Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Celiac Disease
Celiac Disease
Uploaded by
matrixtrinity0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views8 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views8 pagesCeliac Disease
Celiac Disease
Uploaded by
matrixtrinityCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Celiac Disease
A disease characterized by the
permanent inability to tolerate
gluten (protein found in wheat,
rye oats and barley
Etiology and Incidence
Exact cause unknown
21:100,000
Second leading cause of
malabsorption syndrome
Familial tendencies
Pathophysiology
Ingestion of gluten
Inability to full digest gliadin (fraction of
gluten)
Accumulation of amino acid glutamine
Toxicity to the mucosal cell of the
intestines
Malabsorption of nutrients
Complications (related to unabsorbed
nutrients)
S/Sx
S/Sx
Fats: Steatorrhea
Proteins: Edema
Vitamin D & Calcium:
Osteomalacia
Vitamin K: bleeding
Iron: anemia
Nursing Interventions:
Gluten-free diet
Corn and rice
Supplemental calories,vitmains,
iron and calcium
Parenteral nutrition if indicated
During Celiac Crisis . . .
Acute episode:
Watery diarrhea and vomiting
(precipitated by GI infection, stress)
FVD and metabolic acidosis
IVF and electrolytes
Albumin infusions (prevent shock)
NGT decompression
Steroids
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Intelligence in PsychologyDocument29 pagesIntelligence in PsychologymatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument6 pagesCritical ThinkingmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- antepartumTEST1 MOSBYDocument14 pagesantepartumTEST1 MOSBYmatrixtrinity50% (2)
- Stress and Illness: Castillo, Justine GDocument19 pagesStress and Illness: Castillo, Justine GmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Group Number: Case Title: Year and Section: Group Members: 1. 5. 2. 6. 3. 7. 4. 8Document1 pageGroup Number: Case Title: Year and Section: Group Members: 1. 5. 2. 6. 3. 7. 4. 8matrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Distinguishing Features of Anthropology - Characteristics 1-5 6.78 What Are The3 Unique Approaches of AnthropologyDocument2 pagesDistinguishing Features of Anthropology - Characteristics 1-5 6.78 What Are The3 Unique Approaches of AnthropologymatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Socio - GENDER, ETHNICITY AND RACEDocument22 pagesSocio - GENDER, ETHNICITY AND RACEmatrixtrinity100% (1)
- Intestinal Obstruction Wit Pic2Document2 pagesIntestinal Obstruction Wit Pic2matrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction5Document4 pagesIntestinal Obstruction5matrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Antepartumtest2 LippincottDocument7 pagesAntepartumtest2 Lippincottmatrixtrinity100% (1)
- What Is Intestinal ObstructionDocument5 pagesWhat Is Intestinal ObstructionmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Rochi Paraon Benito, RN Infection Control NurseDocument15 pagesCirculatory System: Rochi Paraon Benito, RN Infection Control NursematrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physio Logic ProcessDocument35 pagesCardiovascular Physio Logic ProcessmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accidents: Rochee P. Benito, RNDocument23 pagesCerebrovascular Accidents: Rochee P. Benito, RNmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Cardio DiseasesDocument17 pagesCardio DiseasesmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentDocument33 pagesBlood Componentmatrixtrinity100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Therapeutic ManagementDocument15 pagesCardiovascular Therapeutic ManagementmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
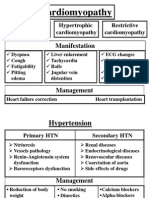
- Cardiomyopathy 02Document2 pagesCardiomyopathy 02matrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Burns and Environmental EmergenciesDocument33 pagesBurns and Environmental EmergenciesmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet