Professional Documents
Culture Documents
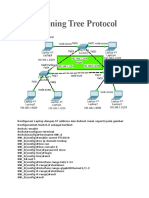
Spanning Tree
Uploaded by
RamonRosarioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spanning Tree
Uploaded by
RamonRosarioCopyright:
Available Formats
packetlife.
net
by Jeremy Stretch v3.0
I
E
E
E
C
i
s
c
o
SPANNING TREE PART 1
BPDU Format
Protocol ID 16
Spanning Tree Protocols
Algorithm
Legacy STP PVST
Defined By
Instances
Trunking
PVST+ RPVST+ MST
Legacy ST
802.1D-1998
1
N/A
Legacy ST
Cisco
Per VLAN
ISL
Legacy ST
Cisco
Per VLAN
802.1Q, ISL
Rapid ST
Cisco
Per VLAN
802.1Q, ISL
Rapid ST
802.1s,
802.1Q-2003
Configurable
802.1Q, ISL
RSTP
Rapid ST
802.1w,
802.1D-2004
1
N/A
Spanning Tree Instance Comparison
STP
C
A B
All VLANs
x
Root
PVST+
C
A B
VLAN 1
VLAN 10
VLAN 20
VLAN 30
xx xx
VLAN 1,10 Root VLAN 20,30 Root
MST
C
A B
MSTI 0 (1, 10)
MSTI 1 (20, 30)
x x
MSTI 0 Root MSTI 1 Root
Field Bits
Version 8
BPDU Type 8
Flags 8
Root ID 64
Root Path Cost 32
Bridge ID 64
Port ID 16
Message Age 16
Max Age 16
Hello Time 16
Forward Delay 16
Spanning Tree Specifications
802.1D-1998
PVST ISL PVST+ RPVST+
802.1w
802.1s
802.1D-2004
802.1Q-2003
802.1Q-1998
802.1Q-2005
Link Costs
4 Mbps 250
Bandwidth Cost
10 Mbps 100
16 Mbps 62
45 Mbps 39
100 Mbps 19
155 Mbps 14
622 Mbps 6
1 Gbps 4
10 Gbps 2
Default Timers
Hello
Forward Delay
Max Age
2s
15s
20s
Port States
Disabled
Discarding
Legacy ST Rapid ST
Blocking
Listening
Learning Learning
Forwarding Forwarding
IEEE 802.1D-1998 Deprecated legacy STP standard
IEEE 802.1w Introduced RSTP
IEEE 802.1D-2004 Replaced legacy STP with RSTP
IEEE 802.1s Introduced MST
IEEE 802.1Q-2003 Added MST to 802.1Q
PVST Per-VLAN implementation of legacy STP
PVST+ Added 802.1Q trunking to PVST
RPVST+ Per-VLAN implementation of RSTP
Port Roles
Root Root
Legacy ST Rapid ST
Designated Designated
Blocking
Alternate
Backup
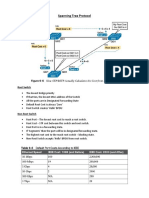
Spanning Tree Operation
Determine root bridge
The bridge advertising the lowest bridge ID becomes the root bridge
Select root port
Each bridge selects its primary port facing the root
Select designated ports
One designated port is selected per segment
Block ports with loops
All non-root and non-desginated ports are blocked
1
2
3
4
IEEE 802.1Q-2005 Most recent 802.1Q revision
20+ Gbps 1
packetlife.net
by Jeremy Stretch v3.0
SPANNING TREE PART 2
PVST+ and RPVST+ Configuration
spanning-tree mode {pvst | rapid-pvst}
! Bridge priority
spanning-tree vlan 1-4094 priority 32768
! Timers, in seconds
spanning-tree vlan 1-4094 hello-time 2
spanning-tree vlan 1-4094 forward-time 15
spanning-tree vlan 1-4094 max-age 20
! PVST+ Enhancements
spanning-tree backbonefast
spanning-tree uplinkfast
! Interface attributes
interface FastEthernet0/1
spanning-tree [vlan 1-4094] port-priority 128
spanning-tree [vlan 1-4094] cost 19
! Manual link type specification
spanning-tree link-type {point-to-point | shared}
! Enables PortFast if running PVST+, or
! designates an edge port under RPVST+
spanning-tree portfast
! Spanning tree protection
spanning-tree guard {loop | root | none}
! Per-interface toggling
spanning-tree bpduguard enable
spanning-tree bpdufilter enable
Troubleshooting
show spanning-tree [summary | detail | root]
show spanning-tree [interface | vlan]
MST Configuration
spanning-tree mode mst
! MST Configuration
spanning-tree mst configuration
name MyTree
revision 1
! Map VLANs to instances
instance 1 vlan 20, 30
instance 2 vlan 40, 50
! Bridge priority (per instance)
spanning-tree mst 1 priority 32768
! Timers, in seconds
spanning-tree mst hello-time 2
spanning-tree mst forward-time 15
spanning-tree mst max-age 20
! Maximum hops for BPDUs
spanning-tree mst max-hops 20
! Interface attributes
interface FastEthernet0/1
spanning-tree mst 1 port-priority 128
spanning-tree mst 1 cost 19
Bridge ID Format
Pri Sys ID Ext MAC Address
4 12 48
System ID Extension
12-bit value taken from VLAN number (IEEE 802.1t)
Priority
4-bit bridge priority (configurable from 0 to 61440 in
increments of 4096)
MAC Address
