Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indicative Content Definition of Economic Growth (Increases in GDP)
Uploaded by
Kazi MohasinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Indicative Content Definition of Economic Growth (Increases in GDP)
Uploaded by
Kazi MohasinCopyright:
Available Formats
GEE Lecture 2 - Tutorial Q (ANSWER GUIDE)
Indicative content
Definition of economic growth (increases in GDP)
Difference between GDP and GNP - Gross Domestic Product (GDP) shows the value
of the output produced within a country in a given time period. Gross National
Product (GNP) is the market value of all products and produced in one year by labour
and property supplied by the residents of a country. While GNP measures the output
generated by a countrys enterprises (whether located domestically or abroad), GDP
measures the total output produced within a countrys borders (whether produced by
that countrys own local firms or by foreign firms).
Calculation of GDP = C+I+G+X-M Discussion of each component of GDP and how
they affect economic growth
Pro economic growth
o People prefer more goods and services rather than fewer. Provided economic
growth outstrips population growth, it will lead to higher income per head and
higher consumption.
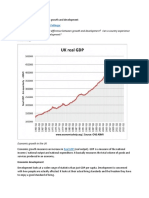
o Using the UK as an example, the poorest families of today are better off than
those of the 19th century as a result of economic growth
o Absolute poverty has been largely eliminated in the UK partly due to the
welfare provisions which have been funded by the proceeds of economic
growth
o Health and living standards continue to improve
o Life expectancy continues to increase as a result of better healthcare facilities
Problems as a result of economic growth
o Social costs of economic growth e.g. congestion, pollution - these may
diminish the quality of life
o Consumption of irreplaceable resources - and dangers associated with
substitutes e.g. nuclear power
o Change in lifestyles and attitudes - complacent, carefree and selfish attitudes
towards life, reliance on the safety net of state benefits and welfare provision.
o Growth may not be fairly distributed - wealth concentrated in the hands of a
small percentage of the population
Mark allocation:
Max 5 marks: Student describes key issues and theories relating to economic growth and its
associated pros and cons.
Max 10 marks: Student applies and/or explains key issues and theories relating to economic growth
and its associated pros and cons.
Max 15marks: Student analyses the key issues and theories relating to economic growth and its
associated pros and cons.
Max 25 marks: Student evaluates the key issues and theories relating to economic growth and its
associated pros and cons.
You might also like
- Economic GrowthDocument7 pagesEconomic GrowthZunaira SafdarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandFundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- DS Lecture Notes For Introduction To DevelopmentDocument11 pagesDS Lecture Notes For Introduction To Developmentchristopher chibuluma100% (1)
- Lecture 1 (ED)Document20 pagesLecture 1 (ED)Nouran EssamNo ratings yet
- Distinguish Economic Growth from Economic DevelopmentDocument7 pagesDistinguish Economic Growth from Economic DevelopmentJoyce KathleenNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Economic Growth and Development ExplainedDocument9 pagesDifference Between Economic Growth and Development ExplainedPrecious NosaNo ratings yet
- Global EconomyDocument7 pagesGlobal EconomyDuyen Pham DieuNo ratings yet
- National Unemployment Rate Rising, Rate of Inflamation FallingDocument8 pagesNational Unemployment Rate Rising, Rate of Inflamation FallingRhea Joy L. SevillaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Economics Revision Notes Economic Growth and Standards of LivingDocument6 pagesGCSE Economics Revision Notes Economic Growth and Standards of LivingNemoSharkyNo ratings yet
- Readers Question: What Is The Difference Between Growth and Development? Can A Country Experience Economic Growth Without Development?Document5 pagesReaders Question: What Is The Difference Between Growth and Development? Can A Country Experience Economic Growth Without Development?abdulNo ratings yet
- ECO 102 NotesDocument76 pagesECO 102 NotesSabira RahmanNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Economic Growth and DevelopmentssDocument5 pagesDifference Between Economic Growth and DevelopmentssabdulNo ratings yet
- GDP As A MeasureDocument16 pagesGDP As A Measurejaganathor100% (1)
- AP Macroeconomics - Chapter 24Document3 pagesAP Macroeconomics - Chapter 24ruchia17No ratings yet
- Chapter: 2 Economic Growth: Limitations of GDP As A Measure of GrowthDocument6 pagesChapter: 2 Economic Growth: Limitations of GDP As A Measure of GrowthAdeeba iqbalNo ratings yet
- Economic Growth & Development StructureDocument33 pagesEconomic Growth & Development Structuremusinguzi francisNo ratings yet
- Economic Growth Economic Development Gross Domestic Product GDP Measuring GDP GDP Measurement in PakistanDocument22 pagesEconomic Growth Economic Development Gross Domestic Product GDP Measuring GDP GDP Measurement in PakistanAwais MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Overview of Macroeconomics - Week01Document20 pagesOverview of Macroeconomics - Week01Dimas Andi DashNo ratings yet
- Difference between growth and developmentDocument4 pagesDifference between growth and developmentabdulNo ratings yet
- The Global Business EnvironmentDocument56 pagesThe Global Business EnvironmentxostudioslriNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Economic Growth and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesDifference Between Economic Growth and DevelopmentfaridkaanNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Economic Development Is The Development of Economic Wealth of CountriesDocument7 pagesEconomic Development Economic Development Is The Development of Economic Wealth of CountriesTamba KendemaNo ratings yet
- Economic Development (Bba)Document9 pagesEconomic Development (Bba)amitsinghbdn0% (1)
- Economic Function of Government - Presentation Transcript: Business-To-Government (B2G) Is A Derivative ofDocument20 pagesEconomic Function of Government - Presentation Transcript: Business-To-Government (B2G) Is A Derivative ofaditibrijptlNo ratings yet
- Question-1: Economic GrowthDocument18 pagesQuestion-1: Economic GrowthRachit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reading Lesson 1Document9 pagesReading Lesson 1AnshumanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3Document10 pagesChapter-3Yasin IsikNo ratings yet
- Eco 316Document36 pagesEco 316Amarin MdNo ratings yet
- Econ2 NotesDocument8 pagesEcon2 NoteshuuihsduidhuiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Measurement of Economic DevelopmentDocument9 pagesModule 4 Measurement of Economic DevelopmentkianamaefaigmaniNo ratings yet
- Economic Growth Factors That Drive GDP and Living StandardsDocument29 pagesEconomic Growth Factors That Drive GDP and Living StandardsAnkita MalikNo ratings yet
- Economic Growth and DevelopmentDocument16 pagesEconomic Growth and DevelopmentShahrukhKhanNo ratings yet
- Economic Growth and DevelopmentDocument17 pagesEconomic Growth and DevelopmentSachin Methree100% (1)
- CH - 13, 14 and 15 (Solved Booklet Page)Document14 pagesCH - 13, 14 and 15 (Solved Booklet Page)Rumana AliNo ratings yet
- EconDocument11 pagesEconh5d4dg4xptNo ratings yet
- Macro 9 - Economic GrowthDocument4 pagesMacro 9 - Economic GrowthGene'sNo ratings yet
- Ecf340 - Economics of DevelopmentDocument42 pagesEcf340 - Economics of DevelopmentDario KabangaNo ratings yet
- Economic GrowthDocument5 pagesEconomic GrowthMay Fleur MayaoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Measuring National IncomeDocument16 pages3.1 Measuring National IncomeAlex AshkarNo ratings yet
- Social Change Comprehensive ReportDocument43 pagesSocial Change Comprehensive ReportGoldie AnnNo ratings yet
- Content Notes 1 (H1) SC - Introduction To Macro (Aims & Indicators)Document8 pagesContent Notes 1 (H1) SC - Introduction To Macro (Aims & Indicators)David LimNo ratings yet
- Economic Growth and Economic DevelopmentDocument7 pagesEconomic Growth and Economic DevelopmentArundhuti RoyNo ratings yet
- Hawassa University: Information Technology 2 Year Section 1 Course Title: EconomicsDocument7 pagesHawassa University: Information Technology 2 Year Section 1 Course Title: EconomicsDuresa GemechuNo ratings yet
- Unemploy Men 1Document3 pagesUnemploy Men 1Mikhaela MacrohonNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Economics + Legal Topic NotesDocument25 pagesYear 10 Economics + Legal Topic NotesAndrea CATANZARITINo ratings yet
- EPMP Principles of Macroeconomics Lecture 3 2020-21-2Document33 pagesEPMP Principles of Macroeconomics Lecture 3 2020-21-2Bilson KwameNo ratings yet
- Umer Mid EcoDocument4 pagesUmer Mid EcoMalik NoraizNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument129 pagesNational IncomeBabli PattanaikNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledGillenne Ashley CaragayNo ratings yet
- Economics Today 17th Edition Roger Leroy Miller Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesEconomics Today 17th Edition Roger Leroy Miller Solutions Manualedwardleonw10100% (28)
- Macroeconomics: Resource Market Resource MarketDocument4 pagesMacroeconomics: Resource Market Resource MarketArnab BaruaNo ratings yet
- 1 Week01 - Overview of MacroeconomicsDocument20 pages1 Week01 - Overview of MacroeconomicsAhmad Ayis AydinNo ratings yet
- Macro Unit 2 6EC02 Revision Notes 2011Document58 pagesMacro Unit 2 6EC02 Revision Notes 2011TheMagicCarpetNo ratings yet
