Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supply Chain Management 2014
Uploaded by
joel leonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supply Chain Management 2014
Uploaded by
joel leonCopyright:
Available Formats
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
FABINA MANI
A30101912154
ABOUT WALMART
Walmart was founded by Sam Walton in 1962 with the opening
of the first Walmart store in Rogers, Ark. The company was
incorporated as Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. in 1969.
Walmart serves customers more than 200 million times per week
at more than 10,900 retail units in 27 countries.
For the fiscal year ended January 2013, Walmart increased net
sales by 5% to $466.1 billion and returned $13 billion to
shareholders through dividends and share repurchases.
Walmart ranked second on the 2012 FORTUNE 500 list of the
worlds largest companies by revenue.
Today in the U.S., Walmart operates more than 4,600 retail
facilities.
For fiscal year 2013, Walmart U.S. net sales were more than $274
billion.
Supply Chain: The sequence of organizations - their facilities,
functions, and activities - that are involved in producing and
delivering a product or service.
Sometimes referred to as value chains
Wal-Marts Procurement
Wal-Mart emphasized the need to reduce purchasing
costs and offer the best price to the customer.
The company directly procured from manufacturers, by
passing all intermediaries.
Wal-Mart finalizes a purchase deal only when it is fully
confident that the products being bought is not available
else where at a lower price.
Vendor-managed inventory
systems
to replenish stocks
Wal-Mart transmitted sales data, orders of products,
delivery plan and reports of warehouse inventory status
to them daily
to plan inventory levels, generate purchase orders, and
ship exactly what was needed
both benefited from reduced inventory costs and
increased sales
Using EDI (Electronic data interchange)for
Procurement
The computer systems of Wal-Mart were connected to
those of its suppliers.
EDI enabled the suppliers to download purchase orders
along with store-to-store sales information relating to
their products sold.
On receiving information about the sales of various
products, the suppliers shipped the required goods to
Wal-Marts distribution centers.
Electronic Data Interchange
Increased productivity
Reduction of paperwork
Lead time and inventory reduction
Electronic transfer of funds
Improved control of operations
Reduction in clerical labor
Increased accuracy
Walmart Supply Chain Flow Chart
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Distribution Center
Company
Headquarter
Satellite System
Retail Store
Retail Store
Bar code, RFID
Retail Store
Radio, headphone
Logistics Management
Walmart is able to move goods to and from distribution
centers because they maintain a private fleet of trucks
and a skilled staff of truck drivers.
Company hired experienced drivers having more than
300,000 accident free miles with no major traffic
violation.
Every year they drive 700 million miles to make millions
of deliveries to our stores and clubs.
Each driver averages around 100,000 miles annually
thats like driving around the world 4 times!
Drivers follow the most efficient routes to their
destinations, and work to minimize the number of empty
miles they drive.
Hub and Spoke System
In the early 1970s, Wal-Mart became one of the
first retailing companies in the world to centralize
its distribution system, pioneering the retail hub-
and-spoke system.
Cross-docking by Wal-mart
Requisitions received for different goods from a store are
converted into purchase or procurement orders.
Purchase orders are then forwarded to the manufacturers
who convey their ability or inability to supply the goods within
a particular period of time.
If manufacturer agrees, goods are directly forwarded to a
place called the staging area.
The goods are packed here according to the orders received
from different stores and then directly sent to the respective
customers.
Wal-mart shifted the focus from supply chainto the demand
chain, which meant that instead of the retailer pushing
products into the system; customers could pull products,
when and where they needed.
The Traditional Supply Chain Includes Inefficient
and Unnecessary Steps
Wal-Mart Simplified Its Supply Chain
Cross-docking in distribution centers results in product flow from inbound to
outbound shipping docks within 48 hours.
Flow-Time Analysis:
Point-of-sale
system
captures data
in real-time
Data is
transmitted to
warehouses
for Inv. Mgmt.
Retail Link
transmits
data to
supplier
Orders are
generated from
previous-day
sales
Merchandise is
loaded onto
trucks using
cross-docking
Merchandise
is delivered to
the store
Merchandise is
manufactured
based on historical
and real-time data
Merchandise
is shipped to
warehouses
Customer
made a
purchase
The store will re-
stock the shelves
with merchandise
Retail Link real-time point-of-sales (POS)
data transmission
Cross Docking
Fleet of 7,000 trucks in US
Inventory Management
Wal-Mart invested heavily in IT and communication
systems to effectively track sales and merchandise
inventories in stores across the country.
With the rapid expansion, it was essential to have a good
communication system.
Hence, Wal-Mart set up its own satellite communication
system in 1983.
Employees at the stores had the Magic Wand, a hand-
held computer which was linked to in-store terminals
through a radio frequency network.
These helped them to keep track of the inventory in
stores, deliveries, and backup merchandise in stock at the
distribution centers.
The order management and store replenishment of
goods were entirely executed with the help of computers
through the Point-of-Sales (POS) system.
