Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RBI Study Material - Gr8AmbitionZ
RBI Study Material - Gr8AmbitionZ
Uploaded by
Ajay BansalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RBI Study Material - Gr8AmbitionZ
RBI Study Material - Gr8AmbitionZ
Uploaded by
Ajay BansalCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Material
for
RBI Assistants
and
Grade B Officers
Exams
Powered by
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
your A to Z competitive exam guide
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
RBI : A Brief Introduction
co
RBI (Reserve Bank of India), India's Central Bank came into existence on 1stApril 1935 as a
private share holders bank.
Functions of RBI :
Monopoly of Note issue
Banker, Adviser and Agent to the Govt. of India
Banker to Banks
Custodian of Foreign exchange and gold.
Re-discounts bills of exchange and hundis.
Lender of last Resort
Maintains stability of foreign value of Rupee.
Acts as clearing house
Credit control
iti
ww
8A
Gr
RBI's central office is in Mumbai.
RBI has 22 regional offices.
It was nationalized on 1st January 1949.
It prints Currency in 15 Languages.
Its predecessor was Imperial Bank of India (1921).
RBI came into existence on the recommendation of Hilton Young (Royal) commission
as per RBI act 1934.
It is the member bank of Asian Clearing Union (ACU) and IMF (International Monetary
Fund).
The general superintendence and direction of the RBI is entrusted with the 21-memberstrong Central Board of Directorsthe Governor (currently Duvvuri Subbarao), four
Deputy Governors, two Finance Ministry representative, ten government-nominated
directors to represent important elements from India's economy, and four directors to
represent local boards headquartered at Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai and New Delhi. Each
of these local boards consists of five members who represent regional interests, as well as
the interests of co-operative and indigenous banks.
The present Governor of RBI is Duvvuri Subba Rao (Second Time).
Deputy Governors :
K.C.Chakravarthi
Urjit Patel
Anand Sinha
Harun Rashid Khan.
w.
mb
Key points to Note :
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
on
Z.
Note : 1st Central Bank in the world : Rick's Bank Sweden in 1656. But in the light of unctions,
Bank of England is the 1st Central Bank 1694.
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Important Points you should Keep in Mind
ww
Bank Rate
Bank rate, also referred to as the discount rate, is the rate of interest which a central bank charges
on the loans and advances that it extends to commercial banks and other financial intermediaries.
Changes in the bank rate are often used by central banks to control the money supply.
Present Bank Rate 8.25 %
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Gr
w.
8A
mb
iti
on
Z.
Currency notes are issued by RBI under "Minimum Reserve System 1957" with backing
of Rs. 200 Cr Reserve (Gold : Rs. 115 Cr + Foreign Securities Rs. 85 Cr)
RBI Invests foreign exchange reserves in multi-currency, multi-market portfolios such as
securities, other central banks and Bank of International Settlements (BIS) and deposits
in foreign commercial banks. The yield on such investments is low.
RBI does not pay interest on Govt. deposits with it.
The following monetary instruments are in the hands of RBI to control credit and to bring
economic stability in the economy :
o Bank Rate : Rate of rediscount at which the RBI discounts the first class bills of
exchange brought by the banks.
o Repo Rate : Injection of liquidity by the RBI is termed as " Repo Rate" . This
was introduced in Dec. 1992 and Reverse Repo Rate in Nov. 1996. RBI buys
Govt. Securities for a short period usually a fortnight, with an agreement to sell it
later. Thus repo rate is a short-term money market instrument to stabilize short
term liquidity in the economy.
o Reverse Repo Rate
Repo Rate is the rate at which the RBI lends to commercial banks where
as the Reverse Repo Rate is the rate at which the RBI borrows from the
commercial banks against securities for a very short period.
Repo and Reverse Repo rates are used as policy instruments for day-today liquidity management under the liquidity adjustment facility.
o Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) : It refers to the percentage of net demand and time
deposits which the scheduled commercial banks have to keep with RBI at zero
interest Rate as per RBI act 1934.
o Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) : It refers to the percentage of net demand and
time deposits which the scheduled commercial banks have to keep with
themselves. i.e. by purchasing Govt. Securities or in the form of cash or gold as
per Banking Regulation Act 1949, Sec 24.
SLR is a mechanism used by Commercial Banks for providing credit to
the Govt.
o Open market operations : RBI buys or sells Govt. Bonds in the second Ratio.
RBI Amendment Bill 2005 provides flexibility to RBI in fixing the CRR and SLR.
Though RBI is responsible for the safety and stability of the Banking sector, it is not
legally independent.
co
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Repo Rate
on
Z.
co
Repo rate is the rate at which our banks borrow rupees from RBI. Whenever the banks have any
shortage of funds they can borrow it from RBI. A reduction in the repo rate will help banks to get
money at a cheaper rate. When the repo rate increases, borrowing from RBI becomes more
expensive.
Present Repo Rate 7.25%
Reverse Repo Rate
mb
iti
This is exact opposite of Repo rate. Reverse Repo rate is the rate at which Reserve Bank of India
(RBI) borrows money from banks. RBI uses this tool when it feels there is too much money
floating in the banking system. Banks are always happy to lend money to RBI since their money
is in safe hands with a good interest. An increase in Reverse repo rate can cause the banks to
transfer more funds to RBI due to this attractive interest rates.
Present Reverse Repo Rate 6.25%
CRR Rate
ww
w.
Gr
SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio) is the amount a commercial bank needs to maintain in the form
of cash, or gold or govt. approved securities (Bonds) before providing credit to its customers.
SLR rate is determined and maintained by the RBI (Reserve Bank of India) in order to control
the expansion of bank credit. SLR is determined as the percentage of total demand and
percentage of time liabilities. Time Liabilities are the liabilities a commercial bank liable to pay
to the customers on their anytime demand. SLR is used to control inflation and propel growth.
Through SLR rate tuning the money supply in the system can be controlled efficiently.
Present SLR 23%
Inflation
Inflation is as an increase in the price of bunch of Goods and services that projects the Indian
economy. An increase in inflation figures occurs when there is an increase in the average level of
prices in Goods and services. Inflation happens when there are fewer Goods and more buyers;
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
SLR Rate
8A
Cash reserve Ratio (CRR) is the amount of funds that the banks have to keep with RBI. If RBI
decides to increase the percent of this, the available amount with the banks comes down. RBI is
using this method (increase of CRR rate), to drain out the excessive money from the banks.
Present CRR 4%
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
this will result in increase in the price of Goods, since there is more demand and less supply of
the goods.
co
Deflation
on
Z.
Deflation is the continuous decrease in prices of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the
inflation rate becomes negative (below zero) and stays there for a longer period.
PLR
iti
The Prime Interest Rate is the interest rate charged by banks to their most creditworthy
customers (usually the most prominent and stable business customers). The rate is almost always
the same amongst major banks. Adjustments to the prime rate are made by banks at the same
time; although, the prime rate does not adjust on any regular basis. The Prime Rate is usually
adjusted at the same time and in correlation to the adjustments of the Fed Funds Rate. Some
banks use the name "Reference Rate" or "Base Lending Rate" to refer to their Prime Lending
Rate.
mb
Deposit Rate
8A
Interest Rates paid by a depository institution on the cash on deposit.
FII
ww
FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) occurs with the purchase of the physical assets or a significant
amount of ownership (stock) of a company in another country in order to gain a measure of
management control (Or) A foreign company having a stake in a Indian Company.
IPO
IPO is Initial Public Offering. This is the first offering of shares to the general public from a
company wishes to list on the stock exchanges.
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
w.
FDI
Gr
FII (Foreign Institutional Investor) used to denote an investor, mostly in the form of an
institution. An institution established outside India, which proposes to invest in Indian market, in
other words buying Indian stocks. FII's generally buy in large volumes which has an impact on
the stock markets. Institutional Investors includes pension funds, mutual funds, Insurance
Companies, Banks, etc.
Disinvestment
co
The Selling of the government stake in public sector undertakings.
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Fiscal Deficit
on
Z.
It is the difference between the governments total receipts (excluding borrowings) and total
expenditure. Present Fiscal Deficit is 4.89%
Revenue deficit
iti
It defines that, where the net amount received (by taxes & other forms) fails to meet the
predicted net amount to be received by the government
mb
GDP
8A
The Gross Domestic Product or GDP is a measure of all of the services and goods produced in a
country over a specific period; classically a year.
GNP
National Income
ww
w.
National Income is the money value of all goods and services produced in a country during the
year.
Per Capita Income
The national income of a country, or region, divided by its population. Per capita income is often
used to measure a country's standard of living.
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Gr
Gross National Product is measured as GDP plus income of residents from investments made
abroad minus income earned by foreigners in domestic market.
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Vote on Account
co
A vote-on account is basically a statement ,where the government presents an estimate of a sum
required to meet the expenditure that it incurs during the first three to four months of an election
financial year until a new government is in place, to keep the machinery running.
on
Z.
Difference between Vote on Account and Interim Budget
Vote-on-account deals only with the expenditure side of the government's budget, an interim
Budget is a complete set of accounts, including both expenditure and receipts.
SDR
mb
iti
The SDR (Special Drawing Rights) is an artificial currency created by the IMF in 1969. SDRs
are allocated to member countries and can be fully converted into international currencies so they
serve as a supplement to the official foreign reserves of member countries. Its value is based on a
basket of key international currencies (U.S. dollar, euro, yen and pound sterling).
SEZ
Corporate governance
ww
w.
The way in which a company is governed and how it deals with the various interests of its
customers, shareholders, employees and society at large. Corporate governance is the set of
processes, customs, policies, laws, and institutions affecting the way a corporation (or company)
is directed, administered or controlled.Is defined as the general set of customs, regulations,
habits, and laws that determine to what end a firm should be run.
RBI Functions
The Reserve Bank of India is the central bank of India, was established on April 1, 1935 in
accordance with the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The Reserve Bank of
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Gr
8A
SEZ means Special Economic Zone is the one of the part of governments policies in India. A
special Economic zone is a geographical region that economic laws which are more liberal than
the usual economic laws in the country. The basic motto behind this is to increase foreign
investment, development of infrastructure, job opportunities and increase the income level of the
people.
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
on
Z.
co
India was set up on the recommendations of the Hilton Young Commission. The commission
submitted its report in the year 1926, though the bank was not set up for nine years.To regulate
the issue of Bank Notes and keeping of reserves with a view to securing monetary stability in
India and generally to operate the currency and credit system of the country to its advantage."
Banker to the Government: performs merchant banking function for the central and the state
governments; also acts as their banker. Banker to banks: maintains banking accounts of all
scheduled banks.
Monetary policy
iti
A Monetary policy is the process by which the government, central bank, of a country controls
(i)
the supply of money,
(ii)
availability of money, and
(iii)
cost of money or rate of interest,
In order to attain a set of objectives oriented towards the growth and stability of the economy.
mb
Fiscal Policy
8A
Fiscal policy is the use of government spending and revenue collection to influence the
economy. These policies affect tax rates, interest rates and government spending, in an effort to
control the economy. Fiscal policy is an additional method to determine public revenue and
public expenditure.
w.
Gr
Core banking is a general term used to describe the services provided by a group of networked
bank branches. Bank customers may access their funds and other simple transactions from any of
the member branch offices. It will cut down time, working simultaneously on different issues and
increasing efficiency. The platform where communication technology and information
technology are merged to suit core needs of banking is known as Core Banking Solutions.
Bank, its Features and Types
ww
A bank is a financial organization where people deposit their money to keep it safe.Banks play
an important role in the financial system and the economy. As a key component of the financial
system, banks allocate funds from savers to borrowers in an efficient manner. Regional Rural
Banks were established with an objective to ensure sufficient institutional credit for agriculture
and other rural sectors. The RRBs mobilize financial resources from rural / semi-urban areas and
grant loans and advances mostly to small and marginal farmers, agricultural labourers and rural
artisans.
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Core Banking Solutions
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
mb
iti
(vii)
co
(ii)
(iii)
The area of operation of RRBs is limited to the area as notified by GoI covering one or
more districts in the State.
Banking services for individual customers is known as retail banking.
A bank that deals mostly in but international finance, long-term loans for companies and
underwriting. Merchant banks do not provide regular banking services to the general
public
Online banking (or Internet banking) allows customers to conduct financial transactions
on a secure website operated by their retail or virtual bank.
Mobile Banking is a service that allows you to do banking transactions on your mobile
phone without making a call , using the SMS facility. Is a term used for performing
balance checks, account transactions, payments etc. via a mobile device such as a mobile
phone.
Traditional banking is the normal bank accounts we have. Like, put your money in the
bank and they act as a security and you will get only the normal interests (decided by RBI
in our case, FED bank in US).
Investment banking is entirely different. Here, people who are having so much money
(money in excess which will yield only less interest if in Banks) will invest their money
and get higher returns. For example, If i have more money instead of taking the pain of
investing in share market, buying properties etc. I will give to investment banks and they
will do the money management and give me higher returns when compared to traditional
banks.
on
Z.
(i)
E-Governance
8A
E-Governance is the public sectors use of information and communication technologies with the
aim of improving information and service delivery, encouraging citizen participation in the
decision-making process and making government more accountable, transparent and effective.
w.
The Right to Information act is a law enacted by the Parliament of India giving citizens of India
access to records of the Central Government and State overnments. The Act applies to all States
and Union Territories of India, except the State of Jammu and Kashmir - which is covered under
a State-level law. This law was passed by Parliament on 15 June 2005 and came fully into force
on 13 October 2005.
ww
Credit Rating Agencies in India
The credit rating agencies in India mainly include ICRA and CRISIL. ICRA wasformerly
referred to the Investment Information and Credit Rating Agency of India Limited. Their main
function is to grade the different sector and companies in terms of performance and offer
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Gr
Right to information Act
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
solutions for up gradation. The credit rating agencies in India mainly include ICRA and
CRISIL(Credit Rating Information Services of India Limited)
co
Cheque
on
Z.
Cheque is a negotiable instrument instructing a Bank to pay a specific amount from a specified
account held in the maker/depositor's name with that Bank. A bill of exchange drawn on a
specified banker and payable on demand. Written order directing a bank to pay money.
Demand Draft
iti
A demand draft is an instrument used for effecting transfer of money. It is a Negotiable
Instrument. Cheque and Demand-Draft both are used for Transfer of money. You can 100% trust
a DD. It is a banker's check. A check may be dishonored for lack of funds a DD can not. Cheque
is written by an individual and Demand draft is issued by a bank. People believe banks more than
individuals.
mb
NBFC
Diff between banking & Finance
ww
Finance is generally related to all types of financial, this could be accounting, insurances and
policies. Whereas banking is everything that happens in a bank only.The term Banking and
Finance are two very different terms but are often associated together. These two terms are often
used to denote services that a bank and other financial institutions provide to its customers.
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
w.
Gr
8A
A non-banking financial company (NBFC) is a company registered under the Companies Act,
1956 and is engaged in the business of loans and advances, acquisition of
shares/stock/bonds/debentures/securities issued by government, but does not include any
institution whose principal business is that of agriculture activity, industrial activity,
sale/purchase/construction of immovable property.
NBFCs are doing functions akin to that of banks; however there are a few differences:
(i)
A NBFC cannot accept demand deposits (demand deposits are funds deposited at a
depository institution that are payable on demand -- immediately or within a very short
period -- like your current or savings accounts.)
(ii)
it is not a part of the payment and settlement system and as such cannot issue cheques to
its customers; and
(iii)
Deposit insurance facility of DICGC is not available for NBFC depositors unlike in case
of banks.
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
10
NASSCOM
on
Z.
co
The National Association of Software and Services Companies (NASSCOM), the Indian
chamber of commerce is a consortium that serves as an interface to the Indian software industry
and Indian BPO industry. Maintaining close interaction with the Government of India in
formulating National IT policies with specific focus on IT software and services maintaining a
state of the art information database of IT software and services related activities for use of both
the software developers as well as interested companies overseas.
President - Mr. Som Mittal
Chairman - Natarajan Chandrasekaran
ASSOCHAM
mb
iti
The Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India (ASSOCHAM), India's premier
apex chamber covers a membership of over 2 lakh companies and professionals across the
country. It was established in 1920 by promoter chambers, representing all regions of India. As
an apex industry body, ASSOCHAM represents the interests of industry and trade, interfaces
with Government on policy issues and interacts with counterpart international organizations to
promote bilateral economic issues.
President-Rajkumar Dhoot
NABARD
SIDBI
ww
The Small Industries Development Bank of India is a state-run bank aimed to aid the growth and
development of micro, small and medium scale industries in India. Set up in 1990 through an act
of parliament, it was incorporated initially as a wholly owned subsidiary of Industrial
Development Bank of India.
Chairman - Sushil Muhnot
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
w.
Gr
8A
NABARD was established by an act of Parliament on 12 July 1982 to implement the National
Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development Act 1981. It replaced the Agricultural Credit
Department (ACD) and Rural Planning and Credit Cell (RPCC) of Reserve Bank of India, and
Agricultural Refinance and Development Corporation (ARDC). It is one of the premiere agency
to provide credit in rural areas. NABARD is set up as an apex Development Bank with a
mandate for facilitating credit flow for promotion and development of agriculture, small-scale
industries, cottage and village industries, handicrafts and other rural crafts.
Chairman - Dr.Prakash Bakshi
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
11
SENSEX and NIFTY
on
Z.
co
SENSEX is the short term for the words "Sensitive Index" and is associated with the Bombay
(Mumbai) Stock Exchange (BSE). The SENSEX was first formed on 1-1-1986 and used the
market capitalization of the 30 most traded stocks of BSE. Where as NSE has 50 most traded
stocks of NSE. SENSEX IS THE INDEX OF BSE. AND NIFTY IS THE INDEX OF NSE.
BOTH WILL SHOW DAILY TRADING MARKS. Sensex and Nifty both are an "index. An
index is basically an indicator it indicates whether most of the stocks have gone up or most of the
stocks have gone down.
SEBI
iti
SEBI is the regulator for the Securities Market in India. Originally set up by the Government of
India in 1988, it acquired statutory form in 1992 with SEBI Act 1992 being passed by the Indian
Parliament. Chaired by U.K. Sinha.
Mutual funds
8A
mb
Mutual funds are investment companies that pool money from investors at large and offer to sell
and buy back its shares on a continuous basis and use the capital thus raised to invest in
securities of different companies. The mutual fund will have a fund manager that trades the
pooled money on a regular basis. The net proceeds or losses are then typically distributed to the
investors annually.
w.
Gr
A company that invests its clients' pooled fund into securities that match its declared financial
objectives. Asset management companies provide investors with more diversification and
investing options than they would have by themselves. Mutual funds, hedge funds and pension
plans are all run by asset management companies. These companies earn income by charging
service fees to their clients.
Non-Performing assets
ww
Non-performing assets, also called non-performing loans, are loans,made by a bank or finance
company, on which repayments or interest payments are not being made on time. A debt
obligation where the borrower has not paid any previously agreed upon interest and principal
repayments to the designated lender for an extended period of time. The nonperforming asset is
therefore not yielding any income to the lender in the form of principal and interest payments.
Recession
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
Asset Management Companies
Study Material for RBI Assistants and Grade B Officers Powered by www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
12
co
A true economic recession can only be confirmed if GDP (Gross Domestic Product)growth is
negative for a period of two or more consecutive quarters.
Foreign exchange reserves
on
Z.
Foreign exchange reserves (also called Forex reserves) in a strict sense are only the foreign
currency deposits and bonds held by central banks and monetary authorities. However, the term
in popular usage commonly includes foreign exchange and gold, SDRs and IMF reserve
positions.
IMF
mb
iti
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international organization that oversees the global
financial system by following the macroeconomic policies of its member countries, in particular
those with an impact on exchange rates and the balance of payments. It is an organization formed
to stabilize international exchange rates and facilitate development.
Managing Director- Christine Lagarde
8A
Thats all for now Friends. Please share this with your friends if you feel its useful.
All the Best
Gr8AmbitionZ Team
We are at Facebook
www.facebook.com/Gr8AmbitionZ
For more Materials and Previous Papers visit us at www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
www.Gr8AmbitionZ.com
ww
w.
Gr
Dont forget to LIKE us there for Daily Updates
You might also like
- Too Big To FailDocument9 pagesToo Big To FailPriyank Hariyani0% (1)
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5Aqilah Nur15No ratings yet
- Regional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementFrom EverandRegional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementNo ratings yet
- Hubspot Digital Marketing TranscripttranscriptDocument110 pagesHubspot Digital Marketing TranscripttranscriptAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On: The General Banking Activites & Analysis of Financial Performance of Basic Bank LimitedDocument69 pagesInternship Report On: The General Banking Activites & Analysis of Financial Performance of Basic Bank LimitedMR RockyNo ratings yet
- John A CahillDocument4 pagesJohn A CahillPopovici LiviuNo ratings yet
- Attachment - RBI Grade B 2020 10 Weeks Plan PDF - Lyst3476Document14 pagesAttachment - RBI Grade B 2020 10 Weeks Plan PDF - Lyst3476Rama BaiNo ratings yet
- Adda EcoDocument120 pagesAdda EcoRaj MathurNo ratings yet
- Risks and Risk Management in Banking by Edutap Rbi CourseDocument13 pagesRisks and Risk Management in Banking by Edutap Rbi CoursePiyush ChauhanNo ratings yet
- RBI Grade B 2019 Phase 2 - Economics & Social IssuesDocument13 pagesRBI Grade B 2019 Phase 2 - Economics & Social IssuesBittuNo ratings yet
- 5 6188293660098953360 PDFDocument254 pages5 6188293660098953360 PDFAviral MishraNo ratings yet
- Attachment DSummary Sheet - Time Value of Money PDFDocument12 pagesAttachment DSummary Sheet - Time Value of Money PDFUnmesh MitraNo ratings yet
- RBI Grade B PDFDocument11 pagesRBI Grade B PDFPratheesh TulsiNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary - Cash Flow Statement PDFDocument5 pagesAttachment Summary - Cash Flow Statement PDFUnmesh MitraNo ratings yet
- RBIDocument1 pageRBIRajaraja CholaNo ratings yet
- Flash Strategy For Grade BDocument6 pagesFlash Strategy For Grade BPrashant KunduNo ratings yet
- Jiga Comp StrategyDocument129 pagesJiga Comp Strategyazsdx100% (2)
- Questions Asked in RBI Grade B 2017: Phase II: Economic and Social IssuesDocument2 pagesQuestions Asked in RBI Grade B 2017: Phase II: Economic and Social IssuesAshirvadNo ratings yet
- RBI Grade B Course DetailsDocument12 pagesRBI Grade B Course DetailsSOMYA JAINNo ratings yet
- RBI Grade B Preparation Strategy GuideDocument16 pagesRBI Grade B Preparation Strategy GuideSOMYA JAINNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Development Part 1Document32 pagesHuman Resource Development Part 1Vineeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Rbi 2019 Esi FM Questions AskedDocument2 pagesRbi 2019 Esi FM Questions AskedVIKASNo ratings yet
- Economic Concept Part 4aDocument13 pagesEconomic Concept Part 4aGirija PriyaNo ratings yet
- Motivation - Part 2Document45 pagesMotivation - Part 2jashuramuNo ratings yet
- MR Siddharth Kain RBI Grade B 2019 Strategy E BookDocument4 pagesMR Siddharth Kain RBI Grade B 2019 Strategy E BookS GovardhaniNo ratings yet
- RBI Grade B 2021 Preparation Strategy, Exam Analysis & Cut OffDocument42 pagesRBI Grade B 2021 Preparation Strategy, Exam Analysis & Cut OffUnprecedented ScienceTVNo ratings yet
- Finance Reforms in The Banking and Finance Sector Revision SheetDocument9 pagesFinance Reforms in The Banking and Finance Sector Revision SheetAditya PawarNo ratings yet
- All Committees (Tabular Format) : by - Anuj JindalDocument41 pagesAll Committees (Tabular Format) : by - Anuj JindalAmit GodaraNo ratings yet
- Finance Commission Report: Anuj JindalDocument13 pagesFinance Commission Report: Anuj JindalAmit GodaraNo ratings yet
- My Preparation JourneyDocument3 pagesMy Preparation JourneySandeep SumanNo ratings yet
- (Question Papers) RBI Grade "B" Officers - Finance and Management Papers of Last 8 Exams (Phase 2) MrunalDocument8 pages(Question Papers) RBI Grade "B" Officers - Finance and Management Papers of Last 8 Exams (Phase 2) MrunalsaymtrNo ratings yet
- Economic & Social Issues Schemes For Rbi Grade B - Sebi Grade A - Nabard 2020Document68 pagesEconomic & Social Issues Schemes For Rbi Grade B - Sebi Grade A - Nabard 2020Amit Godara100% (1)
- DSummary Sheet - Corporate Gov in Banking SectorDocument9 pagesDSummary Sheet - Corporate Gov in Banking Sectorharshmishra94No ratings yet
- Summary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Forex MarketsDocument5 pagesSummary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Forex MarketsSaumyaNo ratings yet
- Free E-Book: For RBI Gr. B Economic & Social Issues (ESI) PreparationDocument8 pagesFree E-Book: For RBI Gr. B Economic & Social Issues (ESI) PreparationDhairya ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Economic and Social Issues For RbiDocument13 pagesEconomic and Social Issues For RbiMohit NegiNo ratings yet
- Previous Years English Descriptive Essay TopicsDocument9 pagesPrevious Years English Descriptive Essay TopicsSteelNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument110 pagesLeadershipAshok YadavNo ratings yet
- 1) RBI GRADE B Preparation - Microsoft OneNote OnlineDocument4 pages1) RBI GRADE B Preparation - Microsoft OneNote OnlineAman JainNo ratings yet
- My Journey To RBI - Naveen KarthikDocument7 pagesMy Journey To RBI - Naveen KarthikGowtham Pallekonda100% (2)
- Economic & Social Issues Schemes FOR Rbi Grade B - Sebi Grade A - Ibps Afo 2019Document59 pagesEconomic & Social Issues Schemes FOR Rbi Grade B - Sebi Grade A - Ibps Afo 2019Amit GodaraNo ratings yet
- Fodder Material Descriptive English For Phase 2 Batch 1 For NABARD Grade A/B 2019Document45 pagesFodder Material Descriptive English For Phase 2 Batch 1 For NABARD Grade A/B 2019PrabalNo ratings yet
- RBI Grade B Quantitative Aptitude Questions PDFDocument6 pagesRBI Grade B Quantitative Aptitude Questions PDFDream leagueNo ratings yet
- 6.2.social Justice - Positive Discrimination in Favor of Underprivileged Part2Document54 pages6.2.social Justice - Positive Discrimination in Favor of Underprivileged Part2jashuramuNo ratings yet
- RBI Grade B 2021 English Descriptive Question PaperDocument2 pagesRBI Grade B 2021 English Descriptive Question Papersajal agarwalNo ratings yet
- Basic Notes JaiibDocument42 pagesBasic Notes JaiibSanjeev Miglani100% (1)
- RBI Grade B Exam Preparation StrategyDocument17 pagesRBI Grade B Exam Preparation StrategysahilNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy: ESI Notes For RBI Grade B ExamDocument11 pagesMonetary Policy: ESI Notes For RBI Grade B ExamVidushi pandeyNo ratings yet
- COst of Capital Edutap-Rbi SummaryDocument11 pagesCOst of Capital Edutap-Rbi SummaryashishNo ratings yet
- RBI Grade B 100 Days Study PlanDocument18 pagesRBI Grade B 100 Days Study PlanAyushi MauryaNo ratings yet
- Mapping of FM Syllabus in Official Notification To FM in EduTap Course Lyst4273Document4 pagesMapping of FM Syllabus in Official Notification To FM in EduTap Course Lyst4273Akshay WankhadeNo ratings yet
- TEST-8: Lesson 12 InfrastructureDocument24 pagesTEST-8: Lesson 12 InfrastructureDeepak ShahNo ratings yet
- Committee Table Questions Lyst6919Document106 pagesCommittee Table Questions Lyst6919Amit GodaraNo ratings yet
- (Question Papers) RBrtI Grade "B" Officers - Finance and Management Papers of Last 8 Exams (Phase 2) MrunalDocument10 pages(Question Papers) RBrtI Grade "B" Officers - Finance and Management Papers of Last 8 Exams (Phase 2) Mrunalguru1241987babuNo ratings yet
- RBI - Grade B Swapnil DeoreDocument12 pagesRBI - Grade B Swapnil Deoresaurabhmakta100% (3)
- Summary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Human Resource Development-Part-2 - RBI Grade B 2018Document18 pagesSummary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Human Resource Development-Part-2 - RBI Grade B 2018Soumava PalNo ratings yet
- Alternative Sources of Finance - Private and SocialDocument13 pagesAlternative Sources of Finance - Private and SocialSkanda KumarNo ratings yet
- Risks and Risk Management in Banking by Edutap Rbi Course PDFDocument19 pagesRisks and Risk Management in Banking by Edutap Rbi Course PDFPiyush Chauhan0% (1)
- TEST-8: Lesson 6 India's External SectorDocument28 pagesTEST-8: Lesson 6 India's External SectorDeepak ShahNo ratings yet
- Previous Years English Descriptive Essay Topics NABARD GRADE ADocument9 pagesPrevious Years English Descriptive Essay Topics NABARD GRADE APrem KumarNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary PPPDocument9 pagesAttachment Summary PPPdevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- RBI Question Paper and Analysis - 2023Document659 pagesRBI Question Paper and Analysis - 2023iamnerror404100% (1)
- Banking Awareness Quick Reference Guide - Gr8AmbitionZDocument11 pagesBanking Awareness Quick Reference Guide - Gr8AmbitionZSanjeet MohantyNo ratings yet
- Top 50 Banking Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesTop 50 Banking Interview QuestionschoprahridyeshNo ratings yet
- Proceedings: Integrated Pest Management in Indian AgricultureDocument279 pagesProceedings: Integrated Pest Management in Indian AgricultureAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- IIL Annual Report 2020 21Document214 pagesIIL Annual Report 2020 21Anudeep KumarNo ratings yet
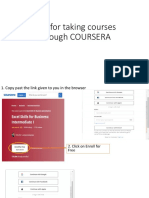
- SOP For Coursera CoursesDocument5 pagesSOP For Coursera CoursesAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Monthly ReportDocument16 pagesMonthly ReportAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Indofil June Price List - UP, UKDocument4 pagesIndofil June Price List - UP, UKAnudeep Kumar67% (3)
- Products ListDocument5 pagesProducts ListAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Crop Language Ludhiana Bathinda: Paddy Hindi Paddy Punjabi 10000 8000 Cotton Hindi Cotton Punjabi 5000Document5 pagesCrop Language Ludhiana Bathinda: Paddy Hindi Paddy Punjabi 10000 8000 Cotton Hindi Cotton Punjabi 5000Anudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Rallis Price Approval 21-22 Jun'2021 Hisar RegionDocument6 pagesRallis Price Approval 21-22 Jun'2021 Hisar RegionAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Digital Marketing Fundamentals TranscriptDocument13 pagesDigital Marketing Fundamentals TranscriptAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Willowood Bonanza: Brand GRDocument1 pageWillowood Bonanza: Brand GRAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Apr'21 - Godrej Non Generic-Pgr Inhose Price Circualr For Kharif 21Document3 pagesApr'21 - Godrej Non Generic-Pgr Inhose Price Circualr For Kharif 21Anudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Paid Search Advertising - TranscriptDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Paid Search Advertising - TranscriptAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- LESSON How To Create A Successful Video Marketing Strategy SCRIPTDocument7 pagesLESSON How To Create A Successful Video Marketing Strategy SCRIPTAnudeep Kumar100% (1)
- Revised+Tropical and Subtropical VegetablesDocument18 pagesRevised+Tropical and Subtropical VegetablesAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument64 pagesSupply Chain ManagementAnudeep KumarNo ratings yet
- SOP Accounting Cycle Process - DraftDocument8 pagesSOP Accounting Cycle Process - DraftAndres Dony WijayaNo ratings yet
- Accounting AssignmentDocument7 pagesAccounting AssignmentGui Xiang KhooNo ratings yet
- Public Sector Accounting March 2021Document23 pagesPublic Sector Accounting March 2021severinmsangiNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Federal Taxation 2017 24th Edition Murphy Test Bank DownloadDocument40 pagesConcepts in Federal Taxation 2017 24th Edition Murphy Test Bank DownloadLuis Moore100% (21)
- Crypto and Law FinalDocument19 pagesCrypto and Law Finalharshvardhan dinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eleven: Commercial Banks: Industry OverviewDocument26 pagesChapter Eleven: Commercial Banks: Industry OverviewroBinNo ratings yet
- AR11Document241 pagesAR11Mohib Ullah YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 Fa ReviewerDocument3 pagesQuiz 4 Fa ReviewerKristine Jewel PacursaNo ratings yet
- Organizer: Rajendra Adhikari Presenter Anish OjhaDocument11 pagesOrganizer: Rajendra Adhikari Presenter Anish Ojhaanish ojhaNo ratings yet
- Airline Industry: Stan Li, Jessica Liu, Ben Mui, Edison Pei, Tony YeungDocument89 pagesAirline Industry: Stan Li, Jessica Liu, Ben Mui, Edison Pei, Tony YeungSakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 AnswersDocument4 pagesChapter 30 AnswersSHRI NIVETHA GANESHMOORTY CSI CBENo ratings yet
- LatihanDocument5 pagesLatihanJimmy LimNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Financial Statement and Cash Flows BBS Notes EduNEPAL - InfoDocument1 pageUnit 2 Financial Statement and Cash Flows BBS Notes EduNEPAL - InfoGrethel Tarun MalenabNo ratings yet
- Types of Decisions Made by A Finance ManagerDocument3 pagesTypes of Decisions Made by A Finance ManagerAadil HanifNo ratings yet
- AB Limited Provides You The Following DataDocument2 pagesAB Limited Provides You The Following DataRajarshi DaharwalNo ratings yet
- 04 Notes - The Net Present Value (NPV) PDFDocument7 pages04 Notes - The Net Present Value (NPV) PDFAlberto ElquetedejoNo ratings yet
- CORPORATE ACCOUNTING IA2-pdf 2Document12 pagesCORPORATE ACCOUNTING IA2-pdf 2Surya GowdaNo ratings yet
- Merchant BankingDocument25 pagesMerchant BankingLMT indiaNo ratings yet
- FRANSABANKDocument7 pagesFRANSABANKJn90No ratings yet
- Corporate Financial StrategyDocument14 pagesCorporate Financial StrategyHammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- HPD - 0502 - Mills EscrowDocument16 pagesHPD - 0502 - Mills EscrowUlisesNo ratings yet
- Organizational Health IndexDocument21 pagesOrganizational Health IndexSukamto PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Rockwell Land CorporationDocument26 pagesGroup 5 Rockwell Land CorporationIsabelle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- SIDBI and IFCIDocument5 pagesSIDBI and IFCIharsha bobbaNo ratings yet
- Sbi & IciciDocument31 pagesSbi & IciciAnu_Yadav_633275% (4)