Professional Documents
Culture Documents
#Include: Ofstream Fout Fout Open I I I Fout I Endl Fout Close
#Include: Ofstream Fout Fout Open I I I Fout I Endl Fout Close
Uploaded by
Anand MajumderOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
#Include: Ofstream Fout Fout Open I I I Fout I Endl Fout Close
#Include: Ofstream Fout Fout Open I I I Fout I Endl Fout Close
Uploaded by
Anand MajumderCopyright:
Available Formats
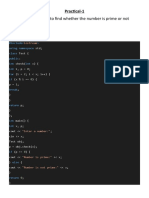
1 Write a C++ program to write number 1 to 100 in a data file NOTES.TXT.
#include<fstream.h>
int main()
{
ofstream fout;
fout.open("NOTES.TXT");
for(int i=1;i<=100;i++)
fout<<i<<endl;
fout.close();
return 0;
}
2 Write a C++ program, which initializes a string variable to the content
"Time is a great teacher but unfortunately it kills all its pupils. Berlioz"
and outputs the string to the disk file OUT.TXT. you have to include all the
header files if required.
#include<fstream.h>
int main()
{
ofstream fout;
fout.open("out.txt");
char str[300]="Time is a great teacher but unfortunately it kills
all its pupils. Berlioz";
fout<<str;
fout.close();
return 0;
}
3 Write a user-defined function in C++ to read the content from a text file
OUT.TXT, count and display the number of alphabets present in it
void alphabets()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("out.txt");
char ch;
int count=0;
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin.get(ch);
if(isalpha(ch))
count++;
}
cout<<"Number of alphabets in file are "<<count;
fin.close();
}
4 Write a function to count the number of blank present in a text file named
"OUT.TXT".
void blankspace()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("out.txt");
char ch;
int count=0;
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin.get(ch);
if(ch==' ')
count++;
}
cout<<"Number of blank spaces in file are "<<count;
fin.close();
}
5 Write a function to count number of words in a text file named
"OUT.TXT".
void countwords()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("out.txt");
char word[30];
int count=0;
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin>>word;
count++;
}
cout<<"Number of words in file are "<<count;
fin.close();
}
6 Write a function in C++ to print the count of word the as an independent
word in a text file STORY.TXT.
for example, if the content of the file STORY.TXT is
There was a monkey in the zoo. The monkey was very naughty.
Then the ouput of the program should be 2.
void countword()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("STORY.TXT");
char word[30];
int count=0;
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin>>word;
if(strcmpi(word,"the")==0)
count++;
}
cout<<"Number of the word in file are "<<count;
fin.close();
}
7 Write a function in C++ to count and display the number of lines not
starting with alphabet 'A' present in a text file "STORY.TXT".
Example:
If the file "STORY.TXT" contains the following lines,
The rose is red.
A girl is playing there.
There is a playground.
An aeroplane is in the sky.
Numbers are not allowed in the password.
The function should display the output as 3.
void countlines()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("STORY.TXT");
char str[80];
int count=0;
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin.getline(str,80);
if(str[0]!='A')
count++;
}
cout<<"Number of lines not starting with A are "<<count;
fin.close();
}
8 Assuming that a text file named FIRST.TXT contains some text written
into it, write a function named copyupper(), that reads the file FIRST.TXT
and creates a new file named SECOND.TXT contains all words from the
file FIRST.TXT in uppercase.
void copyupper()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("FIRST.TXT");
ofstream fout;
fout.open("SECOND.TXT");
char ch;
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin.get(ch);
ch=toupper(ch);
fout<<ch;
}
fin.close();
fout.close();
}
9 Assuming that a text file named FIRST.TXT contains some text written
into it, write a function named vowelwords(), that reads the file
FIRST.TXT and creates a new file named SECOND.TXT, to contain only
those words from the file FIRST.TXT which start with a lowercase vowel
(i.e., with 'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u').