Through this system, it was possible to monitor and track
the sales and merchandise stock levels on the store
shelves.
Inventory Management
(quick replenishment)
Since the floor area of any Wal-Mart store varied
between 40,000 to 200,000 square feet, movement of
goods within the store was an important part of logistics
operations.
Wal-Mart made significant investments in IT to quickly
locate and replenish goods at the stores.
Voice-based Order Filling
(VOF)
In 1998, Wal-Mart installed a voice-based order filling
(VOF) system in all its grocery distribution centers.
Each person responsible for order picking was provided
with a microphone/speaker headset, connected to the
portable (VOF) system that could be worn on waist belt.
They were guided by the voice to item locations in the
distribution centers.
Inventory Management
(pretty darn quick displays)
The company asked its suppliers to ship goods in store-
ready displays called pretty darn quick (PDQ) displays.
Goods were packed in PDQ displays that arrived at the
stores ready to be boarded on the racks.
Wal-Marts employees could directly replace the empty
racks at the stores with fully packed racks, instead of
refilling each and every item at the racks.
Distribution center Layout
Walmarts distribution centers are hubs of activity for their business.
Their distribution operation is one of the largest in the world.
There are 9 disaster distribution centers, strategically located across
the country and stocked to provide rapid response to struggling
communities in the event of a natural disaster.
Each distribution center is more than 1 million square feet in size,
and uses more than 5 miles of conveyor belts to keep products
moving to their stores 24 hours a day.
Every distribution center supports 90 to 100 stores in a 200-mile
radius.
Benefits
Able replenish stores within 48 hrs against 5 days for
competitors.
Shipping cost of walmart 3% against 5% for competitors
Higher profits
Shorter lead time
Working of Distribution Center
The distribution centers ensured steady flow & consistent flow of
products.
Large-scale use of sophisticated technology such as Bar code, hand
held computer systems (Magic Wand) and now, RFID.
Every employee had information regarding products at distribution
center.
They make 2 scans- one for identifying the pallet, and other to
identify the location from where the stock had to be picked up.
The hand held computers guide employee to the location of the
specific product.
The quantity of the product required from the center is entered in
the hand held computer, which updates the information on the main
central server.
The computers also enabled the packaging department to get
accurate information such as storage, packaging & shipping
Bar Code System
Standardized bar code system
Applied by every supplier
Helps facilitating large scale operation
Pallets/Cases passed through conveyor
belt are scanned automatically
Product codes are transferred to
centralized computer system
Matching with the computer database
and generate useful information
What it is. What quantity it is. Which
packing compartment and truck to go.
Which store to go.
RFID
In efforts to implement new technologies to reduce costs
and increase the efficiency, in July 2003, Wal-Mart asked
its top 100 suppliers to be RFID compliant by January,
2005.
Wal-Mart planned to replace bar-code technology with
RFID technology.
The company believed that this replacement would
reduce its supply chain management costs and enhance
efficiency.
Because of the implementation of RFID, employees were
no longer required to physically scan the bar codes of
goods entering the stores and distribution centers, saving
labor cost and time.
RFID helps to locate where the pallet is and the condition of it
temperature
Humidity
Automatic sensor avoid scanning codes one by one.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- 1800 Juana Rosa Del CastilloDocument20 pages1800 Juana Rosa Del CastilloDeyvis Gonzales GuevaraNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- 01 Brochure Mining Products - DragerDocument20 pages01 Brochure Mining Products - Dragerjoel leonNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Volcan Corp Presentation BTG (Chile)Document32 pagesVolcan Corp Presentation BTG (Chile)Edgar Joel Leon RosalesNo ratings yet
- Giacomini - Modelo A7BP y Piton Policarbonato A7BP y Bronce A7BDocument4 pagesGiacomini - Modelo A7BP y Piton Policarbonato A7BP y Bronce A7Bjoel leonNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Abraaj Latam Final Gaston AcurioDocument23 pagesAbraaj Latam Final Gaston Acuriojoel leonNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- XTIRPA - Bulletin (2300-110-MC - EN) 2016-08Document20 pagesXTIRPA - Bulletin (2300-110-MC - EN) 2016-08joel leonNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 5555-576-Mc - Food Manufacturing Safety IssuesDocument2 pages5555-576-Mc - Food Manufacturing Safety Issuesjoel leonNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Aureos Invests in Leading Peruvian Restaurant GroupDocument2 pagesAureos Invests in Leading Peruvian Restaurant Groupjoel leonNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- IESE Optical Capital Structure PDFDocument17 pagesIESE Optical Capital Structure PDFGustavo JimenezxNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Conferencia Nuevas Regulaciones BEPS y PT PWC Chile PDFDocument113 pagesConferencia Nuevas Regulaciones BEPS y PT PWC Chile PDFFrancisco Hormazábal LópezNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Industrial Business Group PDFDocument19 pagesIndustrial Business Group PDFjoel leonNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 011 Startup APEC Luis TorresDocument11 pages011 Startup APEC Luis Torresjoel leonNo ratings yet
