Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diffusion Lab Report
Uploaded by
api-268773070Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diffusion Lab Report
Uploaded by
api-268773070Copyright:
Available Formats
Alanis Ciccitto
Mr. Cottman
Diffusion and Osmosis Lab
February 7, 2013
Introduction
How does NaCl concentration affect potato slices? During this lab, the masses of objects
before and after being put into different types of water were being experimented. The importance
of this lab was to see solution concentration compared to the movement of particles. Also,
another reason was to describe and fully understand the process of diffusion.
Diffusion is the process of spreading molecules from high concentration to low
concentration. When diffusion is taking place, it is going down concentration gradient, which is
the difference of concentration in a given area. A concentration gradient allows particles to travel
to a lower area of concentration after being in a higher area of concentration.
In the cell, solvent is the thing that there is more of, which is usually water. The thing that
there is less of is known as the solute. The solvent dissolves the solute and when they combine,
they create a solution. Sodium chloride is known as NaCl, also it is more commonly known as
table salt. For example, sodium chloride is used in flavoring our foods. In this experiment, the
average concentration of NaCl in each potato slice is 0.25M. Diffusion is used in to get
equilibrium in each slice.
The process of diffusion is crucial to all living things. It helps them operate efficiently.
All cells have energy and are able to move and do certain things. All cells contain particles that
collide into each other trying to go from high to low concentration. They will continue to do so
until they are balanced, which is known as equilibrium.
Osmosis is a special type of diffusion that transports water across a cell membrane.
Aquaporins are protein molecules that surround the phospholipid bilayer in several cells. They
are important because they transport water through the cell membrane (Bowen, 2000). The
effects of hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic environments are all different to the cell.
Hypertonic environments have a higher solute concentration and a lower H
2
0 concentration.
Hypotonic environments are the opposite, they have a lower solute concentration and a higher
H
2
0 concentration. Isotonic environments have an equal solute concentration on each side.
Passive and active transport are used in these environments. Passive transport and active
transport are ways that help osmosis function.
Passive transport is the diffusion of cell membranes across a cell membrane without
energy. Molecules will move from where the substance is more concentrated to where it is less
concentrated. Simple diffusion is an example of passive transport. This specific type is when
molecules diffuse directly through the cell membrane. Another example is facilitated diffusion,
this is when molecules need to use a carrier protein or channel protein to diffuse through the cell
membrane. The carrier proteins are a specific shape and will allow a particular molecule or
groups of molecules to bind to it and be carried through the membrane (Honee). Active transport
is another way that cell membranes diffuse across the cell.
Active transport is similar to passive transport except it requires energy. It uses ATP as
its primary active transport and as its secondary active transport it uses electrochemical gradient.
Some examples of active transport are endocytosis and exocytosis (Zaromytidou, 2011). An
example of active transport and passive transport that can be related to real-world scenario when
you are driving on a highway and using cruise control. This relates to passive transport because
when cruise is on it does not require the use of energy, and for active transport when it is off the
use of the pedal is needed to get the car to move.
Diffusion and osmosis is important to all cells. Also, they were both a critical part to this
experiment. The purpose of this lab was to fully understand how diffusion and osmosis affects
objects. Also, to study the way objects react to a concentration gradient.
Materials and Methods
First, the cups were labeled with tap water, 0.2m NaCl, 0.5m NaCl, respectively. Then,
the potato slices were measured and their masses were recorded. The slices were placed in the
corresponding cups. 150 ml of each solution was added to the matching cups. The cups were
then let to sit over night.
A chicken egg was placed into a premeasured cup and the mass of both was determined.
The mass of the cup was subtracted from the mass of the egg and the cup. Then, the vinegar was
pored over the egg until covered. The egg was observed for two minutes and was recorded. The
cup was then let to sit over night. The next day, the mass of the egg was measured and recorded.
Then, the percent change in mass was calculated. The percent change in mass was calculated
with the formula below. After, the vinegar was discarded, day ones process was repeated with
syrup and distilled water.
