Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Central Line
Uploaded by
Chanyut TuranonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Central Line
Uploaded by
Chanyut TuranonCopyright:
Available Formats
Thammasat Medical Journal, Vol. 14 No.
1, January-March 2014
79
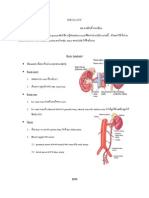
hemodynamics
: , internal jugular, subclavian
:
80
Hemodynamic monitoring ,
.
,
superior vena cava
internal jugular
(internal jugular vein) subclavian
(subclavian vein)
inferior vena cava femoral,
internal jugular subclavian
Internal jugular vein
Subclavian vein
Trendelenburg
Cardiopulmonary
resuscitation (CPR)
(ambulatory)
venous thrombosis
(Anatomy)
internal jugular
subclavian
. internal jugular
internal jugular
jugular foramen anteromedial mastoid
process subclavian
Femoral vein
Congestive heart failure
(CHF)
CPR
lateral head clavicle
medial clavicle
sternal head
clavicular head sternocleidomastoid
carotid
cricoid cartilage, ,
Thammasat Medical Journal, Vol. 14 No. 1, January-March 2014
81
internal jugular
. subclavian
subclavian
axillary
lateral
anterior scalene subclavian
subclavian subclavian
internal jugular
brachiocephalic trunk superior vena
cava
subclavian
thoracic duct subclavian
internal jugular
subclavian
(apex)
subclavian medial anterior scalene
subclavian
subclavian
subclavian
82
internal jugular
subclavian
hematoma
, subclavian
(landmark)
internal
jugular central, anterior
posterior
subclavian
infraclavicular supraclavicular
internal jugular
Central
Anterior
Landmark
medial
sternocleidomastoid
heads
thyroid cartilage
sternocleidomastoid
skin
(Aim toward)
Posterior
lateral
sternocleidomastoid
mastoid process
sternocleidomastoid
Sternal notch
Thammasat Medical Journal, Vol. 14 No. 1, January-March 2014
internal jugular
central approach
83
internal jugular
anterior approach
internal jugular posterior approach
84
subclavian
Infraclavicular approach
Supraclavicular approach
Landmark lateral
midclavicular line
clavicular head
sternocleidomastoid
coronal plane
coronal
bevel
medially and caudally
medially
J-wire
sternal notch
(Aim toward)
sternal head
sternocleidomastoid
subclavian infraclavicular approach
Thammasat Medical Journal, Vol. 14 No. 1, January-March 2014
85
subclavian supraclavicular approach
(Indication), , ,
. (caustic)
. central venous pressure
. pulmonary artery catheter
transvenous pacing
(absolute contraindication), , ,
.
. (thrombosis)
(relative contraindication), , ,
. (coagulopathy)
partial thromboplastin time (PT)
activated thromboplastin time (aPTT) / International
Normalized Ratio (INR)
(platelet)
fresh frozen plasma (FFP)
platelet count ,
, INR .
,
.
(sedation)
peripheral line
.
(deformities) (hematoma)
86
subclavian
anterior
landmark
subclavian
subclavian
internal jugular carotid
atherosclerosis
plaque
stroke
(penetrating injury)
. left bundle branch block
(guidewire) right
ventricle complete heart block
, ,
- Povidone iodine solution chlorhexidine
- sterile
-
-
- 5 ml syringe
- Finder needle ( )
- Introducer needle or catheter over-the-needle
- (guidewire)
-
- sterile
- central venous line
- Dilator
-
- Suture material needle holder
- Normal saline
- dressing
Thammasat Medical Journal, Vol. 14 No. 1, January-March 2014
central line
central line single lumen, multiple lumen
percutaneous sheath multiple lumen
central venous pressure
multiple lumen
lumen
lumen catheter
single lumen
lumen
(French)
percutaneous sheath
pulmonary artery catheter transvenous pacing
wire
(hypotensive hypovolemia), ,
Trendelenburg
internal jugular
air embolism
subclavian
deltoid
ECG pulse oximetry noninvasive
blood pressure monitoring
ventricular ectopy
right ventricle
87
sterile
mask sterile
sterile
landmark
(clavicular area) povidone iodine
chlorhexidine
sterile
(pneumothorax)
portable , , ,
superior vena cava
internal
jugular (internal jugular vein)
subclavian (subclavian vein)
inferior vena cava
femoral,
internal jugular subclavian
internal jugular
central approach
landmark approach
landmark
landmark
approach
ultrasound-guidance
ultrasound central
approach
carotid posterior approach
internal jugular lateral
carotid
variation
internal jugular carotid
approach
ultrasound-guidance
88
internal
jugular central approach, ,
. sterile
.
. flush normal saline
lumen
. finder needle syringe normal
saline negative
pressure
sternocleidomastoid
internal jugular
.
finder needle
. introducer needle syringe
finder needle
carotid medial
lateral
negative pressure
negative pressure
pressure
pressure
medial
. introducer
needle syringe
carotid
syringe
(free flow)
fix
. syringe introducer needle
(needle hub)
air embolism
. (sleeve)
J
. introducer needle
.
ventricular ectopy
. introducer
needle fix
.
