Professional Documents
Culture Documents
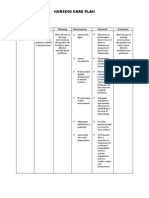
Definition of Terms
Uploaded by
Jhevilin RMCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of Terms
Uploaded by
Jhevilin RMCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of Terms
Communicable disease capable of being transmitted from one person to another direct or
indirect transmission.
Disparities Inequality or difference
Inadequacies lack of an adequate quantity or number
Proliferation to grow or multiply by rapidly producing new tissue, parts, cells, or offspring.
Conscientious controlled by or done according to one's inner sense of what is right;
governed by conscience; principled
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic A significant human
pathogenic bacterium major cause of pneumonia in the late 19th century, and is the
subject of many humoral immunity studies.
Haemophilus influenzae formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or Bacillus influenzae, is a
Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. A member of the Pasteurellaceae family, it is
generally aerobic, but can grow as a facultative anaerobe
.
Moraxella catarrhalis is a fastidious, nonmotile, Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase-positive
diplococcus that can cause infections of the respiratory system
Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the
lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose fermenting,
facultative anaerobic, rod shaped bacterium. Although found in the normal flora of the
mouth, skin, and intestines,
[1]
it can cause destructive changes to human lungs if aspirated.
Immunocompromised pertaining to an immune response that has been weakened by a
disease or an immunosuppressive agent.
Dissemination To scatter widely
Empiric antibiotic therapy is a medical term referring to the initiation of treatment prior
to determination of a firm diagnosis.
Immunocompetent Able to develop an immune response.
Discrepancy a conflict or variation, as between facts, figures, or claims.
Recuperate To return to health or strength; recover.
Tangible Something palpable or concrete.
Ingenuity Inventive skill or imagination; cleverness.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Anesthesia - State of Narcosis, Analgesia, Relaxation, and Loss of Reflex. Effects of AnesthesiaDocument3 pagesAnesthesia - State of Narcosis, Analgesia, Relaxation, and Loss of Reflex. Effects of AnesthesiaJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Classification Action Adverse Effect Indication Contraindicat Ion Nursing InterventionDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Classification Action Adverse Effect Indication Contraindicat Ion Nursing InterventionJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Hemmorhagic StrokeDocument2 pagesHemmorhagic StrokeJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument1 pageAntidotesRichard Ines Valino100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJhevilin RM100% (1)
- Ischemic StrokeDocument2 pagesIschemic StrokeJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- PIPAYDocument1 pagePIPAYJhevilin RM0% (1)
- PIPAY ReactionDocument1 pagePIPAY ReactionJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Bells PalsyDocument2 pagesBells PalsyJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
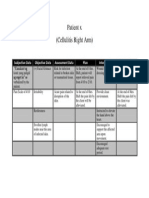
- Patient X (Cellulitis Right Arm) : Subjective Data Objective Data Assessment Data Plan Intervention EvaluationDocument1 pagePatient X (Cellulitis Right Arm) : Subjective Data Objective Data Assessment Data Plan Intervention EvaluationJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument2 pagesHead InjuryJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- TrigeminalDocument1 pageTrigeminalJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Our Lady of Fatima University College of Nursing Antipolo CampusDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Our Lady of Fatima University College of Nursing Antipolo CampusJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Our Lady of Fatima University College of Nursing Antipolo CampusDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Our Lady of Fatima University College of Nursing Antipolo CampusJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing: Answer: (C) "With A Pillow, Apply Pressure Against The Incision."Document5 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing: Answer: (C) "With A Pillow, Apply Pressure Against The Incision."Jhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Normal Lab Values - CARDIAC MARKERSDocument1 pageNormal Lab Values - CARDIAC MARKERSJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Normal Lab ValuesDocument4 pagesNormal Lab ValuesJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Overview in NervousSystemDocument3 pagesOverview in NervousSystemJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- SwotDocument1 pageSwotJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Overview of Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesOverview of Nervous SystemJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Normal Blood ValuesDocument1 pageNormal Blood ValuesJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Hyper & Hypothyroidism LectureDocument1 pageHyper & Hypothyroidism LectureJhevilin RMNo ratings yet
- Sympatheticnervous System (SNS) Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS)Document2 pagesSympatheticnervous System (SNS) Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS)Jhevilin RMNo ratings yet