- Geo 10 Unit 4Document4 pagesGeo 10 Unit 4tameratNo ratings yet
- Backup of Economic Readings SummaryDocument21 pagesBackup of Economic Readings Summarybenicebronzwaer0No ratings yet
- Economic Growth and Development Edited NotesDocument16 pagesEconomic Growth and Development Edited Notesvincentmdala19No ratings yet
- What is the difference between economic growth and developmentDocument19 pagesWhat is the difference between economic growth and developmentsdsdawoodNo ratings yet
- Economic Growth and Development PTTDocument76 pagesEconomic Growth and Development PTTRekik TeferaNo ratings yet
- AQA Economics WB2 Answers 2020Document74 pagesAQA Economics WB2 Answers 2020ekenenwokedi59No ratings yet
- Excel Ninja Shortcuts GuideDocument20 pagesExcel Ninja Shortcuts Guidegasman2003No ratings yet
- 458 FullDocument2 pages458 FullKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- Go Mpers and Lerner 2001Document25 pagesGo Mpers and Lerner 2001Kazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- Excel VBA and Excel MacrosDocument29 pagesExcel VBA and Excel MacrosKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- Tech Data Business AnalystDocument1 pageTech Data Business AnalystKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- Miralago Orbita PresentationDocument6 pagesMiralago Orbita PresentationKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- 1 Problem Set 1Document6 pages1 Problem Set 1Kazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- Amendment No. 8 To Registration Statement On Form S-1Document225 pagesAmendment No. 8 To Registration Statement On Form S-1Kazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- ExportDocument1 pageExportKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- DAF Syllabus 2016-2017 PDFDocument2 pagesDAF Syllabus 2016-2017 PDFKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- IkeaDocument17 pagesIkeaKazi Mohasin100% (1)
- People Place Electronics Device Music/ Movies/books/story Food Cloth Animal CarDocument1 pagePeople Place Electronics Device Music/ Movies/books/story Food Cloth Animal CarKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- American Finance Association Article Examines Relationship Between Leasing and DebtDocument12 pagesAmerican Finance Association Article Examines Relationship Between Leasing and DebtKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- 1 Corporate Financial Planing Ch1 2Document96 pages1 Corporate Financial Planing Ch1 2Kazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- 700 StrategiesDocument2 pages700 StrategiesAbhishek2009GWUNo ratings yet
- 6 Month GRE Study Plan For Math Beginners - Magoosh GRE BlogDocument73 pages6 Month GRE Study Plan For Math Beginners - Magoosh GRE BlogKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- 700 StrategiesDocument2 pages700 StrategiesAbhishek2009GWUNo ratings yet
- University of Central Florida Usa: Case Western Reserve University Usa Bennett S. Lebow College of Business UsaDocument3 pagesUniversity of Central Florida Usa: Case Western Reserve University Usa Bennett S. Lebow College of Business UsaKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- MyDocument7 pagesMyKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- 6 Month GRE Study Plan For Math Beginners - Magoosh GRE BlogDocument73 pages6 Month GRE Study Plan For Math Beginners - Magoosh GRE BlogKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- Research Project Proposal For UploadingDocument16 pagesResearch Project Proposal For UploadingKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- Critique of Business ResearchDocument13 pagesCritique of Business ResearchKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- CADocument1 pageCAKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- CADocument1 pageCAKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- 54Document2 pages54Kazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- E NNVBDocument8 pagesE NNVBKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- Jaita HobeDocument1 pageJaita HobeKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- Don't Just Read This Essay Once. Spend Some Time Analysing ItDocument1 pageDon't Just Read This Essay Once. Spend Some Time Analysing ItKazi MohasinNo ratings yet
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The 5 Second Rule: Transform your Life, Work, and Confidence with Everyday CourageFrom EverandThe 5 Second Rule: Transform your Life, Work, and Confidence with Everyday CourageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- The Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeFrom EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- No Bad Parts: Healing Trauma and Restoring Wholeness with the Internal Family Systems ModelFrom EverandNo Bad Parts: Healing Trauma and Restoring Wholeness with the Internal Family Systems ModelRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Eat That Frog!: 21 Great Ways to Stop Procrastinating and Get More Done in Less TimeFrom EverandEat That Frog!: 21 Great Ways to Stop Procrastinating and Get More Done in Less TimeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3224)
- Uptime: A Practical Guide to Personal Productivity and WellbeingFrom EverandUptime: A Practical Guide to Personal Productivity and WellbeingNo ratings yet
- Growth Mindset: 7 Secrets to Destroy Your Fixed Mindset and Tap into Your Psychology of Success with Self Discipline, Emotional Intelligence and Self ConfidenceFrom EverandGrowth Mindset: 7 Secrets to Destroy Your Fixed Mindset and Tap into Your Psychology of Success with Self Discipline, Emotional Intelligence and Self ConfidenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (561)
- Quantum Success: 7 Essential Laws for a Thriving, Joyful, and Prosperous Relationship with Work and MoneyFrom EverandQuantum Success: 7 Essential Laws for a Thriving, Joyful, and Prosperous Relationship with Work and MoneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (38)
- Indistractable: How to Control Your Attention and Choose Your LifeFrom EverandIndistractable: How to Control Your Attention and Choose Your LifeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Summary of Atomic Habits: An Easy and Proven Way to Build Good Habits and Break Bad Ones by James ClearFrom EverandSummary of Atomic Habits: An Easy and Proven Way to Build Good Habits and Break Bad Ones by James ClearRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (557)
- Get to the Point!: Sharpen Your Message and Make Your Words MatterFrom EverandGet to the Point!: Sharpen Your Message and Make Your Words MatterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (280)
- The Secret of The Science of Getting Rich: Change Your Beliefs About Success and Money to Create The Life You WantFrom EverandThe Secret of The Science of Getting Rich: Change Your Beliefs About Success and Money to Create The Life You WantRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Own Your Past Change Your Future: A Not-So-Complicated Approach to Relationships, Mental Health & WellnessFrom EverandOwn Your Past Change Your Future: A Not-So-Complicated Approach to Relationships, Mental Health & WellnessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (85)
- The One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsFrom EverandThe One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (708)
- The High 5 Habit: Take Control of Your Life with One Simple HabitFrom EverandThe High 5 Habit: Take Control of Your Life with One Simple HabitRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think Faster, Talk Smarter: How to Speak Successfully When You're Put on the SpotFrom EverandThink Faster, Talk Smarter: How to Speak Successfully When You're Put on the SpotRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Hidden Potential: The Science of Achieving Greater Things By Adam Grant: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Hidden Potential: The Science of Achieving Greater Things By Adam Grant: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Seeing What Others Don't: The Remarkable Ways We Gain InsightsFrom EverandSeeing What Others Don't: The Remarkable Ways We Gain InsightsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (288)
- Joy on Demand: The Art of Discovering the Happiness WithinFrom EverandJoy on Demand: The Art of Discovering the Happiness WithinRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (19)
- Spark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessFrom EverandSpark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (130)
- Coach Builder: How to Turn Your Expertise Into a Profitable Coaching CareerFrom EverandCoach Builder: How to Turn Your Expertise Into a Profitable Coaching CareerRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think Faster, Talk Smarter: How to Speak Successfully When You're Put on the SpotFrom EverandThink Faster, Talk Smarter: How to Speak Successfully When You're Put on the SpotRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (55)
- Napoleon Hill's Keys to Positive Thinking: 10 Steps to Health, Wealth, and SuccessFrom EverandNapoleon Hill's Keys to Positive Thinking: 10 Steps to Health, Wealth, and SuccessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (306)
- How to Be Better at Almost Everything: Learn Anything Quickly, Stack Your Skills, DominateFrom EverandHow to Be Better at Almost Everything: Learn Anything Quickly, Stack Your Skills, DominateRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (857)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1872)
- A History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationFrom EverandA History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)