Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bolt Spec Review
Uploaded by
Anonymous Re62LKaACCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bolt Spec Review
Uploaded by
Anonymous Re62LKaACCopyright:
Available Formats
focus on
RCSC
Bolt Spec Preview
by Tom Schlafly
Changes in the next edition of RCSCs bolting specification clarify some finer points of washer usage.
he Research Council on Structural Connections (RCSC)
recently voted to include several changes in the Specification
for Structural Joints Using ASTM
A325 or A490 Bolts (also known as the
bolt spec). RCSC will issue a revised
document dated June 30, 2004, and AISC
plans to incorporate the revised specification in the next Manual of Steel Construction when it is published in 2005.
While the amendments will not create
major changes to bolted connections,
they will clarify a few key points. One
change simply emphasizes a current
requirement, and several others provide
options to fabricators and erectors when
5
/16 ASTM F436 washers, or hardened
plates/bars are not readily available.
Slip Critical Connection
Clarification
RCSC felt it was necessary to clarify
the requirement that slip critical connections be designed to meet the strength
requirements as shear/bearing joints
(Sections 5.1, 5.2 and 5.3). These requirements are in addition to meeting the slip
resistance requirements in Section 5.4.
The requirement is not a new one, but it
seemed to require additional emphasis.
The shear/bearing limits are checked in
slip critical joints because the joints may
slip at or near the factored load. In some
cases with class B or C faying surfaces,
the shear/bearing strength may be less
than the slip-critical strength. Under
these conditions, the connection must be
designed for the shear/bearing strength.
Meeting these requirements provides the
strength limit reliability for slip critical
joints.
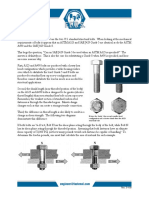
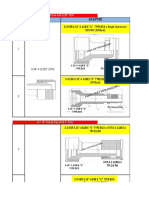
Revised Washer Requirements in
Table 6.1
For many years, the bolt spec has
required washers that are 5/16-thick and
hardened in accordance with ASTM F436
where pretensioned ASTM A490 bolts
greater than 1 diameter are used in
oversized holes or slots in the outer ply.
Similarly, bolted connections with long
slots in the outer ply required 5/16-thick
hardened plate washers or hardened continuous bars. These requirements were in
place because research showed normal
washers deformed under the high loads
generated by tightening ASTM A490
bolts. This, in turn, made achieving the
requisite pretension difficult. The footnotes to the table clearly prohibited the
use of multiple thicknesses of standard
thickness ASTM F436 washers.
While the provision has been in place
for many years, conditions demanding
them are not frequent. Therefore, the
hardened, thick washers and hardened
plates/bars have not always been readily
available. Recognizing the difficulty of
obtaining these washers, the RCSC has
added alternatives to 5/16 hardened
washers, hardened plate washers and
hardened bars. In connections with longslotted holes in the outer ply and using
ASTM A490 bolts, the revised bolt spec
will permit an ASTM F436 washer of
standard thickness with a 3/8 structural
grade plate washer. It will also permit an
ASTM F436 washer with a structural
grade 3/8-thick continuous bar. Connections with oversized or short-slotted
holes in the outer ply using ASTM A490
bolts can now use either ASTM F436
hardened washers 5/16-thick, as before,
or a 3/8-thick plate washer and an ordinary thickness ASTM F436 washer. A
form of the revised table appears below.
Where ASTM A490 bolts are pretensioned in connections and the connected
material has yield strength less than 40
ksi (usually ASTM A36), the existing bolt
spec requires washers under the head
and nut to prevent galling of the connected material. The requirement for the
washer under the head is waived when
twist-off bolts with bearing diameters
under the head equal to or greater than
the diameter of an ASTM F436 washer
are used. Recent research indicates that
this exception is also valid for all twistoff bolts with a bearing circle diameter
meeting the requirements of ASTM
F1852. (Schnupp, K.O., and T.M. Murray,
Table 6.1 Washer Requirements for Bolted Joints with
Oversized and Slotted Holes in the Outer Ply
ASTM Designation
A325 or F1852
Nominal Bolt
Diameter, db,
in.
b
c
d
Oversized
Short-Slotted
>1
Long-Slotted
ASTM F436a
5/16-thick plate
washer or continuous barb, c
ASTM F436 with 5/16 thicknessb, d
ASTM F436
washer with
either a 3/8-thick
structural grade
plate washer or
continuous barb
1
1
A490
Hole Type in Outer Ply
This requirement shall not apply to heads of round head tension-control bolt assemblies meeting the
requirements in Section 2.7 and providing a bearing circle diameter meeting the requirements of ASTM
F1852.
Multiple washers with a combined thickness of 5/16 or larger do not satisfy this requirement.
The plate washer or bar shall be of structural-grade steel material but need not be hardened.
Alternatively, a 3/8-thick plate washer and an ordinary thickness F436 washer may be used. The plate
washer need not be hardened.
October 2004 Modern Steel Construction
Effects of Head Size on the Performance
of Twist-Off Bolts, Virginia Polytechnic
Institute and State University, CC/VTIST 03/09, July 2003.) In other words,
twist-off bolts with the smaller head
diameter may be used without a washer
under the head.
Further changes are under consideration by RCSC, particularly with regard to
slip critical design strength, the use of
bolts with welds, the treatment of thick
fills in slip-critical connections and the
nominal strength of a bolt in shear with
threads included in the shear plane.
RCSCs current revisions to the bolt spec,
however, will not change the number or
size of bolts required in a connection if it
was designed properly using the provisions of the 2000 edition. Nevertheless,
the exception to the washer requirements
may make life a little easier for fabricators and erectors.
Tom Schlafly is director of research for the
American Institute of Steel Construction,
Inc., and is also a member of the RCSC.
October 2004 Modern Steel Construction
You might also like
- Dimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyFrom EverandDimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyNo ratings yet
- Bolt Spec ReviewDocument2 pagesBolt Spec ReviewameensderajNo ratings yet
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataFrom EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Structural Steel BoltsDocument7 pagesStructural Steel BoltsMark OglesbyNo ratings yet
- All-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceFrom EverandAll-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Anchor Bolt and Anchor Base PlateDocument2 pagesAnchor Bolt and Anchor Base PlateHugo Mario Ariza PalacioNo ratings yet
- ASTM F3125 - Six Into OneDocument2 pagesASTM F3125 - Six Into OneDaren NeradNo ratings yet
- Behavior and Design of Trapezoidally Corrugated Web Girders for Bridge Construction: Recent AdvancesFrom EverandBehavior and Design of Trapezoidally Corrugated Web Girders for Bridge Construction: Recent AdvancesNo ratings yet
- Are Washers Required To Be Used With An A325 or A490 Structural Bolt?Document3 pagesAre Washers Required To Be Used With An A325 or A490 Structural Bolt?armydgNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsFrom EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- ASIC Steel Interchange - Shear Flow in Plastic DesignDocument2 pagesASIC Steel Interchange - Shear Flow in Plastic DesignMikeNo ratings yet
- Article - Structural BoltsDocument6 pagesArticle - Structural Boltsing_weroNo ratings yet
- Steel Tips Committee of California Parte 3Document237 pagesSteel Tips Committee of California Parte 3RigobertoGuerraNo ratings yet
- Table 6.1 - Washer RequirementsDocument1 pageTable 6.1 - Washer RequirementsUpadrasta HarishNo ratings yet
- HSS Steel AvailabilityDocument2 pagesHSS Steel Availabilityaams_sNo ratings yet
- 30 Rules For Good Connections.5Document4 pages30 Rules For Good Connections.5chipchipperson100% (1)
- Aashto 167M PDFDocument8 pagesAashto 167M PDFjodasi30No ratings yet
- Studded Outlet HSB News Letter PDFDocument4 pagesStudded Outlet HSB News Letter PDFG.SWAMINo ratings yet
- Scope: General Requirements For Bolted JointsDocument1 pageScope: General Requirements For Bolted Jointsrondana1No ratings yet
- Are You Properly Specifying Materials - Part 3 PDFDocument3 pagesAre You Properly Specifying Materials - Part 3 PDFasmasm123No ratings yet
- A307-14 Standard Specification For Carbon Steel Bolts, Studs, and Threaded Rod 60000 PSI Tensile StrengthDocument6 pagesA307-14 Standard Specification For Carbon Steel Bolts, Studs, and Threaded Rod 60000 PSI Tensile Strengthmasv792512No ratings yet
- ASTM F 432 - 95 Roof and Rock Bolts and AccessoriesDocument15 pagesASTM F 432 - 95 Roof and Rock Bolts and AccessoriesNdoro BeiNo ratings yet
- Revised RCSC Specification-Simplified, Clarified, AndImprovedDocument5 pagesRevised RCSC Specification-Simplified, Clarified, AndImprovedCarlos Javier Goez TarraNo ratings yet
- Astm A307Document6 pagesAstm A307thakrarhits100% (3)
- Structural Design of Reinforcements For Fittings in Factory-Made Corrugated Steel Pipe For Sewers and Other ApplicationsDocument18 pagesStructural Design of Reinforcements For Fittings in Factory-Made Corrugated Steel Pipe For Sewers and Other ApplicationsAleksei AvilaNo ratings yet
- HSS - American Institute of Steel ConstructionDocument4 pagesHSS - American Institute of Steel ConstructionJagatheesh RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Air 5065Document11 pagesAir 5065niky186No ratings yet
- Si 10 2013 PDFDocument2 pagesSi 10 2013 PDFhector diazNo ratings yet
- High-Strength Bolts For Structural Steel Joints (Metric)Document5 pagesHigh-Strength Bolts For Structural Steel Joints (Metric)carlokandiNo ratings yet
- Steel Quiz AnswersDocument2 pagesSteel Quiz AnswerspmjoshirNo ratings yet
- A325 and A490 BoltsDocument9 pagesA325 and A490 BoltsCHECcorp100% (1)
- Standard Specification for Corrugated Steel Structural PlateDocument17 pagesStandard Specification for Corrugated Steel Structural Platejun floresNo ratings yet
- Reinforcing Bar Specifications - tcm45-340903Document3 pagesReinforcing Bar Specifications - tcm45-340903Anonymous vGKYNSPNo ratings yet
- Welding and bolting requirements for structural steelDocument10 pagesWelding and bolting requirements for structural steelIndra SidikNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument2 pagesQuizMamu ToothNo ratings yet
- 30 Good RulesDocument4 pages30 Good RulesSamet Karataş100% (1)
- Detailing Considerations Design Guide 7 - bk745 PDFDocument5 pagesDetailing Considerations Design Guide 7 - bk745 PDFFunkNo ratings yet
- A FEDS Structural BoltsDocument6 pagesA FEDS Structural BoltsCrimsonPoshNo ratings yet
- SANS EN 14399 BOLTING ASSEMBLIESDocument4 pagesSANS EN 14399 BOLTING ASSEMBLIESClaudioDuarteNo ratings yet
- Steel Framing ConnectioDocument21 pagesSteel Framing ConnectioJamesNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Installation, Inspection, MaintenanceDocument23 pagesGuidelines For The Installation, Inspection, MaintenanceantiacidoNo ratings yet
- Steelwise: Are You Properly Specifying Materials?Document9 pagesSteelwise: Are You Properly Specifying Materials?Muhammad AhsunNo ratings yet
- Types of Welding JointDocument6 pagesTypes of Welding JointTesema TeshomeNo ratings yet
- The Use of Serrated Metallic Gaskets On Air CoolersDocument12 pagesThe Use of Serrated Metallic Gaskets On Air Coolerssammar_10No ratings yet
- Selecting and Designing Branch ConnectionsDocument8 pagesSelecting and Designing Branch ConnectionsLorenaNo ratings yet
- Sa 307Document8 pagesSa 307Web LogueandoNo ratings yet
- E9d0' R""o .: Indian StandardDocument26 pagesE9d0' R""o .: Indian Standards_samirkumar1008100% (1)
- ASTM A307-2003 Standard Specification For Carbon Steel Bolts and Studs, 60 000 PSI Tensile StrengthDocument6 pagesASTM A307-2003 Standard Specification For Carbon Steel Bolts and Studs, 60 000 PSI Tensile Strengthmasv792512No ratings yet
- Course Content A) Bolted ConnectionsDocument18 pagesCourse Content A) Bolted Connectionsram894uNo ratings yet
- Revised RCSC Specification-Simplified, Clarified, Andimproved PDFDocument5 pagesRevised RCSC Specification-Simplified, Clarified, Andimproved PDFfarhadmrt6923No ratings yet
- 1993 - 10 Heavy Structural Shapes in Tension ApplicationsDocument6 pages1993 - 10 Heavy Structural Shapes in Tension ApplicationsHenry HoyosNo ratings yet
- Steel Tips Committee of California Parte 3Document237 pagesSteel Tips Committee of California Parte 3MladenMarkovicNo ratings yet
- Astm F 435-03Document6 pagesAstm F 435-03Jorge ToribioNo ratings yet
- Centrifugally Cast (Spun) Iron Pressure Pipes For Water, Gas and Sewage - SpecificationDocument26 pagesCentrifugally Cast (Spun) Iron Pressure Pipes For Water, Gas and Sewage - SpecificationPrapa KaranNo ratings yet
- Astm A-1005Document6 pagesAstm A-1005dennis_ugarteNo ratings yet
- Engineering & Construction Bulletin: Owned Special Provisions Sections 6.03 (Structural Steel) and M.06 (Metals)Document6 pagesEngineering & Construction Bulletin: Owned Special Provisions Sections 6.03 (Structural Steel) and M.06 (Metals)Hector CarreraNo ratings yet
- ASTM BoltsDocument3 pagesASTM BoltsAnonymous IwqK1NlNo ratings yet
- Bondek UWS CompositeBeam ShearConnectionDocument15 pagesBondek UWS CompositeBeam ShearConnectionRada IoanNo ratings yet
- Podešavanje Eq MontažeDocument19 pagesPodešavanje Eq MontažeArmagedon KommtNo ratings yet
- YatesDocument4 pagesYatesAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Week 5 2019Document11 pagesTerm 2 Week 5 2019Anonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Yates Liquid Copper How To ApplyDocument9 pagesYates Liquid Copper How To ApplyAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- c3 Battery Charger DL Broch 2014 Fin HRDocument2 pagesc3 Battery Charger DL Broch 2014 Fin HRAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Visually Similar ResultsDocument2 pagesVisually Similar ResultsAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Equatorial Mount Instruction Manual For Reflector TelescopesDocument3 pagesEquatorial Mount Instruction Manual For Reflector TelescopesAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- c3 Manual Rbau A5 Pp33440 FaDocument8 pagesc3 Manual Rbau A5 Pp33440 FaAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- ComoDocument1 pageComoAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Bass Clef Notes Cheatsheet PDFDocument1 pageFlashcards Bass Clef Notes Cheatsheet PDFAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Golden Dreams-2scan PDFDocument2 pagesGolden Dreams-2scan PDFAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Jaane MaryamDocument2 pagesJaane Maryamhoney80% (5)
- Persian Happy Birthday Sheet MusicDocument1 pagePersian Happy Birthday Sheet MusicAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Lisgar GardensDocument2 pagesLisgar GardensAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Piano 6staff With ClefsDocument1 pagePiano 6staff With ClefsBen HarringtonNo ratings yet
- Middle Harbour Creek LoopDocument5 pagesMiddle Harbour Creek LoopAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Piano - 4 Staff - With ClefsDocument1 pagePiano - 4 Staff - With ClefsAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Bass Clef Notes PDFDocument1 pageFlashcards Bass Clef Notes PDFAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcard Small PDFDocument5 pagesFlashcard Small PDFAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcard Bass Clef Notes v2 Page3Document1 pageFlashcard Bass Clef Notes v2 Page3Anonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcard Treble Clef Notes v2 Page2 PDFDocument1 pageFlashcard Treble Clef Notes v2 Page2 PDFAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcard Treble Clef Notes v2 Page2Document1 pageFlashcard Treble Clef Notes v2 Page2Anonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Treble Clef NotesDocument1 pageFlashcards Treble Clef NotesAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcard Bass Clef Notes v2 Page1Document1 pageFlashcard Bass Clef Notes v2 Page1Anonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Treble Clef Notes PDFDocument1 pageFlashcards Treble Clef Notes PDFAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcard-Big Bass Clef PDFDocument17 pagesFlashcard-Big Bass Clef PDFAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcard Bass Clef Notes v2 Page1 PDFDocument1 pageFlashcard Bass Clef Notes v2 Page1 PDFAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Flashcard-Big Bass ClefDocument17 pagesFlashcard-Big Bass ClefAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Colouring Competition: Name: TeamDocument7 pagesColouring Competition: Name: TeamAnonymous Re62LKaACNo ratings yet
- Brochure DZ20VCDocument6 pagesBrochure DZ20VCDaniNo ratings yet
- Lifting and Handling SolutionsDocument12 pagesLifting and Handling SolutionstarekhocineNo ratings yet
- Technic parts list with missing itemsDocument12 pagesTechnic parts list with missing itemsrlobetNo ratings yet
- Permen Esdm 7Document8 pagesPermen Esdm 7DangolNo ratings yet
- Code Case 2304-2 - Alloy Uns35045Document2 pagesCode Case 2304-2 - Alloy Uns35045uvarajmecheriNo ratings yet
- YMA BrochureDocument9 pagesYMA Brochurenairam2003No ratings yet
- VW NBD Tiguan Allspace R Line Service Pricing GuideDocument1 pageVW NBD Tiguan Allspace R Line Service Pricing GuideNizamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CH 6Document4 pagesTutorial CH 6WinxTynix 8000No ratings yet
- 319 Saf Holland Ball Races BrochureDocument10 pages319 Saf Holland Ball Races BrochureСаша СмоляренкоNo ratings yet
- Steel Pipes (Ashrae) (Schedule 40)Document1 pageSteel Pipes (Ashrae) (Schedule 40)Ahmed SherifNo ratings yet
- Assembly Line: For Automotive Battery ProductionDocument8 pagesAssembly Line: For Automotive Battery ProductionAnonymous q9c7KY1vNo ratings yet
- Rotary Numbering Machine: Operators GuideDocument35 pagesRotary Numbering Machine: Operators GuideZorig IshdoNo ratings yet
- CalcManualGoldEng Dentadas PDFDocument72 pagesCalcManualGoldEng Dentadas PDFGabriel AraujoNo ratings yet
- StackEconomizer CRE-CCE Boiler BookDocument22 pagesStackEconomizer CRE-CCE Boiler BookBorisvukic89No ratings yet
- Mercedes 722 Automatic Transmission Service Manual GuideDocument59 pagesMercedes 722 Automatic Transmission Service Manual GuideNick Speis100% (7)
- Me414 Lecture 4 ShaftDocument14 pagesMe414 Lecture 4 ShaftILEENVIRUSNo ratings yet
- Simple Bending Stress AnalysisDocument14 pagesSimple Bending Stress AnalysisDaniel MukuhaNo ratings yet
- Tep 0066Document7 pagesTep 0066RAMKUMARNo ratings yet
- General Marine EngineeringDocument67 pagesGeneral Marine EngineeringSailorprof100% (3)
- WARTSILA-SG18V34 Manual PDFDocument230 pagesWARTSILA-SG18V34 Manual PDFАндрей ВасильевNo ratings yet
- Method Statement of Chiller Preventive MaintenanceDocument5 pagesMethod Statement of Chiller Preventive MaintenanceBalajiNo ratings yet
- Form Recom Lube TruckDocument2 pagesForm Recom Lube TruckARNo ratings yet
- WorleyParsons Horizontal 2 Phase Separator SizingDocument1 pageWorleyParsons Horizontal 2 Phase Separator SizingDavid Gustavo Duran Tango100% (1)
- Axisymmetric stress function method equationsDocument1 pageAxisymmetric stress function method equationsdskumar49No ratings yet
- VP-PP4-MP-255-PK-1401-0430 - REV.0 - VENDOR DOCUMENT FOR NaOH DOSING PUMPDocument10 pagesVP-PP4-MP-255-PK-1401-0430 - REV.0 - VENDOR DOCUMENT FOR NaOH DOSING PUMPMinh PhamNo ratings yet
- Mathieu Equation (Parametric Oscillator)Document6 pagesMathieu Equation (Parametric Oscillator)Rodrigo Mota AmaranteNo ratings yet
- Comparsion of RCCM & ASMEDocument2 pagesComparsion of RCCM & ASMEsafeer ahmadNo ratings yet
- VG602Document2 pagesVG602LucasNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics: Seminar OnDocument10 pagesSoil Mechanics: Seminar OnTitiksha NegiNo ratings yet
- Wellhead Adapter ListDocument6 pagesWellhead Adapter ListtaufikNo ratings yet
- Collection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsFrom EverandCollection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityFrom EverandThe Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Robotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryFrom EverandRobotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Artificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindFrom EverandArtificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet
- Design and Operation of Human Locomotion SystemsFrom EverandDesign and Operation of Human Locomotion SystemsMarco CecarelliNo ratings yet
- In the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkFrom EverandIn the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityFrom EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.From EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Mastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesFrom EverandMastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!From EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- What to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationFrom EverandWhat to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCFrom EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Create Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandCreate Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceNo ratings yet
- Modeling, Dynamics, and Control of Electrified VehiclesFrom EverandModeling, Dynamics, and Control of Electrified VehiclesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Learning Robotics, with Robotics, by Robotics: Educational RoboticsFrom EverandLearning Robotics, with Robotics, by Robotics: Educational RoboticsNo ratings yet
- Visions Of Technology: A Century Of Vital Debate About Machines Systems AFrom EverandVisions Of Technology: A Century Of Vital Debate About Machines Systems ARating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)