Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ups 090419105235 Phpapp01
Uploaded by
eryaryasaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ups 090419105235 Phpapp01
Uploaded by
eryaryasaCopyright:
Available Formats
STRATEGIC PLANNING AT UNITED
PARCEL SERVICE
What can
brown do for
you
ABOUT THE COMPANY
The United Parcel Service (UPS) delivers more than 15 million
packages a day to about 6.1 million customers in 200 countries
around the world, making it the worlds largest package delivery
company.
UPS is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia and operates primarily
in the United States with about 428,000 employees.
UPS slogan What can Brown do for you emphasizes the
companys ability to provide services to almost any one in the
world, at any address.
ABOUT THE COMPANY
Before the $42 billion company grew into a worldwide name, it
was started as a small messenger company in 1907 by two aspiring
teenagers, Jim Casey and Claude Ryan in Seattle, Washington
with just $100.
Top competitors of UPS include Federal Express (FedEx), DHL
International and the United States Postal Service.
POWER OF
BUYERS
THREAT OF NEW
ENTRANTS
POWER OF
SUPPLIERS
THREAT OF
SUBSTITUTES
COMPETITIVE
RIVALRY
Highly consolidated
industry
Strong brand images
High capital expenditures
Economies of scale
Trade tariffs and
international regulations
Low switching costs
but customers too
small to have any
individual
advantage
There are no real
substitutes for air
freight
Labor problems
Capacity constraints
Fuel costs
HIGH
LOW
MODERATE
LOW
HIGH
INDUSTRY PROSPECTS AND OVERALL
ATTRACTIVENESS
The alliance between air freight companies and ITES
companies will bring exponential growth to the Air
Freight industry.
This industry should remain attractive, with concentration
on competition for market share, service differentiation,
and brand image.
Current Advertising has been aimed at being better than
the competitor for different reasons.
SWOT ANALYSIS
STRENGTHS WEAKNESSES
Global brand
Strong distribution network
Perception of ground delivery
instead of overnight
Heavy union presence
OPPORTUNITIES THREATS
Expansion of online shopping
Emergence of international
middle class
Increasing fuel costs
Competitive landscape (DHL,
FedEx)
Potentially slowing global
economy
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS (Marketing)
OBJECTIVE: Provide a complete logistics infrastructure to businesses of
any size.
UPS is targeting a global market of producers and consumers, while
making a move to become the supply chain integrator of choice in
e-commerce.
They offer products and services that are state of the art in logistics,
which include the use of bar codes and RFID, high speed package
routing systems, and consulting services.
UPS charges package prices that are in alignment with the industry
and is willing to raise prices alongside FedEx. It has been able to
charge fuel surcharges successfully.
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS (Marketing)
A sales force is maintained to reach business customers and
producers crucial to UPS mission in expanding its role in logistics
to become the supply chain integrator of choice.
There are 150,000 different places to access UPS, worldwide.
Customers can reach them by phone, web, retail outlets, customer
service centers, distribution centers and any of the drivers will
pick up packages. This level of reach to customers is necessary if
UPS expects to gain market share from FedEx.
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS (Operations\ Tech)
OBJECTIVE: Highly integrated operations support product offerings to
offer low cost delivery operations.
UPS is seeking to integrate into freight with larger haul trucks
and it is adding capacity in Asia and Europe with acquisitions of
Sinotrans, a Chinese joint venture and Stolica, a Polish parcel and
express company.
UPS is the 11th largest airline world, with nearly 600 planes, 15
airport hubs worldwide and 900 airports served. Connecting these
airports hubs to customers are 1,750 distribution facilities that sort
packages into 90,000 trucks for deliveries to the home, office, and
72,000 retail outlets. All this requires the integration of air,
ground, logistics and trade financing that UPS maintains is a key
competitive strength.
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS (Human resource)
OBJECTIVE: A high sense of culture and esprit, stock participation
plan, and promotion opportunities contributes to a low turnover
rate of employees.
The company is managed from a highly centralized Management
Committee organized along for the most part in to functions as
opposed to business units. There are business unit presidents in
the Management Committee but only to the extent that the
business unit is organized at a global or firm wide level.
UPS is the USs 3rd largest employer with nearly 400,000
employees worldwide.
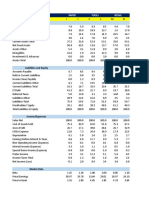
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS (Finance)
OBJECTIVE: Highly liquid company has been investing at a faster rate
than returning cash to investors, which are for most employees.
