit.
61 / 0
Learning Objective: 1.= Analysing current+ voltage and resistance in a parallel circuit
__
6
X100 = %
$ased on the diagram+ underline the correct answer in the statement below.
#he total current flowing in the circuit is )e0uals / does not e0ual! to the sum of the
current passing through each bulbs.
2. #he diagram below shows the voltages across the components in parallel circuit.
$ased on the diagram+ underline the correct answer in the statement below.
#he voltage that flows across each component in a parallel circuit is
)the same /not the same! as the voltage of the battery.
,. Underline the correct answer to describe resistance in a parallel circuit.
<hen more resistance is added in a parallel circuit+ the voltage
)remains the same / decreases! and the total current flowing in the circuit is
)e0uals / does not e0ual! to the sum of the current passing through each bulbs.
Learning Outcomes:
*'plain the advantage and disadvantage of a parallel circuit
8ompare and contrast a series circuit and a parallel circuit in terms of current+
voltage and resistance
1. Underline the answer in the statements below to e'plain the advantage and
disadvantage of a parallel circuit
a. 7arallel circuits )allows / does not allow! other components to be functional when
one component is switch off or burnt out.
b. 7arallel circuit )allows / does not allow! more components to be added in parallel
without the need for more voltage.
62 / 0
Learning Objective: 1. .nderstanding magnetism
__
10
X100 = %
2. Complete the diagram below to compare and contrast a series circuit and a parallel
circuit in terms of current+ voltage and resistance using the formula given.
Learning Outcomes:
&raw the directions of the magnetic field.
(elate magnetic field lines and strength to magnetic field
*'plain the use of a magnet in a compass
1. #he diagram shows a bar magnet with several compass placed at different positions
around it.
Dra ) ! on all the compasses to show the directions of the magnetic field
below.
6, / 0
4eries 8ircuit
7arallel 8ircuit
Differences
#otal voltage
#otal current
6 M 6
1
N 6
2
6 M 6
1
M 6
2
I M I
1
N I
2
I M I
1
M I
2
9 !
Learning Objective: 1. .nderstanding magnetism
__
2
X100 = %
2. Underline the correct answer to relate the magnetic field lines and the strength to the
magnetic field.
a! #he magnetic field is strongest at the )middle / end!.
b! #he closer the magnetic field line+ the )stronger / wea1er! the magnet.
c! #he magnetic field always point from the )north / south! pole to the )north / south!
pole.
d! #he direction of a magnetic field can be detected by using a
)compass / stop watch !
,. Complete the statement to e'plain the use of a magnet in a compass using the
words given.
A magnetic compass wor1s because the earth is surrounded by a large
""""""""""""""""""""""""""". #his magnetic field causes the needle of the
magnetic compass to rest in the """"""""""""""""""""" position.
Learning Outcomes:
&escribe what a magnetic field
&raw the magnetic field of a bar magnet
1. Underline the correct answer below to describe what a magnetic field is.
A magnetic field is the space around a )magnet / current! under the influence of a
magnet.
2. #he diagram below shows iron filings being sprin1led onto a piece of sheet glass
65 / 0
magnetic field Dorth34outh
)Iron filing are
sprin1led over!
)$ar magnet beneath!
)4heet glass!
9
!
Learning Objective: 1./ .nderstanding electro3magnetism
__
6
X100 = %
a! Dra the pattern to show the direction of the magnetic field formed by the iron
filing below.
Learning Outcomes:
(elate the current flow through a conductor with magnetism
&escribe what an electromagnet is
1. #he diagram below shows an e'periment to relate the current flow through a
conductor with magnetism
69 / 0
9 !
8ardboard
'
!
8opper wire
8ompass
+
#
Learning Objective: 2.1 .nderstanding the generation of electrical energy
__
=
X100 = %
a. Dra arrows ) ! at #, +, ' and ! to show the direction of the magnetic field
line around the copper wire.
b. Dra the pattern of magnetic field line in the bo' given.
2. Underline the correct answer to describe what an electromagnet is.
An electromagnet is a magnet when a )current / resistance! flow through the coil of
wire.
Learning Outcomes:
%ist the various types of generators
&escribe the generation of electrical energy in various types of power stations
1. Dra lines to match the type of generator with the correct e'planation.
Type of generator -xplanation
&iesel generator Duclear energy is produced in a nuclear reactor by
nuclear fission
Fas turbine generator A diesel engine is used to rotate the dynamo
8ompressed air mi'ed with gas is burnt. #he gas
66 / 0
.
Learning Objective: 2.1 .nderstanding the generation of electrical energy
__
=
X100 = %
Duclear *lectric
generator
mi'ture e'pands and rotates the turbine
:ydroelectric generator
<ater from a reservoir rotates a turbine
#hermal *lectric
generator
;uel such as petrol and natural gas is burnt to boil
water to produce steam which will rotate the turbine
2. Complete the statements below to describe the generation of electrical energy in
various types of power stations using the words given.
a! <ater flowing at high speed and pressure from the dam forces the
""""""""""""""""""""" to rotate the generator.
b! (adioactive substances such as uranium are use to produce heat by
"""""""""""""""""""""""""""" in a reactor.
c! In a thermal power station +fossil fuels such as """"""""""""""""""""+coal
and natural gas are used to heat water to produce steam
d! #wo alternative source of energy that can be used to generate electrical energy
are """""""""""""""""""" and the sun.
Learning Outcomes:
8ompare and contrast the generation of electrical energy in various types of power
stations
Five e'amples of alternative sources of energy.
1. Complete the diagram below to compare and contrast the generation of electrical
energy in various types of power stations using the words given.
2enerators !haft is turned by: Types of fuels used:
6= / 0
turbines petroleum biomass nuclear reactions
&iesel motor Duclear reactions 4team Fas
<ater flowing at high speed
Learning Objective- 2.2 .nderstanding transformer
__
/
X100 = %
#hermal 7etrol+ 8oal+ Fas
:ydroelectric Done
Duclear 4team
Fas 4team
&iesel &iesel
2. Underline the correct answer in the statement below to give e'amples of alternative
sources of energy.
a. )$iomass / 4un! produces methane gas by the decomposition of the remains and
wastes of living things by bacteria.
b. 4olar cells convert energy from the )4un / biomass! into electrical energy.
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the different parts of a transformer.
&escribe how a transformer wor1s.
1. Label the diagram below to identify the different parts of a transformer using the
words given.
6 / 0
7
C
(
4 #
2utput 7rimary coil 4econdary coil Iron core Input
Learning Objective- 2.2 .nderstanding transformer
__
X100 = %
7 - """"""""""""""""""""""""""""
C - """"""""""""""""""""""""""""
( - """"""""""""""""""""""""""""
4 - """"""""""""""""""""""""""""
# - """"""""""""""""""""""""""""
2. Complete the statement below to describe how a transformer wor1s using the words
given.
In a transformer+ when the """"""""""""""""""" passes through coil+ the iron core
becomes an """"""""""""""". As the direction of alternating current 1eeps
changing the """"""""""""" created also 1eeps changing. #he changing magnetic
field """""""""" an alternating current in the secondary coil.
Learning Outcomes:
8ompare and contrast a step3up transformer and a step3down transformer
&escribe the roles of transformer in the transmission and distribution of electricity
1. Underline the correct answer in the table below to compare and contrast a step3up
and a step3down transformer.
6/ / 0
electromagnet magnetic field alternating current induces
!imilarity
!tep&up transformer !tep&don transformer
<hich has more
numbers of coilsJ
6oltage output
)7rimary / 4econdary!
)%ower / :igher!
)7rimary / 4econdary!
)%ower / :igher!
.ses #o )increase / decrease!
output voltage
#o )increase / decrease!
output voltage
It consists of two coil around a laminated soft iron
It is used to change the value of an A8 voltage
+ ' #
8onsum
er /
residenti
al
7ylons
>ain
substati
ons
!
T
:eavy
industries
Learning Objective- 2., Analysing the electricity transmission and distribution system
__
11
X100 = %
2. #he diagram below shows a transmission and distribution system of electricity.
>dentify the types of transformers / and 3
X - """"""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
H - """"""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
Learning Outcomes:
Arrange in order the components in the electricity transmission and distribution
system
&escribe the function of the components in the electricity transmission and
distribution system.
&escribe how electricity is transmitted and distributed from power stations to
consumer.
1. Label the diagram below shows the components in the electricity transmission and
distribution system using the words given.
