Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transformer
Transformer
Uploaded by
kushah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views3 pagesj
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views3 pagesTransformer
Transformer
Uploaded by
kushahj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
3.
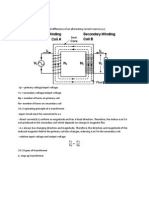
4 TRANSFORMER
3.4.1 TRANSFORMER
- used to change the potential difference of an alternating current source (a.c)
Vp = primary voltage/input voltage
Vs = secondary voltage/output voltage
Np = number of turns on primary coil
Ns= number of turns on secondary coil
3.4.2 operating principle of a transformer
-input circuit must be connected to a.c
- direct current(d.c) uniform in magnitude and has a fixed direction. Therefore,
the induce e.m.f is not produced in the secondary coil which depends on change
in magnetic flux
- A.c always has changing direction and magnitude. Therefore, the direction and
magnitude of the induced magnetic field in the primary coil also changes,
inducing e.m.f in the secondary coil.
- relation input voltage and output voltage
Vs Ns
=
Vp Np
3.4.3 types of transformer
A. step-up transformer
Increase the potential difference
Ns > Np
Is < Ip
Vs > Vp
B. Step-down transformer
Reduce potential difference
Ns < Np
Is > Ip
Vs < Vp
3.4.4 realtionship between input power and output power
Ideal transformer
o Efficiency 100 % no heat loss
o Input power = output power
Pi = Po
IpVp = IsVs
3.4.5 Efficiency
3.4.6 Factors that effect the efficiency of a transformer
Factors
Heating effect of a current in coil
Power lost as heat P = I2R
Heating effect of induced eddy current
Eddy currents are generated within
the iron core
Magnetization of the iron core
Energy used in the magnetization and
demagnetization of the iron core
every time the current changes its
direction is known as hysteresis. This
energy is lost as heat which
subsequently heats up the iron core
Flux leakage
Some of the induced magnetic flux
from the primary coil is not
transferred to the secondary coil.
Methods to increase efficiency
o Use thicker copper wires of low
resistance
o Use coolant to decrease the
temperature of the transformer
o Use laminated iron core where
each layer is insulated with
enamel paint to prevent flow of
eddy currents
o Use soft iron core that is easily
magnetized and demagnetized.
Secondary coils are interwined
tightly with the primary coils
*eddy current = circulating electrical currents that are induced in electrically
conductive elements when exposed to changing magnetic field, creating an
opposing force to magnetic flux.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Answer All The Questions GivenDocument5 pagesAnswer All The Questions GivenkushahNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji SPMDocument46 pagesUlangkaji SPMkushahNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji SPMDocument46 pagesUlangkaji SPMkushahNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji SPMDocument46 pagesUlangkaji SPMkushahNo ratings yet
- Answer All The Questions GivenDocument5 pagesAnswer All The Questions GivenkushahNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument3 pagesTransformerkushahNo ratings yet
- LPKPM SPM 2012 Physics Paper 3Document0 pagesLPKPM SPM 2012 Physics Paper 3Sk BalanNo ratings yet
- Analisis Item - Sheet1Document2 pagesAnalisis Item - Sheet1kushahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 P2Document18 pagesChapter 9 P2faisal850720035887No ratings yet