The company is highly liquid with 1 times the cash necessary
to cover current liabilities. UPS increased its dividends at 20% per
year for the past five years with an even higher growth in the rate
it has been buying back stock, at 47% over the same period.
The firm has been paying down debt over the last five years while
steadily increased Fixed Assets and Working Capital, in line with
developing the infrastructure to support the latest in logistics
technology and their customers push towards JIT manufacturing.
Over the past five years, Working capital has increased 24% per
year.
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS (Finance)
The firms capital structure is in line with a company that has been
run by traditional long time employees. 50% of the capital structure
is equity with the remaining sources of capital split between current
liabilities at 20% and long term debt at 14%.
The company is investing its cash in to Working Capital. The
evidence there is a 28% growth rate in cash versus a 14% rate for
Retained Earnings, which is experiencing a decelerating growth rate
for the past five years.
CHALLENGES
To make strategic technology group from a small strategic planning
process. This was basically required for finding major gap in
technologies.
Competition from both private companies and large government
supported agencies.
Execution of Scenario-planning session.
To tackle the impact of axis of uncertainty.
Formation of scenarios for future strategic planning.
CHALLENGES
To manage the strategy road map and implement the centennial
plan.
To tackle the implication for technology and infrastructure
initiatives, growth strategies and options, and workforce
development at both the global and region level.
Since most managers in the company were focused on short term
goals. It was difficult to keep the perception in mind that this was
not about UPS but rather how the world affected UPS.
To resolve the strategic integration responsibility.
STEPS TAKEN BY UPS TO FACE THE
CHALLENGES
As opportunities arose, UPS had shifted from message delivery to
package delivery.
Several steps that unfolded over a period of years were involved
in the implementation of the new strategic process. The senior
management completed a crucial second step two years later in
1999,when they drafted the UPS charter, redefining UPSs mission
and purpose and providing a detailed statement of the companys
values and strategies.
UPS moved from leadership in package distribution to enabler
of global commerce due to the new mission and purpose.
STEPS TAKEN BY UPS TO FACE THE
CHALLENGES
The centennial plan, the third step in the strategic process was
formed from the outcomes of that meeting. As UPSs version of a
five year strategic plan, it was designed to guide the company to
its centennial anniversary by providing themes and broad,
overarching direction.
Strategy road map, which was the fourth step in the strategic
process was developed to take the centennial plan to an
executable level of detail.
STRATEGIES ADOPTED BY UPS
Investing in the core business of worldwide distribution and
logistics.
Building competencies in the integration of goods, funds, and
information.
Using technology to create new services.
Attracting talented people.
Studying customer behavior and anticipating their needs.
Practicing innovation that leads to growth.
Developing an environment that enables them to treat each
customer as if he or she were the only one.
MAIN LESSONS
UPS has done a remarkable job of leveraging their core
competencies for the new world of e-commerce. They have
figured out how to deliver their core business services in new
ways, while leveraging their tremendous infrastructure assets.
They haven't forgotten where they came from. In that they have
managed to preserve their company culture. It has served them
very well in promoting the creative thought necessary to come up
with new ways to do business and grow the company.
They were brave enough to change the vision, starting at the top,
and committing themselves to it from the top all the way down
through every employee of the company. They managed to do it
quickly by making changes in their processes and organizational
structure.
MAIN LESSONS
UPS has been aggressive in finding new revenue streams with
existing and new customers. They understand not only their
customers and related needs, but have also figured out ways to
deliver more value. They have expanded the roles they can play in
the overall value web by leveraging their infrastructure and
expertise.
THANK YOU !!
