Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiratory Findings in Dental Laboratory Technicians in Rasht (North of Iran) .
Respiratory Findings in Dental Laboratory Technicians in Rasht (North of Iran) .
Uploaded by
heartbreakingse600 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageBACKGROUND:
There are several occupations that can expose people to some air pollutan
Original Title
Respiratory findings in dental laboratory technicians in rasht (north of iran).
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBACKGROUND:
There are several occupations that can expose people to some air pollutan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageRespiratory Findings in Dental Laboratory Technicians in Rasht (North of Iran) .
Respiratory Findings in Dental Laboratory Technicians in Rasht (North of Iran) .
Uploaded by
heartbreakingse60BACKGROUND:
There are several occupations that can expose people to some air pollutan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Respiratory findings in dental laboratory technicians in
rasht (north of iran).
BACKGROUND:
There are several occupations that can expose people to some air pollutants. Dental technicians are
exposed to inorganic dust and chemical vapors when making dental prosthesis that can put them at
risk for respiratory problems. This study was performed to assess respiratory dysfunction in a group
of dental technicians.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
This was a cross-sectional study designed to ascertain the prevalence of respiratory disorders in
dental laboratory technicians in Rasht, a city located in north of Iran. A Structured questionnaire
was adapted according to the European Community Respiratory Health Survey questionnaire and
used to elicit information regarding sociodemographic characteristics and medical status of the
study participants. The ventilation status, protective measures and direct exposure to materials in
the laboratories were directly observed by the observers and subjects underwent respiratory tests
and chest x-ray.
RESULTS:
The mean age of dental technicians was 31.31 yrs (range 18-56 years) and 83% were males with a
mean dental work experience of 9.04 years. In dental Boston MA 54.8% of cases, the work
environment did not have air conditioning system. The most common signs and symptoms were
cough (38.1%) and wheezing (16.7%). There was a significant correlation between smoking and
respiratory signs. Restrictive airway pattern and air trapping were two prevalent findings which
were observed in 85.7% and 33.3% of the subjects. Cigarette smoking had a negative effect on
FEV1, FEF25%-75%, and TLC causing a significant reduction in all three parameters (p < 0.05). The
most prevalent finding was interstitial opacity which was observed in 10 individuals (23.8%). This
finding was not significantly associated with age, gender, cigarette smoking, or daily work hours.
However, there was a http://www.ssdentalgroup.com/doctors-staff/ significant statistical association
between work experience and interstitial opacity.
CONCLUSION:
The prevalence of respiratory dysfunction and chest x-ray findings were high as in several similar
studies. In order to reduce the hazards of respiratory disorders in risky occupations and provide
dental workers with technical preventive measures, a more comprehensive study should be
conducted throughout the country and further evaluations through biopsy and CT-scan need to be
performed in suspicious cases when necessary.
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Suzuki SV1000: Half-Faired Naked Bike Motorcycles Suzuki Displacement V-Twin Honda VTR1000FDocument2 pagesSuzuki SV1000: Half-Faired Naked Bike Motorcycles Suzuki Displacement V-Twin Honda VTR1000FHategan PaulNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
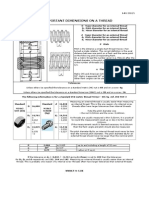
- Meteric ThreadDocument1 pageMeteric Threadmanish_chaturvedi_6No ratings yet
- Deed of Absolute Sale of An Unregistered LandDocument2 pagesDeed of Absolute Sale of An Unregistered LandJhon Antonio Abad84% (31)
- Rigging Plan FormatDocument3 pagesRigging Plan FormatuzairmetallurgistNo ratings yet
- Official Invitation Letter Malaysia Open Source Conference 2012 (MOSC2012)Document1 pageOfficial Invitation Letter Malaysia Open Source Conference 2012 (MOSC2012)LinuxMalaysia MalaysiaNo ratings yet
- Specification For Stone PitchingDocument6 pagesSpecification For Stone PitchingparathasiNo ratings yet
- Flowchart For AcetaldehydeDocument2 pagesFlowchart For Acetaldehydeyigitilgaz0% (1)
- A4 Art Folder TutorialDocument10 pagesA4 Art Folder Tutorialthimbelinas67% (6)
- Database Creation Using DBCADocument11 pagesDatabase Creation Using DBCAG.R.THIYAGU ; Oracle DBANo ratings yet
- D-Link DWC-1000 PDFDocument2 pagesD-Link DWC-1000 PDFjackcomau3472No ratings yet
- 9/11 Oral Histories (7060 Pages)Document7,060 pages9/11 Oral Histories (7060 Pages)Cantankerous BuddhaNo ratings yet
- KWP 2000Document4 pagesKWP 2000mazacotesNo ratings yet
- FMCG - Hul - BCDocument11 pagesFMCG - Hul - BCInderjit SinghNo ratings yet
- AR HVAC Load Calculation WorksheetDocument2 pagesAR HVAC Load Calculation WorksheetSooraj VsNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Reports PE Exam Diagnostic Report and Interpretation1Document2 pagesDiagnostic Reports PE Exam Diagnostic Report and Interpretation1imoomexNo ratings yet
- QM1 2 PDFDocument3 pagesQM1 2 PDFGabino Corona100% (1)
- Ultimate 8043 Instructions Part 1Document15 pagesUltimate 8043 Instructions Part 1Catalin JipescuNo ratings yet
- Beta Case Study (Nirbhay Chauhan)Document10 pagesBeta Case Study (Nirbhay Chauhan)Nirbhay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ansi MV Gis 8dadb Flyer enDocument2 pagesAnsi MV Gis 8dadb Flyer enNBWNo ratings yet
- Panasonic R134A QA SerisDocument2 pagesPanasonic R134A QA SerisChalitha Nayana Hewawasam0% (2)
- LDNDocument2 pagesLDNShaharyar KhanNo ratings yet
- 33 Relative and TrueDocument32 pages33 Relative and TrueArun Ketu SethNo ratings yet
- Offshore Rig Survey For TRS PersonnelDocument1 pageOffshore Rig Survey For TRS PersonnelrageshmvNo ratings yet
- ETHANOL VAPOR PRESSURE AntoineCalculatio PDFDocument2 pagesETHANOL VAPOR PRESSURE AntoineCalculatio PDFTasic NenadNo ratings yet
- The Accidental Native by J.L. TorresDocument257 pagesThe Accidental Native by J.L. TorresArte Público PressNo ratings yet
- Biotech EssayDocument2 pagesBiotech EssayPatel SuraiyaNo ratings yet
- Bhu SuktamDocument2 pagesBhu SuktamCrystal Roberts100% (1)
- PomcDocument8 pagesPomcAnirudh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- EE 442 642 IntroductionDocument14 pagesEE 442 642 IntroductionUSERNAME12340987No ratings yet
- BL - CM MP19.F0Document2 pagesBL - CM MP19.F0arifiyumNo ratings yet