Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study Guide
Study Guide
Uploaded by
Cheyenne MartinsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Guide
Study Guide
Uploaded by
Cheyenne MartinsCopyright:
Available Formats
STUDY GUIDE
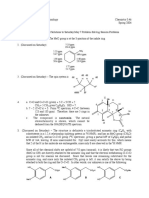
Experiment 4&5:
(C
7
H
8
)Mo(CO)
3.
(C
7
H
7
)Mo(CO)
2
I are pseudo C
s
symmetry (brown/orange,yellow)
(C
7
H
7
)Mo(CO)
+
is pseudo C
3v
(green)
CO is a sigma-donor, pi-acceptor (also known as pi-complexes)
Frequency/wavenumber order: (Lowest -> Highest)
o (C
7
H
8
)Mo(CO)
3 .
(C
7
H
7
)Mo(CO)
2
I. (C
7
H
7
)Mo(CO)
+
.
Experiment 3:
4 KMnO
4
+ 12 C
5
H
8
O
2
+ 2 H
2
O 4 Mn(C
5
H
8
O
2
)
3
+ 4 KOH + 7 O
2
Mn(C
5
H
8
O
2
)
3
+ CHCl
3
MnCl(C
5
H
8
O
2
)
2
+ CHCl
2
+
+ C
5
H
8
O
2
-
Mn(acac)
3
is:
o High spin, paramagnetic
o (t
2g
)
3
(e
g
)
1
o Octahedral
o D
3
, pseudo O
h
symmetry
o Black Precipitate
Two methods:
o Gouy Method
o Evans Method (calculation)
Procedure
Exactly 0.375 grams of KMnO
4
were weighed and added to a 25mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 7.5
mL of H
2
O. The solution was heated to 80
o
C and then allowed to cool to room temperature. Once
cooled, 1.7 mL of acetylacetonate was carefully added and the solution boiled once more. After 5
minutes, the solution was removed from the hot plate and subsequently cooled in an ice bath. Vacuum
filtration was performed, crystals were collected and weighed, and NMR analysis was performed with
both the product (Mn(acac)
3
) and the solvent (CHCl
3
).
Calculations:
X
M
(Molar Susceptibility) =
)
) where ) ) , Q = 1 for electromagnet or 2 for
superconducting magnet; and c is the concentration of solute in mole/L.
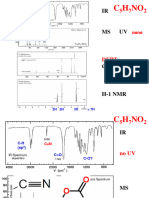
Experiment 2
H
2
TPP has D
2h
symmetry which becomes D
4h
in the presence of a metal.
Copper and Zinc complex were red shifted (shift towards longer wavelength, lower energy);
copper less than zinc.
Reactions:
4C
6
H
5
CHO + 4C
4
H
4
NH + 3/2 O
2
C
44
H
30
N
4
+ 7H
2
O
H
2
TPP + Cu(O
2
CCH
3
)
2
(H
2
O) Cu(TPP) + 2HO
2
CCH
3
+ H
2
O
H
2
TPP + ZnCl
2
Zn(TPP) + 2HCl
Experiment 1
CuCl
2
2DMSO (green) and PdCl
2
2DMSO (orange) are square planar complexes
RuCl
2
* 4DMSO (yellow) forms an octahedral complex
CuCl
2
+ 2DMSO CuCl
2
2DMSO
PdCl
2
+ 2DMSO PdCl
2
2DMSO
RuCl
3
+ 4DMSO RuCl
3
4DMSO RuCl
2
4DMSO
If:
o S-O < wavenumber, then bonded to oxygen and compound is a hard acid (copper and
ruthenium)
o S-O > wavenumber, then bonded to sulfur and compound is a soft acid (palladium)
DMSO functions as both a soft and hard base
Soft goes with soft, hard with hard
High charge states coupled with being weakly polarizable lead to a title application of
hard acid. In the same way, low charge states that are highly polarizable have the title
of soft.