=0 / 0
/ 3
7ower
station
8onsumer / (esidential
7ylons
4tep up transformer 4tep down transformer 7ower station
4tep up transformer 4tep down transformer
8onsum
er /
residenti
al
Learning Objective: 2.5 .nderstanding the electrical supply and wiring system at home
__
9
X100 = %
2. Dra lines to match the components with its functions.
Components $unctions
Dational Frid networ1 a. Allows the electrical energy to be transmitted
through the Dational Frid networ1
#ransformer station b. A step3up transformer increases the voltage
4witch Eone c. ;urther step3down the voltage of electrical power to
suitable values
>ains substation d. 8onnects all power stations in the country
4ubstation e. #ransformer that step3down the voltage of electrical
power to suitable values to be distributed to its
branches
,. Complete the statement below to describe how electricity is transmitted and
distributed from power stations to consumer using the words given.
a. #he Dational Frid Detwor1 connects power stations at different places together
and transmits electrical power to """"""""""""""""throughout the country.
b. #he substations have """"""""""""""""" that step down the voltage of electrical
power to a suitable value to its branches.
c. *ach branch also has transformers to further """"""""""""""""the voltage
suitable for consumers.
Learning Outcomes:
4tate the value of the main voltage
4tate the types of current
Identify the type of electric current supplied to homes
4tate the types of electrical wiring system
1. Circle the correct value of the main voltage.
2. Complete the statement below to state the types of current.
=1 / 0
step down substations transformers
#: """"""""""""""""""""
+- """""""""""""""""""
'- """"""""""""""""""""
!: """"""""""""""""""""
T: """"""""""""""""""""
1106 2506 5906
Learning Objective: 2.5 .nderstanding the electrical supply and wiring system at home
__
X100 = %
#here are two types of electric current+ namely direct current and """"""""""""
current.
,. Underline the correct answer below to Identify the type of electric current supplied to
homes.
#he current supplied to our homes is )direct current+ alternation current!.
5. Underline the correct answer in the statements below to state the types of
electrical wiring system.
a. Fenerally+ the electrical wiring at our home is the )single3phase+ two3phase!
wiring.
b. #he )single3phase+ three3phase! wiring is usually used in places where the
electrical energy consumption is higher.
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the parts in an electrical wiring system
&escribe the functions of the parts of an electrical wiring system
1. Label the diagram below to identify the parts in an electrical wiring system using the
words given.
=2 / 0
soc1et circuit brea1er electric meter
live wire neutral wire
%-
>-
D-
Learning Objective: 2.5 .nderstanding the electrical supply and wiring system at home
__
6
X100 = %
A
$ main fuse bo'
8
& main switch
*
;
F earth wire
:
2. Underline the correct answer in the statement below to describe the functions of the
parts of an electrical wiring system.
a. #he )electric meter+ circuit brea1er! measures the amount of electrical energy
used.
b. #he electrical power from the distribution substation is brought into our homes
through the )earth+ live! wire.
c. #he )circuit brea1er+ main switch! function the same way as a fuse.
Learning Outcome:
&escribe the wiring in a , pin3plug.
1. a. Label the diagram to describe the structure of a , pin3plug using the words given.
=, / 0
%ive wire Deutral wire *arth wire
Learning Objective: 2.9 Analysing the cost of electrical energy usage
__
6
X100 = %
b. Complete the table below to show the international colour code for the ,3pin plug
using the words given.
Type of ire Colour Code
*arth
Deutral
%ive
Learning Outcome:
4tate the power and voltage rating of home electrical appliances.
8alculate the amount of current flowing through an electrical appliance.
(ecall the relationship between electrical energy usage+ power and time.
4olve problems by calculating the cost of electricity used.
1. Underline the correct answers below to state the power and voltage rating of
home electrical appliances.
A hair dryer is mar1ed 2506 /00<.
#he power rating is the hair dryer is )2506 / /00<! and the voltage rating is
)2506 / /00<!.
2. Calculate the current that flows in an air conditioner mar1ed 2506 1200< when it is
connected to the mains.
Assuming
)7owerM 6oltage ' 8urrent! or )7 M 6 ' I!