PREPARED BY GROUP 9:
Amitanshu Srivastava
Amrita Das
Anamika Dey
Aneema
Anand Kumar
What can
brown do for
you
You might also like
- (PIO YP64B) Dina Rizkia Rachmah - Mid TestDocument5 pages(PIO YP64B) Dina Rizkia Rachmah - Mid TestDina Rizkia RachmahNo ratings yet
- Royal Bank of ScotlandDocument10 pagesRoyal Bank of ScotlandAthena ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- KPC's Struggles with Knowledge Management and Organizational LearningDocument11 pagesKPC's Struggles with Knowledge Management and Organizational LearningWiasta GuegueNo ratings yet
- RODAMAS Group: Identifying External Factors Stated in The CaseDocument26 pagesRODAMAS Group: Identifying External Factors Stated in The CaseRizki EkaNo ratings yet
- (2020) MM5006-Business EconomicsDocument21 pages(2020) MM5006-Business EconomicsRaka KiranaPratamaNo ratings yet
- Krakatau Steel (A)Document12 pagesKrakatau Steel (A)Fez Research Laboratory100% (4)
- UPS Company Profile and Case AnalysisDocument16 pagesUPS Company Profile and Case AnalysisNazzala Zakka WaliNo ratings yet
- Krakatau Steel (B) CaseDocument6 pagesKrakatau Steel (B) CaseWidyawan Widarto 闘志No ratings yet
- Investment Detective SG8Document11 pagesInvestment Detective SG8Mr SecretNo ratings yet
- Boeing Vs Airbus - Game TheoryDocument3 pagesBoeing Vs Airbus - Game Theoryaatifkamal100% (1)
- Aditya Birla Group Under Kumar Mangalam Birla (Case)Document10 pagesAditya Birla Group Under Kumar Mangalam Birla (Case)Ertania NirmalaNo ratings yet
- Issues and Solutions in Rizal CaseDocument6 pagesIssues and Solutions in Rizal CaseZafar Nur HakimNo ratings yet
- Business Economics: Sisdjiatmo K. WidhaningratDocument35 pagesBusiness Economics: Sisdjiatmo K. WidhaningratHisyam FarabiNo ratings yet
- UPS Case Study Assignment Ayesha Ikram MBA ProfessionalDocument2 pagesUPS Case Study Assignment Ayesha Ikram MBA ProfessionalUmt Bbis100% (2)
- Risk-Adjusted Performance Measures MatterDocument56 pagesRisk-Adjusted Performance Measures Matterabhishek210585No ratings yet
- Analisis Krakatau Steel (B)Document6 pagesAnalisis Krakatau Steel (B)JonathanSomba100% (1)
- AppleDocument11 pagesAppleKeerthana Raghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Midterm Bisek Chapter 2Document4 pagesMidterm Bisek Chapter 2FiqriNo ratings yet
- Krakatau Steel A ReportDocument6 pagesKrakatau Steel A ReportSoniaKasellaNo ratings yet
- The Investment DetectiveDocument9 pagesThe Investment DetectiveFadhila Nurfida HanifNo ratings yet
- Krakatau Steel A - Syndicate 5Document12 pagesKrakatau Steel A - Syndicate 5I Nyoman Sujana GiriNo ratings yet
- (MM5012) 29111328 Individual Assignment EditDocument6 pages(MM5012) 29111328 Individual Assignment EdithendrawinataNo ratings yet
- Elco Mandiri Case: How Innovation and Human Resources Can Help a Medical Equipment Business GrowDocument6 pagesElco Mandiri Case: How Innovation and Human Resources Can Help a Medical Equipment Business GrowNindy DaristaNo ratings yet
- Berlin Airport Case - MistakesDocument19 pagesBerlin Airport Case - Mistakesnatya lakshitaNo ratings yet
- Syndicate 1 - Krakatau Steel (B) - Global Competition - YP64BDocument16 pagesSyndicate 1 - Krakatau Steel (B) - Global Competition - YP64BrizqighaniNo ratings yet
- TN38 Primus Automation Division 2002Document11 pagesTN38 Primus Automation Division 2002mylittle_pg100% (1)
- Flybaboo's Route to Regional Airline SuccessDocument11 pagesFlybaboo's Route to Regional Airline SuccessHashina Nurul NidaNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Group Task on Exxon Valdes Oil SpillDocument2 pagesDecision Making Group Task on Exxon Valdes Oil SpillI Nyoman Sujana GiriNo ratings yet
- CC2 - The Financial Detective, 2005Document4 pagesCC2 - The Financial Detective, 2005Aldren Delina RiveraNo ratings yet
- Case Study GE's Jeff ImmeltDocument10 pagesCase Study GE's Jeff ImmeltAndhika KautsarNo ratings yet
- Rizal CaseDocument7 pagesRizal CaseFadhila Nurfida HanifNo ratings yet
- SG 5 - MITE - Electrolux PlusDocument16 pagesSG 5 - MITE - Electrolux PlusFadhila Nurfida HanifNo ratings yet
- Case 3 OasisDocument17 pagesCase 3 OasisGinanjarSaputraNo ratings yet