Thammasat Medical Journal, Vol. 14 No. 1, January-March 2014
. dilator
. catheter
catheter multiplelumen catheter lumen distal
lumen hub catheter
. catheter
hub
catheter
Peres formular
right atrium proximal
inferior vena cava (IVC)
right subclavian
right internal jugular
left subclavian
left internal jugular
catheter
Right internal jugular
Left internal jugular
Right infraclavicular subclavian
Left infraclavicular subclavian
central venous
H/10
(H/10) + 4
(H/10) - 2
(H/10) + 2
*H =
.
catheter
catheter
. syringe normal saline
catheter
flush
. heparin lock
catheter multiple-lumen catheter
lumen
. fix
silk nylon
89
. sterile
.
superior vena cava
superior vena cava right atrium
subclavian infraclavicular approach,
internal jugular
medial lateral
lateral
medial
bevel introducer
needle (caudal)
coronal plane
suprasternal notch
guide
internal jugular
Seldinger technique
J
superior vena cava
internal jugular
ultrasound guidance
ultrasound guidance
hematoma (hemothorax)
ultrasound probe
internal jugular carotid
echogenic
subclavian color flow
subclavian ,
90
internal jugular
mechanical
mechanical
(thrombotic)
.
colonize hub
lumen hematogenous
seeding catheter The Institute for Healthcare
Improvement
chlorhexidine
mechanical
antiseptic ointment
, ,
. mechanical
mechanical
hematoma
(arrhythmia)
internal jugular subclavian
ultrasound guidance,
(venous thromboembolism)
Internal jugular
Subclavian
Femoral
Pneumothorax (%)
< .
Hemothorax (%)
NA*
Infection
.
(rate per 1,000 catheter-days)
Thrombosis
.
(rate per 1,000 catheter-days)
Arterial puncture (%)
Malposition
*NA = (Not applicable)
. .
. .
NA*
NA*
.
Thammasat Medical Journal, Vol. 14 No. 1, January-March 2014
superior
vena cava inferior vena cava
(atrium)
cardiac tamponade
,
right tracheobronchial angle
hemodynamics
landmark
.
.
.
Hanson CW. Procedures in critical care. New York:
McGraw Hill; 2009.
Feldman R. Central venous access. In: Richman E,
Simon M, editors. Emergency medicine procedure.
United States: McGrawHill; 2002.
Fraenkel DJ, Rickard C, Lipman J. Can we achieve
consensus on central venous catheter-related infections?
Anaesth Intensive Care 2000;28:475-90.
91
. Raad I. Intravascular-catheter-related infections. Lancet
1998;351:893-8.
. Graham AS, Ozment C, Tegtmeyer K, Lai S,
Braner DAV. Central venous catheterization. N Engl J
Med. 2007;356:e21.
. Braner DAV, Lai S, Eman S, Tegtmeyer K. Central
venous catheterization subclavian vein. N Engl J
Med 2007;357:e26.
. Haas B, Chittams JL, Trerotola SO. Large-bore tunneled
central venous catheter insertion in patients with
coagulopathy. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2010;21:212-7.
. Foster PF, Moore LR, Sankary HN, Hart ME, Ashmann
MK, Williams JW. Central venous catheterization in
patients with coagulopathy. Arch Surg 1992;127:273-5.
. Gomella LG, SA H. Bedside procedures. Clinician's
pockets reference: McGraw Hill; 2007.
. Murray MJ. Critical care medicine: perioperative
management. Philadelphia:Lippincott Williams &
Wilkins; 2002.
. Bannon MP, Heller SF, Rivera M. Anatomic
considerations for central venous cannulation. Risk
Manag Healthc Policy 2011;4:27-39.
. Peres PW. Positioning central venous catheters--a
prospective survey. Anaesth Intensive Care 1990;
18:536-9.
. Kim WY, Lee CW, Sohn CH, Seo DW, Yoon JC,
Koh JW, et al. Optimal insertion depth of central
venous catheters--is a formula required? A prospective
cohort study. Injury 2012;43:38-41.
. Ray BR, Mohan VK, Kashyap L, Shende D, Darlong
VM, Pandey RK. Internal jugular vein cannulation: A
comparison of three techniques. J Anaesthesiol Clin
Pharmacol 2013;29:367-71.
. Agarwal A, Singh DK, Singh AP. Ultrasonography: a
novel approach to central venous cannulation. Indian J
Crit Care Med 2009;13:213-6.
92
Abstract
Central venous catheterization
Yajai Apibunyopas
Emergency Department, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University
Central venous catheterization has variety of indications. It is indicated for emergency patients, critical patients and
chronically ill patients. The utilization of central line includes providing route for administration of large volume resuscitation
and caustic agents, and hemodynamics monitoring. Apart from indications, to learn about contraindications, appropriate sites
for placement, preparation, procedure and all possible complications, is very crucial for practitioner. In order to achieve the
maximum benefit and the most safety result from central venous catheterization, one must learn all before attempting to
do the procedure.
Key words: Central venous catheter, Internal jugular vein, Subclavian vein
You might also like
- CPG TraumaDocument10 pagesCPG TraumaChanyut Turanon0% (1)
- บทนำDocument11 pagesบทนำChanyut TuranonNo ratings yet
- 40 UrologyDocument18 pages40 UrologyChanyut TuranonNo ratings yet
- การบริหารยาสำหรับการกู้ชีพขั้นDocument24 pagesการบริหารยาสำหรับการกู้ชีพขั้นChanyut Turanon100% (1)