- XTIRPA - Bulletin (2300-110-MC - EN) 2016-08Document20 pagesXTIRPA - Bulletin (2300-110-MC - EN) 2016-08joel leonNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- 3M, Una Estrategia Emergente para El Crecimiento IDocument75 pages3M, Una Estrategia Emergente para El Crecimiento Ijoel leonNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Msa Advantage 200Document12 pagesMsa Advantage 200joel leonNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- 0815 27 MC HazmatcadgdeDocument4 pages0815 27 MC Hazmatcadgdejoel leonNo ratings yet
- WTSB Freight Services Company ProfileDocument10 pagesWTSB Freight Services Company ProfileIzza NasirNo ratings yet
- What Is Value Chain: N.aspDocument4 pagesWhat Is Value Chain: N.aspCharisse VisteNo ratings yet
- The Impacts of Natural Disasters On Global Supply Chains: Ye, Linghe Abe, MasatoDocument29 pagesThe Impacts of Natural Disasters On Global Supply Chains: Ye, Linghe Abe, MasatomurungirakeeliNo ratings yet
- Bijoy Korembeth - OriginalDocument6 pagesBijoy Korembeth - OriginalHamid SaifNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- SDM 4Document15 pagesSDM 4Anonymous 9oL9HS0% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Ballou, R. - Logistics Customer ServiceDocument34 pagesBallou, R. - Logistics Customer ServiceGhani Rizky100% (1)
- Formulario Bill of Lading en EspañolDocument1 pageFormulario Bill of Lading en EspañolrichivalensNo ratings yet
- Inventories QuestionnaireDocument9 pagesInventories QuestionnaireKristine JavierNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Lean Six Sigma Overview - White Belt TrainingDocument35 pagesLean Six Sigma Overview - White Belt TrainingSteven Bonacorsi100% (4)
- (Chapter - 4) MEng 5361 (IEng 5241) - Industrial Management & Engineering EconomyDocument19 pages(Chapter - 4) MEng 5361 (IEng 5241) - Industrial Management & Engineering Economydawit tadewoseNo ratings yet
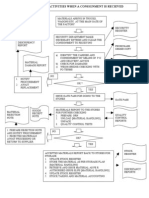
- Flow Diagram (Stores Activities When Consignment Is Received)Document1 pageFlow Diagram (Stores Activities When Consignment Is Received)Vinay Singh71% (7)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Chapter 5 - Controlling Inventory CostsDocument22 pagesChapter 5 - Controlling Inventory CostsAngelica CastilloNo ratings yet
- Asad CV - SCM FunctionalDocument4 pagesAsad CV - SCM Functionalptcl1No ratings yet
- Hill e Scudder (2002)Document13 pagesHill e Scudder (2002)Igor MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Building Competitive Advantage Through Functional Level StrategyDocument50 pagesBuilding Competitive Advantage Through Functional Level Strategykawsar_cow2819No ratings yet
- MK CVDocument3 pagesMK CVlalitchauha_nNo ratings yet
- Basic Steps Involved in ProcurementDocument10 pagesBasic Steps Involved in ProcurementBilal AliNo ratings yet
- SC - Lazada - Introduction and BackgroundDocument9 pagesSC - Lazada - Introduction and Backgroundtrung thành trầnNo ratings yet
- Jakki Mohr, Sanjit Sengupta, Stanley Slater Marketing of High-Technology Products and InnovationsDocument569 pagesJakki Mohr, Sanjit Sengupta, Stanley Slater Marketing of High-Technology Products and InnovationsArshed Rosales100% (3)
- MBA Seeks Challenging RoleDocument5 pagesMBA Seeks Challenging RolePriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Warehouse Management of REB: A Case Study of Central Warehouse, DhakaDocument127 pagesA Study On Warehouse Management of REB: A Case Study of Central Warehouse, Dhakapravincs_007No ratings yet
- Important Sap Ewm TablesDocument9 pagesImportant Sap Ewm TableshalwanvNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Decathlon - Group 2 - ContentDocument43 pagesDecathlon - Group 2 - ContentBảo Châuu100% (6)
- Post Graduate Diploma in ManagementDocument3 pagesPost Graduate Diploma in ManagementSandeep SonawneNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Shipping & Port Management SyllabusDocument7 pagesDiploma in Shipping & Port Management SyllabusMercyNo ratings yet
- Acccob2-Chapter5-Inventories - ExercisesDocument65 pagesAcccob2-Chapter5-Inventories - ExercisesMelyssa Dawn GullonNo ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDocument1 pageReflection PaperLiezel Miles BacaroNo ratings yet
- Case1 Central TransportDocument1 pageCase1 Central TransportCarolina0% (1)
- Minimum Automotive Quality Management System Requirements For Sub Tirev2Document9 pagesMinimum Automotive Quality Management System Requirements For Sub Tirev2Marco SilvaNo ratings yet
- Eng Thesis FinalDocument61 pagesEng Thesis FinalanzaniNo ratings yet