Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Casparian Strip
Casparian Strip
Uploaded by
rubanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Casparian Strip
Casparian Strip
Uploaded by
rubanCopyright:
Available Formats
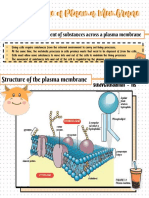
Casparian Strip
- Casparian strips are waterproof bands which run around the cell wall of endodermal
cells in plant roots.
- Their purpose is to force water which has been following the apoplastic pathway, into
the living protoplast of the endodermal cell.
- Mineral ions in the water are actively transported into the xylem, meaning the xylem
now has a lower water potential than the endodermal cell, causing the water to move
into the xylem through osmosis
Translocation
-The movement of assimilates (sugars and other chemicals made by plant cells) is
called translocation. Sugars are transported in the phloem in the form of sucrose. A
part of the plant that releases sucrose into the phloem is called a source. A part of the
plant that removes sucrose from the phloem is called a sink.
- Sucrose is actively loaded into the phloem. ATP is used by companion cells.
- At the source, sucrose entering the sieve tube element reduces the water potential
inside the sieve tube. As a result, water molecules move into the sieve tube element
by osmosis from surrounding tissues.. This increases the hydrostatic pressure in the
sieve tube at the source.
-Sucrose is used in the cells surrounding the phloem. The sucrose may be converted
to starch for storage, or may be used in a metabolic process such as respiration. This
reduces the sucrose concentration in these cells. Sucrose molecules move by diffusion
or active transport from the sieve tube element into the surrounding cells. This
increases the water potential in the sieve tube element, so water molecules move into
the surrounding cells by osmosis. This reduces the hydrostatic pressure in the phloem
in the sink.
You might also like
- Endodermis and Casparian StripDocument2 pagesEndodermis and Casparian StripYap Hooi CheinNo ratings yet
- The Uptake and Transport of Water and MineralsDocument40 pagesThe Uptake and Transport of Water and MineralsDeanne Saz100% (1)
- MF009 5C Transportation James L2Document19 pagesMF009 5C Transportation James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Biologyical EssayDocument4 pagesBiologyical Essayruben.debiereNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals: Right Atrium Left Atrium Pump BloodDocument8 pagesTransport in Animals: Right Atrium Left Atrium Pump BloodLim Tze ErNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Transport in Vascular Plants Student NoteDocument3 pagesLesson 6 Transport in Vascular Plants Student NoteallaboutamaliaNo ratings yet
- Xylem and PhloemDocument35 pagesXylem and PhloemAvanish PratapNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants 2Document7 pagesTransport in Plants 2Pankaj PatelNo ratings yet
- 3.3. Transport in PlantsDocument5 pages3.3. Transport in PlantsFatima NissaNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument15 pagesTransport in PlantsUsama AhmadNo ratings yet
- 1.8 The Transport of Organic Substances and Water in Plants 5JDocument29 pages1.8 The Transport of Organic Substances and Water in Plants 5JfatinmyNo ratings yet
- BOTANYDocument2 pagesBOTANYBella Loriega ÜNo ratings yet
- How Translocation WorksDocument23 pagesHow Translocation WorksAqeela SyakiraNo ratings yet
- Transport in Vascular PlantsDocument21 pagesTransport in Vascular PlantsFahami WahidNo ratings yet
- STPM BiologyDocument2 pagesSTPM BiologyArthas Rhee HermanNo ratings yet
- Transport in Phloem Lesson 3Document13 pagesTransport in Phloem Lesson 3Kajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- ch11 170122071310Document25 pagesch11 170122071310Honleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT IN PLANTS Updated ZimsecDocument24 pagesTRANSPORT IN PLANTS Updated ZimsecnatashamautsiNo ratings yet
- Transportation in PlantDocument9 pagesTransportation in PlantrohitvermashakyaNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 8 Transport in Plants - CIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 8 Transport in Plants - CIE Biology IGCSE PDFMd A RAZZAK100% (1)
- Water Movement ... AwaisDocument41 pagesWater Movement ... AwaisGabi TuriNo ratings yet
- Topic:: Submitted To: Prof. Hina TariqDocument6 pagesTopic:: Submitted To: Prof. Hina TariqZubair BalouchNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants. CAPE Biology.Document5 pagesTransport in Plants. CAPE Biology.Rocheal WhittinghamNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesTransport in PlantsKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- BIOL102Alaie NotesDocument93 pagesBIOL102Alaie NotesBarukh B. RohdeNo ratings yet
- 113-Transport in Plants Chapter 36Document38 pages113-Transport in Plants Chapter 36daniellealexa7No ratings yet
- 3.2.2 Transport in Plants The Need For A Transport SystemDocument36 pages3.2.2 Transport in Plants The Need For A Transport SystemImperia Galea100% (1)
- Transport in Plants: Unit 2Document23 pagesTransport in Plants: Unit 2SashidaeNo ratings yet
- Transport in Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesTransport in Flowering PlantsChic BoosterNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants NotesDocument14 pagesTransport in Plants NotesUsama KhanNo ratings yet
- Translocation in The PhloemDocument37 pagesTranslocation in The PhloemDanae ForresterNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument25 pagesTransport in Plantsruthmahase12No ratings yet
- Transport in Plants HandoutDocument5 pagesTransport in Plants HandoutAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Level Transport: Transport in Plants Occurs On Three LevelsDocument5 pagesCellular-Level Transport: Transport in Plants Occurs On Three LevelsTanisha LewisNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 2 NotesDocument80 pagesBiology Form 2 NotesLutern RayNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: K C Meena PGT Biology KV Vikaspuri Ii ShiftDocument24 pagesTransport in Plants: K C Meena PGT Biology KV Vikaspuri Ii ShiftKaviyaNo ratings yet
- Bio F5 C4: Transport in PlantsDocument18 pagesBio F5 C4: Transport in PlantsRuksana AshrufNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Water Absorption: Lecture - 3Document32 pagesMechanism of Water Absorption: Lecture - 3Santhosh SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument4 pagesTransport in PlantsdarielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- Mass Flow - Structure of The PhloemDocument2 pagesMass Flow - Structure of The PhloemMonique NelsonNo ratings yet
- Transportation in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransportation in Plants1445800No ratings yet
- II. Parts of The Plant InvolvedDocument3 pagesII. Parts of The Plant InvolvedJoash Carl DiazenNo ratings yet
- CHP .5.2Document2 pagesCHP .5.2laracassar22No ratings yet
- A Level Transport FinestDocument25 pagesA Level Transport FinestBaguma alexNo ratings yet
- Transport System AutorecoveredDocument8 pagesTransport System Autorecovereduser alohaNo ratings yet
- ch7 NotesDocument6 pagesch7 Notesisabella cucumberNo ratings yet
- 10TH PPT - 2Document22 pages10TH PPT - 2Anshika BhattNo ratings yet
- SJDFKSXDHJFDocument2 pagesSJDFKSXDHJFapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Bio CH3 F4Document20 pagesBio CH3 F4YARSHANA A/P SIVAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Transport in Vascular PlantsDocument23 pagesTransport in Vascular PlantsAnonymous u7cQyr3QYNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsDocument49 pagesBiology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsPeter Osundwa Kiteki100% (3)
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsAbhyudaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9Document7 pagesTopic 9Talia Elan VickeryNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT in PLANTSDocument27 pagesTRANSPORT in PLANTSRish HeeNo ratings yet
- Water Pathway and TranspirationDocument23 pagesWater Pathway and TranspirationZalfa FarukNo ratings yet
- Transportation in PlantsDocument5 pagesTransportation in PlantsMitali PatelNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants IIDocument19 pagesTransport in Plants IIMarko ĆaletaNo ratings yet
- Biology MidtermDocument18 pagesBiology MidtermLeo SukhumvatNo ratings yet
- Bouldering in St. Ives: This Guide Is Available Online As A Free Download atDocument22 pagesBouldering in St. Ives: This Guide Is Available Online As A Free Download atrubanNo ratings yet
- Alpha Particle ScatteringDocument2 pagesAlpha Particle ScatteringrubanNo ratings yet
- Vegan Bodybuilding Meal Plan Bulk VeganioDocument1 pageVegan Bodybuilding Meal Plan Bulk VeganiorubanNo ratings yet
- 01-Magnetic Flux Density For Wires and CoilsDocument1 page01-Magnetic Flux Density For Wires and CoilsrubanNo ratings yet
- 02-Force On A Conductor (Qualitative) 1Document1 page02-Force On A Conductor (Qualitative) 1rubanNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel BlockersDocument2 pagesCalcium Channel BlockersrubanNo ratings yet