=5 / 0
Hellow with green stripes $lue $rown
Learning Objective: 2.6 .nderstanding the functions of fuse and earth wire
__
11
X100 = %
,. Underline the correct answers below to recall the relationship between electrical
energy usage+ power and time .
1 1<h is the energy consumed by a )100< / 1000<! electrical appliance in
) 1 minutes / 1 hour!.
5. !olve the following problem below by calculating the cost of electricity used.
An electric fan of 0.2 1< operates for hours. <hat is the cost of electrical
energy used if the cost per unit is ,0 centsJ
Assuming:
8ost of electrical energy used M *nergy used in units ' ,0 cent per unit
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the types of fuses.
4tate the ratings of fuses.
&escribe the function of fuses in electrical wiring system
&etermine the suitable rating of a fuse for an electrical appliance.
&escribe the role of earth wire in electrical wiring system.
1. Label the type of fuse below using the words given.
A- """""""""""""""""""" $-"""""""""""""""""""""
=9 / 0
8artridge fuse (eplaceable wire fuse
Learning Objective: 1.1 Analysing the 4un
__
X100 = %
2. 8ommon fuse ratings are 1A+ 2A+ ,A+ 9A+ 10A.
Underline the correct fuse rating which is also common. )12A! )1,A!
,. Underline the correct answers in the statement below to describe the function of
fuses in electrical wiring system
a. <hen a short circuit occurs+ there is a )low / high! resistance and a )large / small!
amount of current flowing in the circuit.
5. Complete the table below to determine the suitable rating of a fuse for an
electrical appliance
-lectrical appliances Current used (.* !uitable fuse (7.,?.,@.,7?.*
(ice coo1er 5.5
*lectric 1ettle =.9
;an 0.,
(efrigerator 9.5
9. Underline the correct answers in the statements below to describe the role of earth
wire in electrical wiring system.
a. #he )neutral wire / earth wire! help to prevent electric shoc1 caused by a loose
livewire in an electrical appliance.
b. <hen a loose live wire touches the metal part of an appliance+ the electric current
will flow to the ground through the )neutral wire / earth wire!.
Learning Outcomes-
&escribe the characteristics of the sun.
Identify the structures of the sun.
1. 0rite #rue )#! or ;alse );! for the statements below to describe the characteristics of
the sun.
a. #he diameter of the sun is 1 ,/2 000 1m.
b. #he mass of the sun is 2 ' 10 1g.
c. #he relative density of the sun to the earth is 0.29
d. #he surface temperature of the sun is 990 8 U 600 8.
e. #he density of the sun is only a 0uarter that of the *arth
because it is primarily made up of gases.
=6 / 0
Learning Objective: 1.1 Analysing the 4un
__
11
X100 = %
2. Label parts /, 3 and 4 based on the information below.
Learning Outcomes:
Identify the phenomena occurring on the surface of the sun.
*'plain the effects of the phenomena on the surface of the sun on the earth.
4tate how energy is generated by the 4un.
1. Label the diagram below to identify the phenomena occurring on the surface of the
sun using the words given.
== / 0
X-
H-
K-
8hromospheres 8orona 7hotosphere
7rominences 4olar flares 4un spots
/ - """""""""""""""""""""
3 - """""""""""""""""""""
4 - """""""""""""""""""""
Learning Objective- 1.2 .nderstanding the star and gala'ies in the .niverse
__
10
X100 = %
2. Underline the correct answer in the statement below to e'plain the effects of the
phenomena on the surface of the sun on the earth.
a. )4olar wind+ solar flare! is a flow of gases from the sun that disturbs and sha1es
the *arthLs magnetic field.
b. )4olar flares+ 4unspots! often give off ultraviolet light and X3ray that heat up the
*arthLs upper atmosphere and can change the orbits of satellites and shorter their
lifespan.
,. Complete the statement to state how energy is generated by the 4un using the
words given.
a. *nergy is generated by the sun through """"""""""""""""""""" in the core of
the sun.
b. #he sun is mainly made up of """"""""""""""""".
c. .nder high temperature in the core of the sun+ hydrogen atoms undergo nuclear
fusion to form """""""""""""" atoms and a large amount of """"""""""""is
produced.
d. #he energy produced is in the form of""""""""""""""""and """"""""""""""""
Learning Outcomes-
&efine what a star is
Identify the 4un as a star
Identify the bright stars in the s1y.
8ompare and contrast the stars based on certain characteristics
Complete 0uestions 1+ 2 and , using the words given.
1. a. A """""""""" is different from a planet because it can give off its own light.
b. #he """""""""" is the nearest star to the *arth.
c. #he coolest stars are """""""""" in colour.
d. #he hottest stars are """""""""" in colour.
2. #he brightest star seen from the *arth is """""""""".
,. """""""""" is an e'ample of a bright star that emits a bluish light.
= / 0
light hydrogen nuclear fusion heat helium energy
red blue star sun 4irius (igel
Learning Objective- 1.2 .nderstanding the star and gala'ies in the .niverse
__
12
X100 = %
5. Dra lines to match the various types of stars with the correct characteristics.
Learning Outcomes-
&escribe the formation of stars
&escribe the death of stars.
4tate the types of gala'ies
4tate the position of the 4olar 4ystem in the .niverse
&escribe the >il1y <ay
1. Label the diagram below to describe the formation and death of a star using the
words given.
=/ / 0
Fiants
Deutron 4tars
very dense+ small stars
<hite dwarf
4uper giants
dim compact star
large stars
large stars with diameters more than 100 times
that of the 4un
Deutron star Debula $lac1 hole 4upernova (ed Fiant 4tar
a. b. c. e.
d.
2. Label the following type of gala'y using the words given.
,. Complete the statements below to state the position of the 4olar 4ystem in the
.niverse and to describe the >il1y <ay using the words given.
a. #here are millions of gala'ies in our """""""""""""""""""".
b. #he 4olar 4ystem is located in the """""""""""""""""" gala'y.
c. #he >il1y <ay is a """"""""""""""" gala'y and contains about 200 billion stars.
d. A gala'y is a group of stars held together by """""""""""""""".
0 / 0
4piral gala'y *lliptical gala'y Irregular gala'y
gravity .niverse >il1y <ay spiral3shaped
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Fun With Flashcards - English Teachers Cookbook For Teaching English With Flashcards PDFDocument349 pagesFun With Flashcards - English Teachers Cookbook For Teaching English With Flashcards PDFZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan-1Document4 pagesSkema Jawapan-1Zarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Soalan Pertengahan TahunDocument19 pagesSoalan Pertengahan TahunZarith Hidayah Ismile100% (1)
- PEMBETULANDocument1 pagePEMBETULANZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- RPT Bahasa Inggeris PeralihanDocument1 pageRPT Bahasa Inggeris PeralihanZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Pem Bet UlanDocument1 pagePem Bet UlanZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Sains Form1 Final ExamDocument11 pagesSains Form1 Final ExamZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Competition: DATE: 23 /3/15 Day: Wednesday TIME: 3.30-4.30Document4 pagesChemistry Competition: DATE: 23 /3/15 Day: Wednesday TIME: 3.30-4.30Zarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Soalan Kimia k2 NewDocument19 pagesSoalan Kimia k2 NewZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Soalan Ujian Matematik Tahun SatuDocument11 pagesSoalan Ujian Matematik Tahun SatuZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Skema Kimia Ujian Bulan 1Document4 pagesSkema Kimia Ujian Bulan 1Zarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Jadual Target ADocument1 pageJadual Target AZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Answer All The Question: P Measure The Temperature of An Object Measure The Mass of An ObjectDocument16 pagesAnswer All The Question: P Measure The Temperature of An Object Measure The Mass of An ObjectZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Form2 RPPBS20.3.2013Document4 pagesForm2 RPPBS20.3.2013Zarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- International Chemistry Crossword Puzzle: Across DownDocument2 pagesInternational Chemistry Crossword Puzzle: Across DownZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- SMK Tinggi Port Dickson Test 2 Remove Class NAME: .. CLASSDocument4 pagesSMK Tinggi Port Dickson Test 2 Remove Class NAME: .. CLASSZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Soalan PeralihanDocument5 pagesSoalan PeralihanZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Woody Plant Non Woody Plant Aquatic PlantDocument4 pagesWoody Plant Non Woody Plant Aquatic PlantZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Exports SoDocument6 pagesExports SoZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet
- Heat of NeutralisationDocument4 pagesHeat of NeutralisationZarith Hidayah IsmileNo ratings yet