Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elements 03
Uploaded by
DocenciaUniversitariaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elements 03
Uploaded by
DocenciaUniversitariaCopyright:
Available Formats
Value
Color
Value:
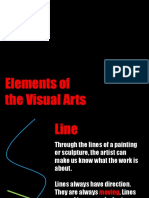
Signies the relative diferences of light and dark
Grayscale:
The full range of values simplied into a graduated scale.
Hue:
Designates the common name of a color,
determined by the specic wavelength of a ray
of light and/or its position in the spectrum or
color wheel.
Saturation
Refers to the relative purity of a color or its
inherent light.
Luminosity:
Refers to hue's inherent light; lighter colors are
more luminous than darker colors, but a lighter
color is not necessarily more saturated.
Color:
Primary Triad:
primary colors, yellow, blue and red, form an
equilateral triangle with yellow at the top.
Secondary Triad:
secondary colors, orange, green and violet,
evenly spaced between the primaries are mixed
from adjacent hues (example: red + yellow =
orange)
Intermediate Triad:
intermediate colors, yellow-green, blue-green,
redviolet, etc. are mixtures of a primary color
with a neighboring secondary color.
Color
Wheel:
Analogous:
colors that are adjacent to each other on the color wheel
(example: violet, blue-violet, red-violet). They have the shortest
interval and the most harmonious relationship because three
or four neighboring hues always contain a common color that
dominates the group.
Complements:
colors opposite on the color wheel. This relationship
often produces visual tension, shock, or electricity. This is
often the least harmonious color relationship.
You might also like
- Special Subjects: Basic Color Theory: An Introduction to Color for Beginning ArtistsFrom EverandSpecial Subjects: Basic Color Theory: An Introduction to Color for Beginning ArtistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- 6color Glossary and QuickguideDocument2 pages6color Glossary and QuickguideAndrea EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Colour1 PDFDocument11 pagesColour1 PDFAkhil ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Colour DefinitionsDocument2 pagesColour Definitionsapi-402301365No ratings yet
- Color Theory Final ExamDocument4 pagesColor Theory Final ExamKistan AtroshiNo ratings yet
- 2D Design (Art 107) Color Terminology: Hue Is The Traditional Color "Name", Such As Red, Which Represents A SpecificDocument5 pages2D Design (Art 107) Color Terminology: Hue Is The Traditional Color "Name", Such As Red, Which Represents A SpecificJonathan Marc Fule CastilloNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Color TypesDocument10 pages1.introduction To Color TypesAmrita TomarNo ratings yet
- Color WheelDocument2 pagesColor Wheelapi-301087417No ratings yet
- Colour Art 106Document20 pagesColour Art 106abhishek bansalNo ratings yet
- Color HarmonyDocument32 pagesColor HarmonyHiteshNo ratings yet
- Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Colours. What Is Colour?Document4 pagesPrimary, Secondary and Tertiary Colours. What Is Colour?orionsalinasNo ratings yet
- Prang Color TheoryDocument15 pagesPrang Color TheoryRemya86% (7)
- Colors and Color MixingDocument10 pagesColors and Color MixingCydryck OlivaNo ratings yet
- 5aelements of Arts Saste FinalDocument170 pages5aelements of Arts Saste FinalElaine Mae Guillermo EsposoNo ratings yet
- Color TheorypdfDocument99 pagesColor TheorypdfNews OffbeatNo ratings yet
- Colors Colors: Ar. Diane A. JoseDocument65 pagesColors Colors: Ar. Diane A. JoseTrisha LlamesNo ratings yet
- Color: - Is One of The Most Powerful of Elements. It Has TremendousDocument21 pagesColor: - Is One of The Most Powerful of Elements. It Has TremendousShalley NagpalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Properties of ColorDocument6 pagesLesson 3 Properties of Colorsuhani agrawalNo ratings yet
- BP Comp10 Color PropertiesDocument6 pagesBP Comp10 Color Propertiesmohamed saif el-yazanNo ratings yet
- L 24 - Theory of Colors in ArtDocument20 pagesL 24 - Theory of Colors in ArtVanessa JohnsonNo ratings yet
- D&G 4Document30 pagesD&G 4Harshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Color Theory: Reference Book For The Serious Art Student: "An Introduction To Art Techniques"Document23 pagesColor Theory: Reference Book For The Serious Art Student: "An Introduction To Art Techniques"pacifistlightNo ratings yet
- AR 104 Unit 2Document18 pagesAR 104 Unit 2shaikh safakhalisiNo ratings yet
- Color Chart and Properties of ColorDocument2 pagesColor Chart and Properties of Colorjane barquinNo ratings yet
- ColortheorystudyguideDocument1 pageColortheorystudyguideapi-285692559No ratings yet
- 10.1 Color FundamentalsDocument11 pages10.1 Color FundamentalsCarlo RosaioNo ratings yet
- Basics of Colour Science, Digital Colour CommunicationDocument14 pagesBasics of Colour Science, Digital Colour CommunicationalianasirgillNo ratings yet
- Color TheoryDocument21 pagesColor TheoryRemya71% (7)
- Color HarmonyDocument32 pagesColor HarmonyZutroy Xochihua100% (1)
- "The Fishermen", 1981 by National Artist Ang KiukokDocument35 pages"The Fishermen", 1981 by National Artist Ang KiukokEli Ayase75% (4)
- VISC6311 LU - 1 & 2 Part 4Document16 pagesVISC6311 LU - 1 & 2 Part 4Talented Media & DesignNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtDocument73 pagesElements of ArtJanlawrence JaderNo ratings yet
- Khaled Al Raquib Final Year, B.Sc. in Optometry Faculty of Medicine, University OF ChittagongDocument26 pagesKhaled Al Raquib Final Year, B.Sc. in Optometry Faculty of Medicine, University OF ChittagongKhaled RaquibNo ratings yet
- Colour in Architecture PDFDocument45 pagesColour in Architecture PDFPedro Victor Placides50% (2)
- Color Hues Primary Colors Secondary ColorsDocument7 pagesColor Hues Primary Colors Secondary ColorsJOHNNo ratings yet
- The Most Important Element in Interior DesignDocument23 pagesThe Most Important Element in Interior Designvishi bansalNo ratings yet
- ColorsDocument41 pagesColorsTianboyNo ratings yet
- Color Theory WorksheetDocument2 pagesColor Theory WorksheetSaligan Dolf100% (1)
- StudentDocument67 pagesStudentNaim UddinNo ratings yet
- ColourDocument3 pagesColourapi-279889431No ratings yet
- Tint, Shade and ToneDocument2 pagesTint, Shade and TonesvtjeonsaeriNo ratings yet
- ColourDocument40 pagesColour6krjzrgq8bNo ratings yet
- ColorTheory DONEDocument5 pagesColorTheory DONEErika Joy TacordaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo en Grupo InglesDocument4 pagesTrabajo en Grupo IngleslisbethgamaaNo ratings yet
- Color and Color Psychology 2015Document76 pagesColor and Color Psychology 2015Chaz PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Color - Chapter PDFDocument5 pagesColor - Chapter PDFSona UthyasaniNo ratings yet
- Color Wheel, Combination of Color, Dimention of ColorDocument27 pagesColor Wheel, Combination of Color, Dimention of ColorBisrateab FekaduNo ratings yet
- Black Etc. Color Derives From The Spectrum of Light (Distribution of Light Energy VersusDocument11 pagesBlack Etc. Color Derives From The Spectrum of Light (Distribution of Light Energy VersusRemyaNo ratings yet
- Color VocabularyDocument1 pageColor Vocabularyapi-228274118No ratings yet
- A&G (Color Theory)Document34 pagesA&G (Color Theory)Anushka KhatriNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtsDocument114 pagesElements of ArtsAbia Annieson A. LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtssssDocument165 pagesElements of ArtssssAlyssandra Nicole DaliuagNo ratings yet
- Dip Mod4Document12 pagesDip Mod4sharonsajan438690No ratings yet
- Colour Theory NoteDocument1 pageColour Theory NotechionumaraliaNo ratings yet
- Color (RSW)Document9 pagesColor (RSW)James Nicolo AltreNo ratings yet
- 5B - Elements of Visual ArtsDocument132 pages5B - Elements of Visual Artsk78cwhs6v7No ratings yet
- The Color WheelDocument14 pagesThe Color WheelJenniferCarabotMacasNo ratings yet
- Colour Theory NotesDocument9 pagesColour Theory Notesshivangibiswas.photographyNo ratings yet
- Popsheet Elements of The Visual ArtsDocument2 pagesPopsheet Elements of The Visual ArtsAlexa S. CanillasNo ratings yet
- Q2M1 - Let's ElaborateDocument4 pagesQ2M1 - Let's ElaborateJonathan ParanadaNo ratings yet
- GraafinenohjeistoDocument54 pagesGraafinenohjeistografikeyesNo ratings yet
- Principles of DesignDocument16 pagesPrinciples of DesignDocenciaUniversitariaNo ratings yet
- 33brilliantlycreativemarketingads 140209165631 Phpapp02Document80 pages33brilliantlycreativemarketingads 140209165631 Phpapp02DocenciaUniversitariaNo ratings yet
- 100 Creative Advertising Ideas EbookDocument19 pages100 Creative Advertising Ideas EbookgautamsaraswatNo ratings yet