48-bit unique identifier
Path Selection
1 Bridge with lowest root ID becomes the root
2
3
4
Prefer the neighbor with the lowest cost to root
Prefer the neighbor with the lowest bridge ID
Prefer the lowest sender port ID
Optional PVST+ Ehancements
PortFast
Enables immediate transition into the forwarding state
(designates edge ports under MST)
UplinkFast
Enables switches to maintain backup paths to root
BackboneFast
Enables immediate expiration of the Max Age timer in
the event of an indirect link failure
Spanning Tree Protection
Root Guard
Prevents a port from becoming the root port
BPDU Guard
Error-disables a port if a BPDU is received
Loop Guard
Prevents a blocked port from transitioning to listening
after the Max Age timer has expired
BPDU Filter
Blocks BPDUs on an interface (disables STP)
RSTP Link Types
Point-to-Point
Connects to exactly one other bridge (full duplex)
Shared
Potentially connects to multiple bridges (half duplex)
Edge
Connects to a single host; designated by PortFast
show spanning-tree mst []
You might also like
- Edexcel IGCSE ICT Yearwise Question and AnswersDocument30 pagesEdexcel IGCSE ICT Yearwise Question and AnswersAsif Zubayer Palak83% (12)
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityFrom EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNo ratings yet
- Create Network Connection For 8500 and 9200-DDEDocument34 pagesCreate Network Connection For 8500 and 9200-DDEPepe GarciaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant LinksDocument9 pages3.1.2.12 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant LinksRamiro CollaguazoNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Implement Inter-VLAN RoutingDocument15 pagesLab 5 - Implement Inter-VLAN RoutingShara MerinNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking: For Under-graduate StudentsFrom EverandData Communication and Networking: For Under-graduate StudentsNo ratings yet
- KNX-basic Course FullDocument261 pagesKNX-basic Course Fullluis90000083% (6)
- Training Report On CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate)Document94 pagesTraining Report On CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate)Pankaj Gill100% (4)
- Spanning TreeDocument2 pagesSpanning TreealhersalNo ratings yet
- Spanning TreeDocument1 pageSpanning Treeopexxx100% (2)
- CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Answers Full PDFDocument14 pagesCCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 3 Answers Full PDFعائشة القرشيNo ratings yet
- Lab 2.4Document7 pagesLab 2.4Riia PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w) : Support of RSTP in Catalyst Switches New Port States and Port RolesDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w) : Support of RSTP in Catalyst Switches New Port States and Port Roleskasula-sridhar-kumar-7646No ratings yet
- Improving Performance With Spanning Tree: Medium-Sized Switched Network ConstructionDocument26 pagesImproving Performance With Spanning Tree: Medium-Sized Switched Network ConstructionDonovanNo ratings yet
- Dell FTOS 05 Spanning TreeDocument31 pagesDell FTOS 05 Spanning TreeBambang AdiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)Document17 pagesUnderstanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)Shamsul Aww AwwNo ratings yet
- Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument52 pagesSpanning Tree ProtocolchelohuhuNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting STP IssuesDocument6 pagesTroubleshooting STP IssuesTrending DuniyaNo ratings yet
- Spanning Tree Protocol EnhancementsDocument30 pagesSpanning Tree Protocol EnhancementsSina NeouNo ratings yet
- Thebitbucket - co.Uk-Spanning Tree Protocol Topic NotesDocument25 pagesThebitbucket - co.Uk-Spanning Tree Protocol Topic NotesMeklati YounessNo ratings yet
- STPDocument22 pagesSTPNyinyi LwinNo ratings yet
- Cisco Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)Document15 pagesCisco Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)joshua.lin.2009No ratings yet
- STP - RSTP - MSTP Comparison LabDocument28 pagesSTP - RSTP - MSTP Comparison Labbruce floresNo ratings yet
- Show Spanning-Tree: Syntax DescriptionDocument4 pagesShow Spanning-Tree: Syntax DescriptionTinh BuonNo ratings yet
- Nexus 7000 STP Priority Change in Peer Switch Setup Impact Assessment and Configuration ExampleDocument6 pagesNexus 7000 STP Priority Change in Peer Switch Setup Impact Assessment and Configuration ExampleAlexandra SussainNo ratings yet
- Spanning TreeDocument44 pagesSpanning TreeSubchan RohibNo ratings yet
- CCNA Switching Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesCCNA Switching Cheat SheetSa MirNo ratings yet
- 2.1.2.10 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant Links ListoDocument9 pages2.1.2.10 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant Links ListoMartin SaldañaNo ratings yet
- PVST+Document12 pagesPVST+Dao Thanh GiangNo ratings yet
- iPASOLINK Expert2013 3Document135 pagesiPASOLINK Expert2013 3Doyi100% (3)
- Cis187 4 PVST RSTPDocument66 pagesCis187 4 PVST RSTPJuni ClutersNo ratings yet
- STP Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument28 pagesSTP Spanning Tree ProtocoljohnNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Configuring STPDocument20 pagesUnderstanding and Configuring STProlandhangnilo5136No ratings yet
- SICOM3005A: 6 Switching Ports + 4 Serial Ports Managed Serial Device ServersDocument7 pagesSICOM3005A: 6 Switching Ports + 4 Serial Ports Managed Serial Device ServersAlvaro HerbasNo ratings yet
- Configuring PVST+ and RPVST+Document24 pagesConfiguring PVST+ and RPVST+Santu DindaNo ratings yet
- Difference BW STP, RSTP, PVST & MSTPDocument3 pagesDifference BW STP, RSTP, PVST & MSTPsugapriyaNo ratings yet
- (June-2016) New 200-105 Exam Dumps With PDF and VCE DownloadDocument9 pages(June-2016) New 200-105 Exam Dumps With PDF and VCE Downloadaquey1100% (2)
- Ultimate CCNA ICND Study GuideDocument56 pagesUltimate CCNA ICND Study GuideStephen RamosNo ratings yet
- What Is STPDocument3 pagesWhat Is STPSpartacus CaesarNo ratings yet
- STP Commands + Show + Timers + Port RolesDocument4 pagesSTP Commands + Show + Timers + Port RolesLuis GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) Part-1Document8 pagesMultiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) Part-1jdwhite9No ratings yet
- STP - Spanning Tree Protocol ExplainedDocument9 pagesSTP - Spanning Tree Protocol ExplainedruphydNo ratings yet
- PVST Alcatel CiscoDocument3 pagesPVST Alcatel CiscoMario AlcazabaNo ratings yet
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP & RSTP)Document57 pagesSpanning Tree Protocol (STP & RSTP)Peter R. Egli100% (1)
- Assessment System: Take Assessment - Eswitching Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Lan Switching and Wireless (Version 4.0)Document4 pagesAssessment System: Take Assessment - Eswitching Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Lan Switching and Wireless (Version 4.0)Marin MarianNo ratings yet
- Spanning Tree Protocol: Presented by Arash ForoughiDocument19 pagesSpanning Tree Protocol: Presented by Arash ForoughiAungMonNo ratings yet
- RSTP Cisco WhitepaperDocument15 pagesRSTP Cisco WhitepaperSudipto BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 - Inplementing Spanning TreeDocument43 pagesChap 3 - Inplementing Spanning Treedanneco87No ratings yet
- Manual BridgeDocument10 pagesManual Bridgehrm75No ratings yet
- Lab 2 STPDocument14 pagesLab 2 STPAbhijit PariyarNo ratings yet
- Spanning TreeDocument48 pagesSpanning Treewenyan zhangNo ratings yet
- STP Spanning Tree Protocol Step by Step Configuration TutorialDocument12 pagesSTP Spanning Tree Protocol Step by Step Configuration TutorialVicky VaioNo ratings yet
- STP Interview Questions and Answers (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Networker InterviewDocument3 pagesSTP Interview Questions and Answers (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Networker InterviewmrsrinathNo ratings yet
- BRK-135T CCNA Switching PDFDocument60 pagesBRK-135T CCNA Switching PDFparthasn83No ratings yet
- Connection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksFrom EverandConnection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsFrom EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsNo ratings yet
- IP Telephony: Deploying VoIP Protocols and IMS InfrastructureFrom EverandIP Telephony: Deploying VoIP Protocols and IMS InfrastructureNo ratings yet
- Topology: Computer Networks (Introduction)Document12 pagesTopology: Computer Networks (Introduction)Anjana MagantiNo ratings yet
- WinCC Professional V13 enUS en-US PDFDocument8,314 pagesWinCC Professional V13 enUS en-US PDFDiogoPinhoNo ratings yet
- Data and Computer Comm. Professor George: Stallings - Chapter 16 Wired (A.k.a. High-Speed) Local-Area NetworksDocument57 pagesData and Computer Comm. Professor George: Stallings - Chapter 16 Wired (A.k.a. High-Speed) Local-Area NetworksEhsan Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 3 Computer NetworksDocument8 pages3 Computer NetworksMahesh Machindra MutkuleNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v7 Modules 4-7Document20 pagesCCNA 1 v7 Modules 4-7Adha Estu RizqiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputingDocument2 pagesIntroduction To ComputingFelicity SanchezNo ratings yet
- Computer Awareness Capsule For IBPS RRB PO (By Studyniti)Document59 pagesComputer Awareness Capsule For IBPS RRB PO (By Studyniti)Anuja Kumari100% (2)
- Network Diagramming - OPNET NetMapperDocument2 pagesNetwork Diagramming - OPNET NetMapperOPNET Technologies, Inc.No ratings yet
- Transmission Network Planning and DesignDocument37 pagesTransmission Network Planning and Designrajeshtripathi2004100% (1)
- GS32P01B30 01enDocument13 pagesGS32P01B30 01enDhirender DagarNo ratings yet
- Accessories: ADP45-MSTP-x: Quick Connect MS/TP AdaptersDocument2 pagesAccessories: ADP45-MSTP-x: Quick Connect MS/TP AdaptersBMSNo ratings yet
- cs601 - New HandoutsDocument806 pagescs601 - New HandoutsHumayun Khawar100% (1)
- A Technical Report On Industrial Work Experience Scheme2Document42 pagesA Technical Report On Industrial Work Experience Scheme2Eshiett Badguy Bassey100% (1)
- A Parking Management System Based On Wireless Sensor NetworkDocument10 pagesA Parking Management System Based On Wireless Sensor NetworkKlarizze GanNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide 3 in 1 - Beginners Guide Tips and Tricks Advanced GuideDocument458 pagesCisco CCNA Command Guide 3 in 1 - Beginners Guide Tips and Tricks Advanced GuidekhanjanNo ratings yet
- Spanning Tree ProtocolDocument6 pagesSpanning Tree ProtocolAsifNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Auditing in Cis Environment: I. Operating System - A Set of Highly Complex Set of Programs Designed ToDocument14 pagesModule 1: Auditing in Cis Environment: I. Operating System - A Set of Highly Complex Set of Programs Designed ToRana LinNo ratings yet
- eVD4 - Breaker Integrated Protection RBX615 - Engineering Manual PDFDocument100 pageseVD4 - Breaker Integrated Protection RBX615 - Engineering Manual PDFHans MortenNo ratings yet
- Module 6-Storage Area Network - FC SAN - Participant GuideDocument59 pagesModule 6-Storage Area Network - FC SAN - Participant GuiderhsrtaqNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer IntroductionDocument24 pagesPacket Tracer Introductionpratham.sagittarusNo ratings yet
- E560 RTUtil560 Users Guide R10Document134 pagesE560 RTUtil560 Users Guide R10rps_003100% (1)
- Data Communications Networks Network Types Protocol LayeringDocument48 pagesData Communications Networks Network Types Protocol LayeringiotNo ratings yet
- MIS ReportDocument31 pagesMIS ReportMohit Rijal100% (2)
- Module 1 - Information Processing Study GuideDocument34 pagesModule 1 - Information Processing Study GuideChad-WayneChambersNo ratings yet
- BK Install Guide OpendaylightDocument57 pagesBK Install Guide OpendaylightMohamed IssaouiNo ratings yet