You might also like
- Conquering Chemistry AnswersDocument53 pagesConquering Chemistry AnswersSarthak GargNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2012Document12 pagesFinal Exam 2012Mat MorashNo ratings yet
- Linkage 2 Lab ReportDocument25 pagesLinkage 2 Lab Reportapi-25176084883% (6)
- Memorization List: Ions-Names and ChargeDocument4 pagesMemorization List: Ions-Names and ChargepringlekNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Revision Guide 4. Transition MetalsDocument10 pagesMod 5 Revision Guide 4. Transition MetalsrammiejimjamsNo ratings yet
- Cu ComplexesDocument8 pagesCu ComplexesvicianmNo ratings yet
- 21-Electrospinning Ru Carbon Nanofibers Boost CO2 Reduction in A H2 CO2 Fuel Cell SiDocument15 pages21-Electrospinning Ru Carbon Nanofibers Boost CO2 Reduction in A H2 CO2 Fuel Cell Siee20b044No ratings yet
- 2012 Dec SolutionsDocument8 pages2012 Dec SolutionsBuyu100% (1)
- Sample Paper-02 Chemistry (Theory) Class - XI Time Allowed: 3 Hours Answers Maximum Marks: 70Document8 pagesSample Paper-02 Chemistry (Theory) Class - XI Time Allowed: 3 Hours Answers Maximum Marks: 70Yt Status WorldNo ratings yet
- Last Name: - First Name: - SSN Last 4Document7 pagesLast Name: - First Name: - SSN Last 4nsorsokNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1000 Mid-Year Exam December 2002: Part A. 60 Marks. Answer Each Question (5 Marks Each)Document7 pagesCHEM 1000 Mid-Year Exam December 2002: Part A. 60 Marks. Answer Each Question (5 Marks Each)Geleni Shalaine BelloNo ratings yet
- Orgo Spectroscopy KeyDocument6 pagesOrgo Spectroscopy KeysikandarmirzaNo ratings yet
- Direct Methane Oxidation On La1 Xsrxcr1 Yfeyo3 Perovskite-Typeoxides As Potential Anode For Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxidefuel CellsDocument23 pagesDirect Methane Oxidation On La1 Xsrxcr1 Yfeyo3 Perovskite-Typeoxides As Potential Anode For Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxidefuel CellsNGUYỄN HOÀNG LINHNo ratings yet
- Spectrochemical SeriesDocument6 pagesSpectrochemical SeriesÖmer SaygılıNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Answer Scheme TerengganuDocument17 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Answer Scheme Terengganusherry_christyNo ratings yet
- 4 5 PDFDocument11 pages4 5 PDFRomNo ratings yet
- Prob Session Key PDFDocument3 pagesProb Session Key PDFArangaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Students of Mechanical Engineering Studiengang BachelorDocument9 pagesChemistry For Students of Mechanical Engineering Studiengang BachelorAsif KhanNo ratings yet
- Iitjee Chemistry Sample Paper - Iv: SolutionsDocument3 pagesIitjee Chemistry Sample Paper - Iv: SolutionsAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- 15.d and F Block ElementsExerciseDocument25 pages15.d and F Block ElementsExerciseDevansh ParasharNo ratings yet
- 5 (2) Veto of Life He Our Pitch orDocument27 pages5 (2) Veto of Life He Our Pitch orStephenNo ratings yet
- Concerto in E Sharp Minor by Alfred ReedDocument62 pagesConcerto in E Sharp Minor by Alfred ReedMalcolm TanNo ratings yet
- DPP - 12-21 - PH. CHEM - Abhimanyu - (Sol.)Document21 pagesDPP - 12-21 - PH. CHEM - Abhimanyu - (Sol.)GEETA JUNAWANo ratings yet
- C-13 NMR and DEPTDocument41 pagesC-13 NMR and DEPTV G Viju Kumar100% (1)
- CPM-05-01-2014 Main 13th E WADocument16 pagesCPM-05-01-2014 Main 13th E WAumang dhandhaniaNo ratings yet
- Tejel Et Al-2012-Chemistry (Weinheim An Der Bergstrasse, Germany) .Sup-1Document30 pagesTejel Et Al-2012-Chemistry (Weinheim An Der Bergstrasse, Germany) .Sup-1Claudia Urbina GhinelliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Unit3Document6 pagesChemistry - Unit3123456No ratings yet
- Ffi Ffi: P (T: NVDocument14 pagesFfi Ffi: P (T: NVYoruNgNo ratings yet
- SPEC6A Problems 3-5 AnswersDocument19 pagesSPEC6A Problems 3-5 Answersnonkululekomoya26No ratings yet
- JonesC EndoEndo24Diphosphabicyclo110Butane Orbital Isomers CC 2001 663-4Document2 pagesJonesC EndoEndo24Diphosphabicyclo110Butane Orbital Isomers CC 2001 663-4jazmurdochNo ratings yet
- Shamsuddin M. Azad, Kazi A. Azam, Shariff E. Kabir, Madhu S. Saha, G.M. Golzar HossainDocument6 pagesShamsuddin M. Azad, Kazi A. Azam, Shariff E. Kabir, Madhu S. Saha, G.M. Golzar HossainNikhil BhoumikNo ratings yet
- Solucoes ICHO28 A ICHO24Document38 pagesSolucoes ICHO28 A ICHO24Leonardo FagundesNo ratings yet
- 2º Taller de Química Inorgánica IIDocument2 pages2º Taller de Química Inorgánica IIEMMANUEL ALEJANDRO FERNANDEZ GAVIRIANo ratings yet
- Solutions To Preparatory Problems: Problem 1. Graphite OxideDocument25 pagesSolutions To Preparatory Problems: Problem 1. Graphite OxideNebojsaZecNo ratings yet
- 2007 5 CRCF EPDocument5 pages2007 5 CRCF EPM Zeeshan aliNo ratings yet
- Jee Main 27 Jan 2024 Shift 2 Chemistry Memory Based Paper Solution - PHPDocument9 pagesJee Main 27 Jan 2024 Shift 2 Chemistry Memory Based Paper Solution - PHPdhanu20119381No ratings yet
- P Block Elements in PPT FormDocument138 pagesP Block Elements in PPT FormharshadNo ratings yet
- Hydroxyl at I OnDocument60 pagesHydroxyl at I OngbgbkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Leachate Electrocoagulation ElectrooxidationDocument6 pagesLeachate Electrocoagulation ElectrooxidationQuea ApurimacNo ratings yet
- Proton NMR SpectrosDocument2 pagesProton NMR Spectrosnandhini sunderNo ratings yet
- Class - Xii Chemistry Sample Paper - 3 Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 70 General InstructionsDocument17 pagesClass - Xii Chemistry Sample Paper - 3 Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 70 General Instructionssoumya mazumdarNo ratings yet
- 05 Petrucci10e CSMDocument45 pages05 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument80 pagesOrganic ChemistryHasithaNo ratings yet
- Hydrothermal SolutionsDocument11 pagesHydrothermal SolutionsDedi ApriadiNo ratings yet
- Bab 6Document26 pagesBab 6Risna NurhanisaNo ratings yet
- LT3Document1 pageLT3ReiVanNo ratings yet
- LRERDocument5 pagesLRERuser 12No ratings yet
- Reactions of CopperDocument20 pagesReactions of CopperChaimaaElborki100% (2)
- 1.1.0.1.5 Data Tables For Periodic TableDocument1 page1.1.0.1.5 Data Tables For Periodic TablebashanabilNo ratings yet
- Code 0: Iit - Jee (2011) Paper Ii Question & SolutionsDocument25 pagesCode 0: Iit - Jee (2011) Paper Ii Question & SolutionskapilNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Copper: Percent YieldDocument20 pagesReactions of Copper: Percent Yieldwann711100% (1)
- Zuo 2016Document10 pagesZuo 2016Phạm NgânNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Test 2, Spring 2015Document10 pagesPractice Questions For Test 2, Spring 2015Arianne Foster100% (1)
- Chemistry - Shift 2 - 27 01 2024Document9 pagesChemistry - Shift 2 - 27 01 2024hemacsv2009No ratings yet
- Inorgnic Lecture-06Document20 pagesInorgnic Lecture-06Tejas AsijaNo ratings yet
- Narayana... Iit Jee PaperDocument26 pagesNarayana... Iit Jee PaperAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-01-28 at 5.55.12 AMDocument7 pagesScreenshot 2024-01-28 at 5.55.12 AMNarendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Critical Diameter v. Flow Rate: D@a 2 D@a 3 D@a 5 D@a 8Document2 pagesCritical Diameter v. Flow Rate: D@a 2 D@a 3 D@a 5 D@a 8Cheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- 9-9-13 Biostatistics NotesDocument1 page9-9-13 Biostatistics NotesCheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- How To Play Texas HoldDocument1 pageHow To Play Texas HoldCheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- Genetics Midterm 2 Study Guide PT 2 Molecular GeneticsDocument6 pagesGenetics Midterm 2 Study Guide PT 2 Molecular GeneticsCheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- Preparation of P-NitroanilineDocument11 pagesPreparation of P-NitroanilineRebecca Badour50% (2)
- Experiment 9 DataDocument1 pageExperiment 9 DataCheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- 10 Fluorescence of Polycyclic Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument6 pages10 Fluorescence of Polycyclic Aromatic HydrocarbonsCheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesLecture 4 - Amino AcidsCheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- Preparation of The Paramagnetic Complex MNDocument6 pagesPreparation of The Paramagnetic Complex MNCheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- Chem 3119 Experiment 4Document8 pagesChem 3119 Experiment 4Cheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet
- Pre Lab Assignment: Complete The Pre-Lab Cover Page and Develop A Procedure. Draw TheDocument3 pagesPre Lab Assignment: Complete The Pre-Lab Cover Page and Develop A Procedure. Draw TheCheyenne MartinsNo ratings yet