Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G Proteins
Uploaded by
Carmeline Santi Beronilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
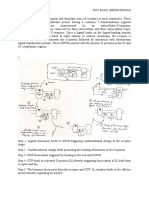
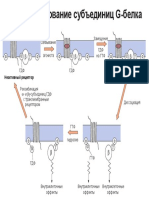
7 views2 pagesWhen a ligand binds to a G-protein coupled receptor, it causes a conformational change in the receptor and attached G-protein. This allows the G-protein's alpha subunit to exchange GDP for GTP, dissociating the alpha subunit from the beta-gamma subunit. Both the alpha and beta-gamma subunits can then interact with intracellular signaling proteins, before GTP is hydrolyzed and the subunits re-associate to terminate signaling.
Original Description:
G Proteins
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWhen a ligand binds to a G-protein coupled receptor, it causes a conformational change in the receptor and attached G-protein. This allows the G-protein's alpha subunit to exchange GDP for GTP, dissociating the alpha subunit from the beta-gamma subunit. Both the alpha and beta-gamma subunits can then interact with intracellular signaling proteins, before GTP is hydrolyzed and the subunits re-associate to terminate signaling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesG Proteins
Uploaded by
Carmeline Santi BeronillaWhen a ligand binds to a G-protein coupled receptor, it causes a conformational change in the receptor and attached G-protein. This allows the G-protein's alpha subunit to exchange GDP for GTP, dissociating the alpha subunit from the beta-gamma subunit. Both the alpha and beta-gamma subunits can then interact with intracellular signaling proteins, before GTP is hydrolyzed and the subunits re-associate to terminate signaling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
G-Protein Activation
1. When not activated, the alpha subunit binds GDP.
2. When the ligand binds to the GPCR, it changes conformation
and, in turn, alters the conformation of the G protein.
3. Altering the conformation of the alpha subunit allows it to
exchange GDP for GTP.
4. The binding of GTP to the alpha subunit results in dissociation
from the beta subunit.
5. These are now two independent entities: the alpha subunit and
the beta-gamma (bg) subunit.
6. GTP binding and dissociation of the bg subunit causes the
alpha subunit to adopt a new conformation enabling it to now
bind to intracellular signaling proteins.
7. The bg subunit does not change conformation, but its
dissociation from the alpha exposes this face of the beta
subunit. It can now also interact with signaling molecules.
8. The cycle is repeated by the hydrolysis of subunit-bound GTP to GDP,
resulting in the re-association of the and subunits.
You might also like
- Annual Plant Reviews, The GibberellinsFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, The GibberellinsPeter HeddenNo ratings yet
- 2 PDFDocument5 pages2 PDFArijit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- ModeofOperationofG ProteincoupledReceptorsDocument2 pagesModeofOperationofG ProteincoupledReceptorsPardeep SonyNo ratings yet
- G Protein Coupled Receptors: Name:-Shaikh Ameeruddin Roll No: - BY3219Document1 pageG Protein Coupled Receptors: Name:-Shaikh Ameeruddin Roll No: - BY3219shaikh ameeruddinNo ratings yet
- GPCR and CAMPDocument5 pagesGPCR and CAMParaneyaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Pathphysiology PT 2Document2 pagesMolecular Pathphysiology PT 2Elisa RoyNo ratings yet
- G-protein receptors overviewDocument18 pagesG-protein receptors overviewLaura RossiNo ratings yet
- G-Protein Coupled Receptors and Their Signaling MechanismDocument21 pagesG-Protein Coupled Receptors and Their Signaling Mechanismaroob9mahamoodaurinNo ratings yet
- Biosignaling 1Document52 pagesBiosignaling 1Javeria DawoodNo ratings yet
- Hilger 2018Document9 pagesHilger 2018احمد صباح مالكNo ratings yet
- Daaka 2012Document9 pagesDaaka 2012iara rocha xavierNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Storage& BreakdownDocument4 pagesCarbohydrate Storage& BreakdownMona DomingoNo ratings yet
- Second Messenger SystemsModDocument49 pagesSecond Messenger SystemsModganotNo ratings yet
- G-protein-Coupled ReceptorsDocument24 pagesG-protein-Coupled ReceptorsNaimi Amalia hatimahNo ratings yet
- Metabotropic: The Second Major Type of Neurotransmitter ReceptorDocument17 pagesMetabotropic: The Second Major Type of Neurotransmitter ReceptorChian WrightNo ratings yet
- Second Messenger Systems: Figs 1.4 1.5Document1 pageSecond Messenger Systems: Figs 1.4 1.5AntonPurpurovNo ratings yet
- Gα-Catalyzed GTP Hydrolysis MechanismDocument25 pagesGα-Catalyzed GTP Hydrolysis MechanismAyberk BinbayNo ratings yet
- CH 17-19 Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesCH 17-19 Learning Objectivespjanu86No ratings yet
- G Protein ReviewDocument17 pagesG Protein ReviewSaray Gordián CastroNo ratings yet
- GPCRs Regulate Physiological FunctionsDocument25 pagesGPCRs Regulate Physiological FunctionsMirza Shaharyar BaigNo ratings yet
- Mech of Action HormonesDocument25 pagesMech of Action HormonesVurla PrabhavathiNo ratings yet
- GPCRDocument2 pagesGPCRanaeshklNo ratings yet
- Arwa Omar Bafail & 439200284: What Are They?Document3 pagesArwa Omar Bafail & 439200284: What Are They?Arwa BafailNo ratings yet
- Pharmacodynamics - Receptors 2016 Membrane ReceptorsDocument25 pagesPharmacodynamics - Receptors 2016 Membrane ReceptorsLilian EdeniNo ratings yet
- 223.21G-Protein Linked Receptors2015Document13 pages223.21G-Protein Linked Receptors2015Abhishek Isaac MathewNo ratings yet
- Cell SignallingDocument37 pagesCell SignallingSreekarWunnava100% (1)
- Sar of BenzodiazepinesDocument3 pagesSar of BenzodiazepinesVISHNU RAJ VNo ratings yet
- Pharm 00 B11Document1 pagePharm 00 B11DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Computational Study On The Different Ligands Induced Conformation Change of b2 Adrenergic Receptor-Gs Protein ComplexDocument10 pagesComputational Study On The Different Ligands Induced Conformation Change of b2 Adrenergic Receptor-Gs Protein ComplexPaul CalbureanNo ratings yet
- With The Name of Allah The Most Gracious and The Most MercifulDocument23 pagesWith The Name of Allah The Most Gracious and The Most MercifulMohammad Noman AkramNo ratings yet
- Exp3 FinalDocument14 pagesExp3 Finalapi-253261856No ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Ion Channels and Cell Signaling ReceptorsDocument10 pagesBiochemistry - Ion Channels and Cell Signaling ReceptorsLejNo ratings yet
- Yoshida2003-Phospho of B-Tubulin by GCPRDocument10 pagesYoshida2003-Phospho of B-Tubulin by GCPR9longerNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Phospholipase C by G Proteins: Bordatella PertussisDocument5 pagesRegulation of Phospholipase C by G Proteins: Bordatella Pertussissant_grNo ratings yet
- Describe The Signalling Pathways Downstream of The Heterotrimeric G Proteins GS, Gi and GQDocument6 pagesDescribe The Signalling Pathways Downstream of The Heterotrimeric G Proteins GS, Gi and GQwavezone113100% (2)
- Biochemistry: Glycogen MetabolismDocument78 pagesBiochemistry: Glycogen MetabolismJoseph YayenNo ratings yet
- 2016 Water Clusters in The Nucleotide-Binding Pocket of The Protein AIF2g From The Archaeon Sulfolobus Solfataricus - Proton TransmissionDocument7 pages2016 Water Clusters in The Nucleotide-Binding Pocket of The Protein AIF2g From The Archaeon Sulfolobus Solfataricus - Proton Transmissionenfermeironilson6321No ratings yet
- Yevenes Et Al 2003 GABA y GlicinaDocument6 pagesYevenes Et Al 2003 GABA y GlicinaJorge ParodiNo ratings yet
- PharmacodynamicsDocument50 pagesPharmacodynamicsMdd AnishNo ratings yet
- Quiz-4-Storage Mechanisms and Control in Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument5 pagesQuiz-4-Storage Mechanisms and Control in Carbohydrate Metabolismaichiii.bearNo ratings yet
- G-Protein Coupled Receptors: Biogenic Amines Amino Acids and Ions: Lipids: Peptides and ProteinsDocument4 pagesG-Protein Coupled Receptors: Biogenic Amines Amino Acids and Ions: Lipids: Peptides and ProteinsPranav NakhateNo ratings yet
- Receptors: Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTK)Document5 pagesReceptors: Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTK)Safiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Cell ProjectDocument2 pagesCell ProjectYazan SalamaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Evals 8 Set GDocument7 pagesBiochem Evals 8 Set GStd Dlshsi0% (1)
- Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology MadrasDocument14 pagesMolecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madrasapi-256504985No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument57 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismYulliza Kurniawaty L100% (1)
- Lesson 4.2. GlycoconjugatesDocument4 pagesLesson 4.2. GlycoconjugatesGemma CabañasNo ratings yet
- Signal Transduction Targets & Receptor TypesDocument46 pagesSignal Transduction Targets & Receptor TypesTanvir FahimNo ratings yet
- Syrovatkina Et Al. - 2016 - Regulation, Signaling, And Physiological FunctionsDocument40 pagesSyrovatkina Et Al. - 2016 - Regulation, Signaling, And Physiological Functionskdh03081995No ratings yet
- Topic Objectives Chapter 15 Biochem Material For EXAM #4Document5 pagesTopic Objectives Chapter 15 Biochem Material For EXAM #4slipper_crazy5335No ratings yet
- JVPT-2012 Vol11Document108 pagesJVPT-2012 Vol11AlphaRaj Mekapogu100% (1)
- Signal Transduction: Biochemistry of MetabolismDocument48 pagesSignal Transduction: Biochemistry of Metabolismarunprakash314No ratings yet
- Signal Transduction and Second Messengers: Karen LounsburyDocument10 pagesSignal Transduction and Second Messengers: Karen LounsburyFranco RoaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chap 14 - Signal Trans Duct IonDocument4 pagesBiochemistry Chap 14 - Signal Trans Duct IonKyle MinorNo ratings yet
- (Amino Acid Residues 76-178)Document8 pages(Amino Acid Residues 76-178)Jessica LauNo ratings yet
- MD ch5Document27 pagesMD ch5malake.a13cj7No ratings yet
- Study Guide for Biol 3090/7800 Final ExamDocument9 pagesStudy Guide for Biol 3090/7800 Final ExamanhminhandnamNo ratings yet
- Molecular Determinants of Glucagon Receptor Signaling: Cecilia G. UnsonDocument18 pagesMolecular Determinants of Glucagon Receptor Signaling: Cecilia G. UnsonLuisa GonzálezNo ratings yet
- G-Protein Coupled ReceptorsDocument8 pagesG-Protein Coupled ReceptorsHyunji KimNo ratings yet
- GLUCONEOGENESISDocument13 pagesGLUCONEOGENESISFrancesca FogliettiNo ratings yet
- Medicine1 Grand PE ScriptDocument10 pagesMedicine1 Grand PE ScriptCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- LyricsDocument2 pagesLyricsCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- Flatulence Diarrhea Abdominal PainDocument2 pagesFlatulence Diarrhea Abdominal PainCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- Histo PointersDocument2 pagesHisto PointersCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- Biochem 2 PDFDocument63 pagesBiochem 2 PDFCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- Versatilefragile Fam TypoDocument2 pagesVersatilefragile Fam TypoCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- Methods and Practices of Urban Filipino Parents in Promoting Mabuting Asal Among Preschool ChildrenDocument26 pagesMethods and Practices of Urban Filipino Parents in Promoting Mabuting Asal Among Preschool ChildrenCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
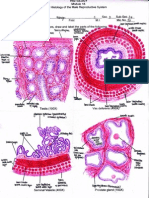
- Qftenh, (W I: Histology of Male, ReproductiveDocument1 pageQftenh, (W I: Histology of Male, ReproductiveCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument16 pagesDigestiveCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- Flatulence Diarrhea Abdominal PainDocument2 pagesFlatulence Diarrhea Abdominal PainCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet