Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nataraja, (Sanskrit:: Hindu God Shiva Shaiva Shiva
Uploaded by
sadhudas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pagesds
Original Title
Nataraj A
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsds
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageNataraja, (Sanskrit:: Hindu God Shiva Shaiva Shiva
Uploaded by
sadhudassds
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
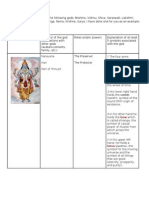
Nataraja, ( Sanskrit: Lord of the Dance) the Hindu god Shiva in his form as the cosmic
dancer, represented in metal or stone in most Shaiva temples of South India.
In the most common type of image, Shiva is shown with four arms and flying locks dancing on
the figure of a dwarf, Apasmara (a symbol of human ignorance; apasmara means
forgetfulness, or heedlessness). Shivas back right hand holds the damaru (hourglassshaped drum); the front right hand is in the abhaya mudra (the fear-not gesture, made by
holding the palm outward with fingers pointing up); the back left hand carries Agni (fire) in a
vessel or in the palm of the hand; and the front left hand is held across his chest in
the gajahasta (elephant-trunk) pose, with wrist limp and fingers pointed downward toward the
uplifted left foot. The locks of Shivas hair stand out in several strands interspersed with the
figures of Ganga (the Ganges River personified as a goddess), flowers, a skull, and the
crescent moon. His figure is encircled by a ring of flames, the prabhamandala. In classic
Sanskrit treatises on dance, this form, the most common representation of Nataraja, is called
thebhujamgatrasa (trembling of the snake).
In the Nataraja sculpture, Shiva is shown as the source of all movement within the cosmos,
represented by the arch of flames. The purpose of the dance is to release humans from
illusion, and the place where it is said to have been performed, Chidambaram (an important
Shaiva centre in South India), called the centre of the universe, is in reality within the heart.
The gestures of the dance represent Shivas five activities (pancakritya): creation (symbolized
by the drum), protection (by the fear-not pose of the hand), destruction (by the fire),
embodiment (by the foot planted on the ground), and release (by the foot held aloft).
Other dances of Shiva seen in sculpture and painting are the wild tandava, which he performs
on cremation grounds in the company of his consort Devi, and the evening dance performed
on Mount Kailasa before the assembly of gods, some of whom accompany him on various
instruments.
You might also like
- Chola BronzeDocument15 pagesChola BronzeWrishi BiswasNo ratings yet
- The Dance of ShivaDocument7 pagesThe Dance of ShivaSri KalyanNo ratings yet
- The Dance of ShivaDocument13 pagesThe Dance of Shivatito154aNo ratings yet
- Temple Architecture 7Document17 pagesTemple Architecture 7kengerisudhir100% (1)
- The Dance of ShivaDocument7 pagesThe Dance of Shivaazai nabihNo ratings yet
- Shiva As NatarajaDocument3 pagesShiva As NatarajaGray HoundyNo ratings yet
- The Dance of ShivaDocument11 pagesThe Dance of Shivachitratr_bala7846100% (1)
- Depiction: (NƏT̪ Ə Ra DƷƏ) Tamil Malayalam Telugu Kannada Shiva BrahmaDocument4 pagesDepiction: (NƏT̪ Ə Ra DƷƏ) Tamil Malayalam Telugu Kannada Shiva BrahmanieotyagiNo ratings yet
- Lord ShivaDocument7 pagesLord ShivaRanjan Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dance of ShivaDocument9 pagesDance of ShivaExotic India ArtNo ratings yet
- NatarajaDocument5 pagesNatarajaBon Lester L. LampareroNo ratings yet
- NatarajaDocument2 pagesNatarajaAspirant AspirantNo ratings yet
- Siddhanta Deepika Volume 13Document599 pagesSiddhanta Deepika Volume 13Sivason100% (1)
- Siddhanta Deepika Volume 13Document599 pagesSiddhanta Deepika Volume 13BosRaj100% (1)
- Devatha Hastha NotesDocument4 pagesDevatha Hastha NotesUmaparvathy KaliappanNo ratings yet
- 07 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument23 pages07 - Chapter 2 PDFKalimuthuNo ratings yet
- Religion CrapDocument1 pageReligion CrapGabi SalvatoreNo ratings yet
- Cosmic Dance of NatrajaDocument2 pagesCosmic Dance of Natrajaabhipar649205No ratings yet
- Indian Performing ArtsDocument21 pagesIndian Performing ArtsShashank Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Chidambara RahasyaDocument11 pagesChidambara RahasyaRajesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- Nataraja-The Dancing SivaDocument8 pagesNataraja-The Dancing SivaSivasonNo ratings yet
- Indian DanceDocument104 pagesIndian Dancebhisham67% (6)
- Shiva GodDocument1 pageShiva GoddeepaliNo ratings yet
- Narayana Hari Part of TrimurtiDocument9 pagesNarayana Hari Part of Trimurtiapi-249153555No ratings yet
- Bharata NatyamDocument9 pagesBharata NatyamkoyasrujanaNo ratings yet
- Shivanataraja 1Document7 pagesShivanataraja 1Gray HoundyNo ratings yet
- ShivaDocument2 pagesShivaALOK FREE FIRENo ratings yet
- NatarajarDocument3 pagesNatarajar11101955100% (1)
- 5 Forms of ShivaDocument20 pages5 Forms of ShivaJatin Yadav100% (1)
- The Mystical Number NineDocument16 pagesThe Mystical Number NineAnonymous 3pTM9WCYNo ratings yet
- Sapta KanniDocument7 pagesSapta KanniAkif HamzahNo ratings yet
- Siva PDFDocument36 pagesSiva PDFSamudra Gupta100% (1)
- Wikipedia - ArdhanarishvaraDocument11 pagesWikipedia - Ardhanarishvarathewitness3No ratings yet
- Pancha Bhoota StalamsDocument8 pagesPancha Bhoota StalamstekleyNo ratings yet
- Ramayana Mahabharata ShvetashvataraDocument2 pagesRamayana Mahabharata ShvetashvataraabhiNo ratings yet
- Search Results: Hindu Goddess Dancing HinduDocument2 pagesSearch Results: Hindu Goddess Dancing HinduFloraNo ratings yet
- Importance of Five Faces of ParameshvaraDocument9 pagesImportance of Five Faces of ParameshvaraKamalakarAthalyeNo ratings yet
- Gods Goddesses and AvatarsDocument55 pagesGods Goddesses and AvatarsTom ReedNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Some of The Major Dance ItemsDocument4 pagesDefinitions of Some of The Major Dance ItemsShimran ZamanNo ratings yet
- Five Powers of Siva EiDocument10 pagesFive Powers of Siva EidbbircsNo ratings yet
- Chidambara RahasyamDocument5 pagesChidambara Rahasyamvijiwrites2u0% (1)
- The Sculpture of NatarajaDocument12 pagesThe Sculpture of NatarajaanupNo ratings yet
- Methodology AssignmentDocument12 pagesMethodology AssignmentanupNo ratings yet
- NavarathiriDocument3 pagesNavarathirisharminiNo ratings yet
- Five Powers of SivaDocument81 pagesFive Powers of SivaRaju GspNo ratings yet
- Bharata NatyamDocument8 pagesBharata NatyamOscar RamirezNo ratings yet
- Bharata NatyamDocument11 pagesBharata NatyamKapil SinghNo ratings yet
- Indian Dance & MusicDocument85 pagesIndian Dance & MusicSunil Upadhyaya0% (1)
- Indian MythologyDocument37 pagesIndian MythologyMich Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Hindu IconographyDocument6 pagesHindu IconographynieotyagiNo ratings yet
- Sanjay More - Indian AstheticsDocument2 pagesSanjay More - Indian Astheticssathis_nskNo ratings yet
- Notes Mam CorrectedDocument14 pagesNotes Mam CorrectedDeeptiNo ratings yet
- Brought Here by DR Uday Dokras: Sabharathnam SivacharyarDocument9 pagesBrought Here by DR Uday Dokras: Sabharathnam SivacharyarudayNo ratings yet
- Spiritual PlaceDocument22 pagesSpiritual Placesathappan dharunNo ratings yet
- Tala-Mana Tala-Mana System of Proportions and Measures GovernsDocument34 pagesTala-Mana Tala-Mana System of Proportions and Measures GovernsCologne AromaNo ratings yet
- Dasa Mahavidyas Sri VidyaDocument23 pagesDasa Mahavidyas Sri VidyaRahul Chaturvedi100% (27)
- Exploring Mysticism: A Methodological EssayFrom EverandExploring Mysticism: A Methodological EssayRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)