Percent change in mass formula: (Current Day Previous Day / Previous Day) X 100
Results
After poring vinegar over the egg, bubbles began to form on the shell. After 24 hours, the
shell had dissolved and the egg appeared larger. Then, the egg floated in the syrup after being
fully covered. The next day, the solution seemed to be thinner, and the eggs mass appeared to
decrease. Also, there was a dent in the egg that made it look shriveled or broken. Then the
distilled water was pored over the egg until it was completely covered and was let to sit over
night. On day four, half of the distilled water was gone and the egg looked larger, fragile, and
soft.
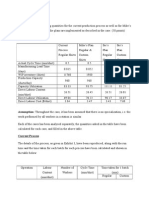
Data Table:
Day One Day Two Day Three Day Four
Mass of Cup 8.9 g 8.9g 8.9g 8.9g
Mass of Cup and
Egg
65g 81.4g 60g 86.5g
Mass of Egg 56.1g 72.5g 51.1g 77.6g
Percent Change
in Mass
29% -29% 44.2%
Discussion
During this lab, the egg changed mass, shape and appearance. On day one, vinegar was
used because there was a positive chance that it would dissolve its shell. On day two, after the
egg had been sitting in the vinegar for 24 hours, it has lost its shell and was swollen. There was
also a positive change in its mass. Because of its positive change, this shows that vinegar is a
hypotonic solution. A hypotonic solution has a higher level of H
2
0 outside the cell and a lower
level inside the cell. In this case, the egg had a lower concentration and the vinegar had a higher
concentration, causing the egg to expand. After being covered in syrup for about a day, water left
the egg and mixed with the syrup making them balanced, equilibrium had occurred. This caused
the egg to become deformed and shrink. The egg had a negative change in mass, which can
suggest that syrup is a hypertonic solution. A hypertonic solution has a higher solute
concentration and a lower H
2
0 concentration. On day 4, the egg had been submerged in distilled
water for about a day. The egg had a positive percent change, and therefore the distilled water
was a hypotonic solution. The water had a higher concentration and the egg had a lower
concentration, causing the egg to expand in size, giving it back its original shape. The purpose
of this lab was to study how objects react in different types of solutions through diffusion and
osmosis.
In the potato lab, the slices were placed in three different solutions to study how they
responded. One slice was placed in pure water. One might think that the solution was hypotonic
and caused it to expand. Another slice was put in a 0.5M NaCl solution. Study suggests that this
solution was hypertonic and would cause the slice to shrink. The last slice was placed in a 0.2M
NaCl solution. It is assumed that the potato slice would stay the same making the solution
isotonic.
Conclusion
The purpose of this study was to describe how water diffuses across a membrane. Models
of cells were placed in different solutions and the movement of water was tracked. The
importance of this lab was to determine how objects would react in different solution with high
and low concentration. These data showed that particles of higher concentration diffuse to areas
of lower concentrations of water. In these specific labs, when an object in placed into something
with a lower concentration the object shrunk. In the future, it would be interesting to study the
way red blood cells react in the same scenarios and observe them under a microscope.
Work Cited
Bowen, R. A. (2000). Colorado state. Retrieved from
http://arbl.cvmbs.colostate.edu/hbooks/cmb/cells/pmemb/osmosis.html.
Honee, V. Biology-online. Retrieved from http://www.biology-
online.org/dictionary/Carrier_protein.
Zaromytidou. (2011). Biology online. Retrieved from
http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Active_transport.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Layers of The EarthDocument26 pagesLayers of The EarthLoo DrBrad100% (1)
- Perkins - General Ti BulletinDocument65 pagesPerkins - General Ti BulletinUTEL CARTERNo ratings yet
- SkepticismDocument5 pagesSkepticismstevenspillkumarNo ratings yet
- States of Matter LessonDocument4 pagesStates of Matter Lessonapi-280793165No ratings yet
- Gravitational Fields 1Document18 pagesGravitational Fields 1Smart linkNo ratings yet
- Overview of Risk Based Audit ProcessDocument17 pagesOverview of Risk Based Audit ProcessAira Nhaira Mecate100% (1)
- GS Ep Tec 260 enDocument61 pagesGS Ep Tec 260 enCesarNo ratings yet
- May 2021 Examination Diet School of Mathematics & Statistics ID5059Document6 pagesMay 2021 Examination Diet School of Mathematics & Statistics ID5059Tev WallaceNo ratings yet
- Final Exam DiassDocument9 pagesFinal Exam Diassbaby rafa100% (3)
- Green ICT: A Study of Awareness, Attitude and Adoption Among IT/Computer Engineering Students of LDRP-ITR, GandhinagarDocument13 pagesGreen ICT: A Study of Awareness, Attitude and Adoption Among IT/Computer Engineering Students of LDRP-ITR, GandhinagarAHMAD ARESYADNo ratings yet
- 01 AirCircuitBreakers LV10 102021 EN 202111301146249676Document136 pages01 AirCircuitBreakers LV10 102021 EN 202111301146249676bkNo ratings yet
- Understanding ISO 9001 Calibration RequirementsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding ISO 9001 Calibration RequirementsAldrin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Preview - ISO+8655 6 2022Document6 pagesPreview - ISO+8655 6 2022s7631040No ratings yet
- Kelley DavisDocument3 pagesKelley Davisapi-626701108No ratings yet
- Nguyen Ngoc-Phu's ResumeDocument2 pagesNguyen Ngoc-Phu's ResumeNgoc Phu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Executive Shirt CompanyDocument6 pagesExecutive Shirt CompanyPramod kNo ratings yet
- Teacher Empowerment As An Important Component of Job Satisfaction A Comparative Study of Teachers Perspectives in Al Farwaniya District KuwaitDocument24 pagesTeacher Empowerment As An Important Component of Job Satisfaction A Comparative Study of Teachers Perspectives in Al Farwaniya District KuwaitAtique RahmanNo ratings yet
- Employment Under Dubai Electricity & Water AuthorityDocument6 pagesEmployment Under Dubai Electricity & Water AuthorityMominur Rahman ShohagNo ratings yet
- Science 8: Learning Activity SheetDocument9 pagesScience 8: Learning Activity SheetVan Amiel CovitaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Grammar of EnglishDocument132 pagesTheoretical Grammar of EnglishMisarabbit NguyenNo ratings yet
- How To Get Jobs in Neom Saudi Arabia 1703510678Document6 pagesHow To Get Jobs in Neom Saudi Arabia 1703510678Ajith PayyanurNo ratings yet
- NRP Grade 11 READING ENHANCEMENT March 1Document3 pagesNRP Grade 11 READING ENHANCEMENT March 1LORELYN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Cantilever Slab Analysis and Design of Cantilever SlabDocument3 pagesAnalysis and Design of Cantilever Slab Analysis and Design of Cantilever SlabMesfinNo ratings yet
- Long PassagesDocument12 pagesLong PassagesAml AmlNo ratings yet
- Switch RotatoriosDocument12 pagesSwitch RotatoriosRoberto AndrésNo ratings yet
- MS Y7 Spelling Bee Memo & List 21 22Document9 pagesMS Y7 Spelling Bee Memo & List 21 22Muhammad Akbar SaniNo ratings yet
- Question 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound CompoundDocument4 pagesQuestion 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound Compoundالموعظة الحسنه chanelNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary: Activity 1Document18 pagesVocabulary: Activity 1Aurora GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Guide For H Nmr-60 MHZ Anasazi Analysis: Preparation of SampleDocument7 pagesGuide For H Nmr-60 MHZ Anasazi Analysis: Preparation of Sampleconker4No ratings yet
- CV LeTranNguyen enDocument4 pagesCV LeTranNguyen enLe Tran NguyenNo ratings yet