- Situation Appraisal Exercise ReferenceDocument20 pagesSituation Appraisal Exercise ReferenceNazzala Zakka WaliNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource Rbs CaseDocument21 pagesStrategic Human Resource Rbs CaseAhmadNo ratings yet
- Syndicate 5 OM - 1-800-FlowersDocument24 pagesSyndicate 5 OM - 1-800-Flowersmeidianiza100% (1)
- GE's Jeff Immelt: From MBA to CEODocument9 pagesGE's Jeff Immelt: From MBA to CEONadya AlyssaNo ratings yet
- Emerson Electric CompanyDocument32 pagesEmerson Electric CompanyJackie TorresNo ratings yet
- Gustavo Hernandez - JetBlue Airways PDFDocument13 pagesGustavo Hernandez - JetBlue Airways PDFCarlos Delgado NietoNo ratings yet
- CPM & PertDocument10 pagesCPM & PertANSHIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Summary Chapter 8,9 Keat N YoungDocument7 pagesSummary Chapter 8,9 Keat N YoungIqbal Faisal AkhmadNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - SectionB - A New Mandate For Human ResourcesDocument5 pagesGroup 8 - SectionB - A New Mandate For Human ResourcesPuneet PareekNo ratings yet
- Jetblue Airways Starting From Scratch (Notes)Document1 pageJetblue Airways Starting From Scratch (Notes)Andika MervinandaNo ratings yet
- 29116520Document6 pages29116520Rendy Setiadi MangunsongNo ratings yet
- Unilever-Future Strategy - Sao ChépDocument3 pagesUnilever-Future Strategy - Sao ChépLan PhanNo ratings yet
- Syndicate 5 - Krakatau Steel ADocument19 pagesSyndicate 5 - Krakatau Steel AEdlyn Valmai Devina SNo ratings yet
- Syndicate 1 - GE Jeff ImmeltDocument6 pagesSyndicate 1 - GE Jeff ImmeltmeidianizaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Chapter 6 OverviewDocument27 pagesManagerial Economics Chapter 6 OverviewYani Rahma100% (2)
- Individual Assignment: MM5009 Strategic Decision Making and NegotiationDocument5 pagesIndividual Assignment: MM5009 Strategic Decision Making and NegotiationSaeful AzizNo ratings yet
- (DMN GM 10) Mid-Term Exam - Bianda Puspita SariDocument6 pages(DMN GM 10) Mid-Term Exam - Bianda Puspita SariBianda Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Oasis Hong Kong Case FinalDocument58 pagesOasis Hong Kong Case FinalTing ZhangNo ratings yet
- Managing Complex Projects with Big Data InsightsDocument14 pagesManaging Complex Projects with Big Data InsightsJessica Ina0% (1)
- Situation Analysis Group Problem: Syndicate 4Document7 pagesSituation Analysis Group Problem: Syndicate 4Tommy YulianNo ratings yet
- Kota FibresDocument10 pagesKota FibresShishirNo ratings yet
- Ge'S Jeff Immelt: The Voyage From Mba To Ceo: Case StudyDocument10 pagesGe'S Jeff Immelt: The Voyage From Mba To Ceo: Case StudyMuhammad Helmi FaisalNo ratings yet
- Syndicate 7 Microsoft Competing On Talent ADocument8 pagesSyndicate 7 Microsoft Competing On Talent ASkf100% (1)
- Syndicate 4 - Carly Fiorina Case - OB 21 Apr 2019Document4 pagesSyndicate 4 - Carly Fiorina Case - OB 21 Apr 2019Zafar Nur HakimNo ratings yet
- Introduction For UPSDocument19 pagesIntroduction For UPSteju_690% (1)
- 1234Document12 pages1234Andhika KautsarNo ratings yet
- UPS AnalysisDocument3 pagesUPS AnalysisMuhammad Mubasher RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Gallery Server ProDocument246 pagesGallery Server ProeryaryasaNo ratings yet
- DIY IT Strategic Plan Less Than 40 CharactersDocument54 pagesDIY IT Strategic Plan Less Than 40 CharacterseryaryasaNo ratings yet
- Interconnecting Cisco Network DevicesDocument5 pagesInterconnecting Cisco Network DeviceseryaryasaNo ratings yet
- Commercial and Private Alarm Response ProcedureDocument5 pagesCommercial and Private Alarm Response ProcedureeryaryasaNo ratings yet
- Business ImpactAnalysis Worksheet 2014Document1 pageBusiness ImpactAnalysis Worksheet 2014eryaryasaNo ratings yet
- SVN Client InstallationDocument17 pagesSVN Client InstallationeryaryasaNo ratings yet
- Using Blueprinting Method For Developing Product-Service SystemsDocument16 pagesUsing Blueprinting Method For Developing Product-Service SystemsAjit ShindeNo ratings yet
- Subject CodesDocument33 pagesSubject CodeseryaryasaNo ratings yet