For example, if the file FIRST.TXT contains
Carry umbrella and overcoat when it rains
Then the file SECOND.TXT shall contain
umbrella and overcoat it
void vowelwords()
{
ifstream fin;
fin.open("FIRST.TXT");
ofstream fout;
fout.open("SECOND.TXT");
char word[30];
while(!fin.eof())
{
fin>>word;
if(word[0]=='a'||word[0]=='e'||word[0]=='i'||word[0]=='o'||word[0]=='u')
fout<<word<<" ";
}
fin.close();
fout.close();
}
1 Write the definition for a class called Rectangle that has floating
point data members length and width. The class has the following
member functions:
void setlength(float) to set the length data member
void setwidth(float) to set the width data member
float perimeter() to calculate and return the perimeter of the
rectangle
float area() to calculate and return the area of the rectangle
void show() to display the length and width of the rectangle
int sameArea(Rectangle) that has one parameter of type
Rectangle. sameArea returns 1 if the two Rectangles have the
same area, and returns 0 if they don't.
1. Write the definitions for each of the above member functions.
2. Write main function to create two rectangle objects. Set the
length and width of the first rectangle to 5 and 2.5. Set the
length and width of the second rectangle to 5 and 18.9.
Display each rectangle and its area and perimeter.
3. Check whether the two Rectangles have the same area and
print a message indicating the result. Set the length and width of
the first rectangle to 15 and 6.3. Display each Rectangle and
its area and perimeter again. Again, check whether the two
Rectangles have the same area and print a message indicating
the result.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class Rectangle
{
private:
float length;
float width;
public:
void setlength(float);
void setwidth(float);
float perimeter();
float area();
void show();
int sameArea(Rectangle);
};
void Rectangle::setlength(float len)
{
length = len;
}
void Rectangle::setwidth(float wid)
{
width = wid;
}
float Rectangle::perimeter()
{
return (2 * length + 2 * width);
}
float Rectangle::area()
{
return length * width;
}
void Rectangle::show()
{
cout << "Length: " << length << " Width: " << width;
}
int Rectangle::sameArea(Rectangle other)
{
float areaf = length * width;
float areas = other.length * other.width;
if (areaf == areas)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
Rectangle first;
Rectangle second;
first.setlength(5);
first.setwidth(2.5);
second.setlength(5);
second.setwidth(18.9);
cout << "First rectangle: ";
first.show();
cout << endl << "Area: " << first.area() << "Perimeter: " <<
first.perimeter() << endl << endl;
cout << "Second rectangle: ";
second.show();
cout << endl << "Area: " << second.area() << "Perimeter: " <<
second.perimeter() << endl << endl;
if (first.sameArea(second))
cout << "Rectangles have the same area\n";
else
cout << "Rectangles do not have the same area\n";
first.setlength(15);
first.setwidth(6.3);
cout << "First rectangle: ";
first.show();
cout << endl << "Area: " << first.area() << "Perimeter: "<<
first.perimeter() << endl << endl;
cout << "Second rectangle: ";
second.show();
cout << endl << "Area: " << second.area() << "Perimeter: "<<
second.perimeter() << endl << endl;
if (first.sameArea(second))
cout << "Rectangles have the same area\n";
else
cout << "Rectangles do not have the same area\n";
getch();
return 0;
}
2 Write the definition for a class called complex that has floating
point data members for storing real and imaginary parts. The
class has the following member functions:
void set(float, float) to set the specified value in object
void disp() to display complex number object
complex sum(complex) to sum two complex numbers & return
complex number
1. Write the definitions for each of the above member functions.
2. Write main function to create three complex number objects.
Set the value in two objects and call sum() to calculate sum and
assign it in third object. Display all complex numbers.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class complex
{
private:
float x;
float y;
public:
void set(float real, float img)
{
x=real; y=img;
}
complex sum(complex);
void disp();
};
complex complex::sum(complex C)
{
complex t;
t.x = x + C.x;
t.y = y + C.y;
return t;
}
void complex::disp()
{
cout<<x<<" + j"<<y<<endl;
}
int main()
{
complex C1,C2,C3;
C1.set(2.5,7.1);
C2.set(4.2,5.5);
C3=C1.sum(C2);
cout<<"\n complex Number 1 = ";C1.disp();
cout<<"\n complex Number 2 = ";C2.disp();
cout<<"\n complex Number 3 = ";C3.disp();
getch();
return 0;
}
3 Write the definition for a class called Distance that has data
member feet as integer and inches as float. The class has the
following member functions:
void set(int, float) to give value to object
void disp() to display distance in feet and inches
Distance add(Distance) to sum two distances & return distance
1. Write the definitions for each of the above member functions.
2. Write main function to create three Distance objects. Set the
value in two objects and call add() to calculate sum and assign it
in third object. Display all distances.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class Distance
{
private:
int feet;
float inches;
public:
void setdist(int ft, float in)
{
feet=ft; inches=in;
}
Distance add(Distance);
void disp();
};
Distance Distance::add(Distance D)
{
Distance t;
t.inches=inches + D.inches;
t.feet =0;
if(t.inches>=12.0)
{
t.inches-=12.0;
t.feet++;
}
t.feet +=feet + D.feet;
return t;
}
void Distance::disp()
{
cout<<feet<<"\'"<<inches<<"\" ";
}
int main()
{
Distance d1,d2,d3;
d1.setdist(10,7.1);
d2.setdist(23,5.5);
d3=d1.add(d2);
cout<<"\n distance 1 = ";d1.disp();
cout<<"\n distance 2 = ";d2.disp();
cout<<"\n distance 3 = ";d3.disp();
getch();
return 0;
}
4 Write the definition for a class called time that has hours and
minutes as integer. The class has the following member
functions:
void settime(int, int) to set the specified value in object
void showtime() to display time object
time sum(time) to sum two time object & return time
1. Write the definitions for each of the above member functions.
2. Write main function to create three time objects. Set the value
in two objects and call sum() to calculate sum and assign it in
third object. Display all time objects.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class time
{
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
public:
void settime(int h, int m)
{
hours=h; minutes=m;
}
time sum(time);
void showtime();
};
time time::sum(time TM)
{
time t;
t.minutes = minutes + TM.minutes;
t.hours=t.minutes/60;
t.minutes=t.minutes%60;
t.hours += hours + TM.hours;
return t;
}
void time::showtime()
{
cout<<hours<<" hours and "<<minutes<<" minutes"<<endl;
}
int main()
{
time T1,T2,T3;
T1.settime(2,45);
T2.settime(3,30);
T3=T1.sum(T2);
cout<<"\n Time 1 : ";T1.showtime();
cout<<"\n Time 2 : ";T2.showtime();
cout<<"\n Time 3 : ";T3.showtime();
getch();
return 0;
}
CERTIFICATE
This is to certify that the project work LIBRARY MANAGEMENT
SYSTEM is a bonafide record of work done by Mr. STUDENT
NAME under my guidance and supervision.
SCHOOL TEACHER NAME
SCHOOL NAME
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
I am extremely grateful to Mr. SCHOOL TEACHER NAME, Teacher of
Department of Computer Science for his able guidance and useful
suggestions, which helped me in completing the project work, in
time.
I would also like to thank all the teaching and non-teaching staff of
Computer Science department who helped me directly or indirectly
in the completion of this project .
Finally, yet importantly, I would like to express my heartfelt thanks
to my beloved parents for their blessings, my friends/classmates for
their help and wishes for the successful completion of this project.
STUDENT NAME
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION. .. 5
SOURCE CODE.. .. 6
OUTPUT SCREEN.. .. 20
LIMITATION AND SUGGESTION .. 27
BIBLIOGRAPHY. .. 27
INTRODUCTION
The project is designed for school library in C++. The title of the
project is Library management system. In this project a student can
issue one book from library. He has to submit it before 15 days.
Otherwise fine will be charged @ Re. 1/- for each day.
Administrator of the project can enter new student record, display
all/specific student record, he can modify and delete student record.
Administrator can enter new book record, display all books modify
book delete book
SOURCE CODE
write source code here copy source code click here
OUTPUT SCREEN
insert output screen / screen shot of project
LIMITATION AND SUGGESTED UPGRADATION
The project needs some upgradation
Program should automatically generate a list of students who does not deposit the book
within time limit.
Program should display information of total available book in stock.
Program should keep account of total collection of fine given by students.
Program should accept date of deposit and date of issued. Number of days should be
automatically calculated
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Sumita Arora Computer Science with C++
E. Balagurusami C++
Robert Lafore Turbo C++
website : www.cppforschool.com
You might also like
- Lab 5 OopDocument6 pagesLab 5 OopHA AimNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 AnswerDocument11 pagesAssignment 1 AnswerAshberi Frene Sibanda0% (1)
- Underground Steam & Condensate Piping PDFDocument26 pagesUnderground Steam & Condensate Piping PDFZacky JoeNo ratings yet
- CARE KM Technical Proposal 2019Document29 pagesCARE KM Technical Proposal 2019simbiroNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: Set-1 Class: Xii Subject: Computer ScienceDocument12 pagesSample Paper: Set-1 Class: Xii Subject: Computer ScienceamishadalalNo ratings yet
- #Include #Include: Class Private PublicDocument5 pages#Include #Include: Class Private PublicRonit DebNo ratings yet
- File Handling in C++Document5 pagesFile Handling in C++Pace InfotechNo ratings yet
- 1 To 11 Slips PDFDocument24 pages1 To 11 Slips PDFdkpatil2929No ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming With C++Document24 pagesObject Oriented Programming With C++Apeksha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment NO:-4: Submitted By:-Raja Kumar RALL NO:-A18 SEC:-D6912Document12 pagesAssignment NO:-4: Submitted By:-Raja Kumar RALL NO:-A18 SEC:-D6912Naveen MahaurNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Board Practical QuestionDocument29 pagesClass Xii Board Practical QuestionVikas SaxenaNo ratings yet
- C++ ProgramDocument10 pagesC++ ProgramsridharanNo ratings yet
- Oop Assignment 1 Fa19-Bee-012Document11 pagesOop Assignment 1 Fa19-Bee-012Arbaz ali0% (1)
- BSC/BCA-2 Object Oriented Programming (SCT-155/CAT-153) Assignment-3Document8 pagesBSC/BCA-2 Object Oriented Programming (SCT-155/CAT-153) Assignment-3AbhinavNo ratings yet
- OOP Assignment 1, FA20-BEE-3C-146Document11 pagesOOP Assignment 1, FA20-BEE-3C-146Souban JavedNo ratings yet
- PPL 7Document12 pagesPPL 7Movie GuyNo ratings yet
- Examination Papers, 2000: (Delhi)Document13 pagesExamination Papers, 2000: (Delhi)Arnab ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Compilation ReyesDocument25 pagesCompilation ReyeskatherineNo ratings yet
- Computer Science WorksheetDocument6 pagesComputer Science WorksheetAman RajNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number - 2.2Document16 pagesExperiment Number - 2.2Sourabh SinghNo ratings yet
- ADS ManualDocument81 pagesADS Manualsrinidhi2allNo ratings yet
- Xii Cs PracticalsDocument21 pagesXii Cs PracticalsKeshav RanaNo ratings yet
- Aryan Cs ProjectDocument28 pagesAryan Cs Projectaryan12gautam12No ratings yet
- HW 4 Cs 32 Ucla Wi 19Document10 pagesHW 4 Cs 32 Ucla Wi 19MariaSaratogaNo ratings yet
- C Plus PlusDocument25 pagesC Plus PlusSarah KhaleelNo ratings yet
- 402 CPPDocument8 pages402 CPPsurajsc2003No ratings yet
- Mbiis Assignment BookletDocument23 pagesMbiis Assignment BookletSebastian MillerNo ratings yet
- Xii Practical Updated On 22-10-22Document31 pagesXii Practical Updated On 22-10-22Vīẞhñû VïçkyNo ratings yet
- Oops Concept All in ProgDocument18 pagesOops Concept All in Progashishpatrick1985No ratings yet
- 01 QP SP 2 CsDocument12 pages01 QP SP 2 CsspcodrNo ratings yet
- OOPs Using C++ (Lab Manual)Document21 pagesOOPs Using C++ (Lab Manual)itsamitdagurNo ratings yet
- Compclass 12Document44 pagesCompclass 12Pubg Gang0% (1)
- Python Programs-From VTU QPDocument6 pagesPython Programs-From VTU QPstudy materialNo ratings yet
- Oodp Week 11Document12 pagesOodp Week 11VIPUL MANOJ KUMAR (RA2111003010646)No ratings yet
- Lab. Sheet One: Linear ListDocument5 pagesLab. Sheet One: Linear ListxzNo ratings yet
- Functions and Conditionals: Define A FunctionDocument15 pagesFunctions and Conditionals: Define A FunctionPambaNo ratings yet
- C AssignmentDocument30 pagesC AssignmentSourav RoyNo ratings yet
- Library Functions - PracticeDocument53 pagesLibrary Functions - PracticeTejasvini YadavNo ratings yet
- Programming Fundamental: Overflow/Under Flow and Character StringDocument15 pagesProgramming Fundamental: Overflow/Under Flow and Character Stringhacker memoryNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming Lab Journal - Lab # 10: Name: Syeda Raiha Batool Enrollment #: 01-134212-181 Class: Bscs 1-ADocument6 pagesComputer Programming Lab Journal - Lab # 10: Name: Syeda Raiha Batool Enrollment #: 01-134212-181 Class: Bscs 1-AsohaibNo ratings yet
- C++ Lab SolutionDocument37 pagesC++ Lab Solutionarpitapanda157No ratings yet
- CS 106B Lecture 3: Vectors, Grids, Big O: Friday, April 7, 2017Document80 pagesCS 106B Lecture 3: Vectors, Grids, Big O: Friday, April 7, 2017imran hameerNo ratings yet
- Akash.0011.Oops LabDocument29 pagesAkash.0011.Oops LabAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- CS Practicle FileDocument53 pagesCS Practicle Filegourav rathodNo ratings yet
- 12 Practical - PythonDocument11 pages12 Practical - PythonTola PtolaNo ratings yet
- FPP Imp Questions (Unit I & II) by MksDocument10 pagesFPP Imp Questions (Unit I & II) by Mks18cse137 navneetkumarshuklaNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Lab ALL EXPERIMENTS FILEDocument84 pagesData Structures Lab ALL EXPERIMENTS FILEManavNo ratings yet
- Javascript ConceptsDocument5 pagesJavascript Conceptshajesh212No ratings yet
- Text File Question Bank SolutionsDocument14 pagesText File Question Bank SolutionssaravananNo ratings yet
- TheoryassignDocument15 pagesTheoryassign12a03anishasabesanNo ratings yet
- CPP Lecture6Document12 pagesCPP Lecture6saif jamalNo ratings yet
- Sahil - Program FileDocument24 pagesSahil - Program Filekunal.1214155669No ratings yet
- Write Instructions Here. Write The Question Here Mark S 1 - A - 2 B 1 C 2Document8 pagesWrite Instructions Here. Write The Question Here Mark S 1 - A - 2 B 1 C 2Amisha DalalNo ratings yet
- Classes&Objects ConstructorsDocument4 pagesClasses&Objects Constructorssaavu0% (1)
- Jessica-PRACTICAL FILEDocument26 pagesJessica-PRACTICAL FILEkunal.1214155669No ratings yet
- Linear List: Data Structure II Lab. HomeworkDocument4 pagesLinear List: Data Structure II Lab. HomeworkxzNo ratings yet
- Java Slips SolutionDocument46 pagesJava Slips Solutionyashkhollam30No ratings yet
- BDA AssignmentDocument55 pagesBDA Assignmentv.tofficial TVNo ratings yet
- Or CR Round4 FinalforIITsDocument36 pagesOr CR Round4 FinalforIITsAnand MajumderNo ratings yet
- Powered by ©: - Download FromDocument5 pagesPowered by ©: - Download FromAnand MajumderNo ratings yet
- Zio 2014 SolutionsDocument1 pageZio 2014 SolutionsAnand MajumderNo ratings yet
- Date Chapters Timings (3 HRS) RemarksDocument2 pagesDate Chapters Timings (3 HRS) RemarksAnand MajumderNo ratings yet
- Aec Ffs Process DocumentationDocument133 pagesAec Ffs Process DocumentationAnand MajumderNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument6 pagesSalt AnalysisNeil Mahaseth72% (29)
- ScheduleDocument2 pagesScheduleAnand MajumderNo ratings yet
- Specs - ABSDocument3 pagesSpecs - ABSBurak KececiNo ratings yet
- How BIOS WorksDocument1 pageHow BIOS WorksNikunj JainNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentLoberiano GeraldNo ratings yet
- 03 Subgrade PDFDocument9 pages03 Subgrade PDFTsegawbeztoNo ratings yet
- V80707 Gresen KCL-RPL Relief Valve SpecificationsDocument4 pagesV80707 Gresen KCL-RPL Relief Valve SpecificationsPaulPaucarCamposNo ratings yet
- An-9006 - IGBT Application Note For Camera StrobeDocument12 pagesAn-9006 - IGBT Application Note For Camera StrobemrgastosoNo ratings yet
- Managing Torque and DragDocument34 pagesManaging Torque and DragMilad Ebrahimi DastgerdiNo ratings yet
- URS B Data SheetDocument4 pagesURS B Data SheetcsmistryNo ratings yet
- Roop Unleashed 02.ipynbDocument15 pagesRoop Unleashed 02.ipynbeternalsoldiergirlNo ratings yet
- Daimler Mercedes Benz Vans at A GlanceDocument17 pagesDaimler Mercedes Benz Vans at A GlanceManasvi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Decks Slab DesignDocument13 pagesDecks Slab DesignAbid Karim TashiNo ratings yet
- Kasami and Gold SequencesDocument21 pagesKasami and Gold Sequencesmaheshwaran50% (2)
- POLEFDNDocument10 pagesPOLEFDNJulio Cesar AyalaNo ratings yet
- English Mongolian 2008-11-15Document28 pagesEnglish Mongolian 2008-11-15RoyMarieNo ratings yet
- Connectome WB Tutorial UserGuide Beta v0.83Document98 pagesConnectome WB Tutorial UserGuide Beta v0.83opensuse1No ratings yet
- Ayse Sarimustafa-CvDocument2 pagesAyse Sarimustafa-CvAnonymous VEZ9ISIpNo ratings yet
- Modified Daily Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesModified Daily Lesson PlanMaribeth TorresNo ratings yet
- Rocklesson 2 NewDocument3 pagesRocklesson 2 Newapi-289573552No ratings yet
- Diamond Chain CatalogueDocument16 pagesDiamond Chain CatalogueShariff DehghanNo ratings yet
- RevaDocument6 pagesRevarashmi377No ratings yet
- Sea Keeping Analysis For Preliminary DesignDocument10 pagesSea Keeping Analysis For Preliminary DesignTullio OpattiNo ratings yet
- Method Statement ST100Document6 pagesMethod Statement ST100tarekNo ratings yet
- Focus Energy Limited - AdDocument1 pageFocus Energy Limited - AdSrinath SaiNo ratings yet
- Thermo L12Document52 pagesThermo L12Pronto P ChirinkaNo ratings yet
- Itto Pmbok 5Document19 pagesItto Pmbok 5imronNo ratings yet
- SAFT Primary Lithium Selector Guide - 2002-06Document10 pagesSAFT Primary Lithium Selector Guide - 2002-06MedSparkNo ratings yet
- 1820 Bib PDFDocument3 pages1820 Bib PDFTarek Med Nejib AttiaNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionsDocument6 pagesRevision QuestionsKwakuNo ratings yet