Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Possible Prices Over A Specified Period of Time
Uploaded by
Alli Whitener0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pageThe document discusses key concepts in economics including the institutions of the market, specialization, and demand and supply. It outlines the main institutions that facilitate market exchange as private property, freedom of enterprise, competition, and limited government. It describes how specialization allows producers to focus on goods where they have a comparative advantage. Finally, it defines demand as the amount consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices over time and notes that demand and price are inversely related, while demand can shift due to factors like tastes, income, and expectations.
Original Description:
boo
Original Title
Notes 2-5-2013
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses key concepts in economics including the institutions of the market, specialization, and demand and supply. It outlines the main institutions that facilitate market exchange as private property, freedom of enterprise, competition, and limited government. It describes how specialization allows producers to focus on goods where they have a comparative advantage. Finally, it defines demand as the amount consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices over time and notes that demand and price are inversely related, while demand can shift due to factors like tastes, income, and expectations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views1 pagePossible Prices Over A Specified Period of Time
Uploaded by
Alli WhitenerThe document discusses key concepts in economics including the institutions of the market, specialization, and demand and supply. It outlines the main institutions that facilitate market exchange as private property, freedom of enterprise, competition, and limited government. It describes how specialization allows producers to focus on goods where they have a comparative advantage. Finally, it defines demand as the amount consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices over time and notes that demand and price are inversely related, while demand can shift due to factors like tastes, income, and expectations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Institutions of the Market:
Private property
Freedom of enterprise
Freedom of choice
Competition
Specialization
Use of money
Limited government
Money facilitates trades when wants do not coincide.
Look @ the circular flow diagram in Figure 2.2 in the textbook. (hydraulic diagram)
Specialization:
-
To have comparative advantage is to be able to produce something at a lower
opportunity cost than something else.
- In a two-good world, fi one producer has a comparative advantage in one
good, the other producer has a comparative advantage in the other.
Specialization is the concentration of productive effort in goods in which the
producer has comparative advantage.
To benefit from specialization requires the existence of trade.
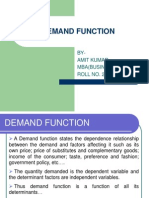
C. 3: Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
Demand is the amount that consumers are willing and able to buy at a series of
possible prices over a specified period of time.
Ceteris Paribus: price and quantity demanded are inversely related. If something
costs more, then less quantity is demanded. Vice Versa.
Income effect means that if price falls, purchasing power increases; like an
increase in income.
Substitution effect means that buyer will substitute more into good if its price
falls.
Change in demand is caused by change in determinant of demand (demand
shifter)
Demand shifters are tastes, number of buyers, income, price of related
goods, expectations
You might also like
- Summary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleFrom EverandSummary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleNo ratings yet
- Surplus Happens When The Quantity Supplied Is Less Than The Quantity DemandedDocument12 pagesSurplus Happens When The Quantity Supplied Is Less Than The Quantity DemandedJannah GasangueNo ratings yet
- Demand Curve Slope Is DownwardDocument10 pagesDemand Curve Slope Is DownwardIram TahiraNo ratings yet
- Eco 211 Topic 3 The Price TheoryDocument25 pagesEco 211 Topic 3 The Price TheoryA KimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Demand and SupplyDocument21 pagesLecture 2 Demand and SupplyMoo-usa BaoNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics (Midterm 1ST Week)Document4 pagesApplied Economics (Midterm 1ST Week)Amor A. Fuentecilla Jr.No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Economics Today The Micro View 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Economics Today The Micro View 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFirisybarrous100% (10)
- Unit-2 Me Demand and SupplyDocument15 pagesUnit-2 Me Demand and Supplydhruvsanghvi040No ratings yet
- Unit:-2 By:-Manoj Kumar GautamDocument78 pagesUnit:-2 By:-Manoj Kumar GautamPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Demand NotesDocument10 pagesDemand Notessara.chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Module App-Econ 03Document8 pagesModule App-Econ 03Ashley TobatsNo ratings yet
- ME 1st Sem by ASRDocument16 pagesME 1st Sem by ASRsubbuNo ratings yet
- Maria Khalid BS (Hons) 3 Semester Section B Economics Assignment: Demand Dated: 23 October 2013Document4 pagesMaria Khalid BS (Hons) 3 Semester Section B Economics Assignment: Demand Dated: 23 October 2013Huzaifah Bin SaeedNo ratings yet
- What Is Demand?Document4 pagesWhat Is Demand?Ravi Prakash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Demand FunctionDocument18 pagesDemand FunctionAmit Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandDocument17 pagesChapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandFarNo ratings yet
- Economics Today The Micro View 19th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesEconomics Today The Micro View 19th Edition Miller Solutions ManualJasonMcculloughfboj100% (48)
- Demand AnalysisDocument15 pagesDemand AnalysisPraveenaNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand: University of Cebu Lapu Lapu and MandaueDocument20 pagesSupply and Demand: University of Cebu Lapu Lapu and MandaueMeljorin LayeseNo ratings yet
- Opportunity CostDocument7 pagesOpportunity CostMayankJhaNo ratings yet
- ISC Exam Notes: Content: Demand and Law of DemandDocument6 pagesISC Exam Notes: Content: Demand and Law of DemandTamasha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- IB Economics Microeconomics NotesDocument26 pagesIB Economics Microeconomics NotesRiddhima SinhaNo ratings yet
- BISK BEC - Chapter 50 Economic TheoryDocument49 pagesBISK BEC - Chapter 50 Economic TheorymyspamoneNo ratings yet
- Aliyah A Ali ECON120 CRN 2028 Individual AssignmentDocument25 pagesAliyah A Ali ECON120 CRN 2028 Individual AssignmentAliyah AliNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument99 pagesDemand and SupplySOOMA OSMANNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 EconomicsDocument80 pagesUnit - 2 EconomicsMohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Demand and Supply and The Market EquilibriumDocument10 pagesLesson 3: Demand and Supply and The Market EquilibriumApril Joy DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Theory of Demand and SupplyDocument46 pagesTheory of Demand and SupplyPrajeshChandra PandeyNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lec MacroeconomicsDocument8 pagesWeek 1 Lec MacroeconomicsCrystal Sheerah S. GarciaNo ratings yet
- SECTION 3a Concept of A MarketDocument15 pagesSECTION 3a Concept of A MarketNeikelle CummingsNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Ii: Demand and SupplyDocument74 pagesManagerial Economics: Ii: Demand and Supplykewani negashNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument42 pagesDemand and SupplykirwanicholasNo ratings yet
- Chap 05Document16 pagesChap 05Syed Hamdan0% (2)
- Module 2Document11 pagesModule 2thelmaNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument8 pagesDemandabNo ratings yet
- Demand AnalysisDocument42 pagesDemand AnalysisTejas PatilNo ratings yet
- Mba 0042Document4 pagesMba 0042Ashish YadavNo ratings yet
- Law of Demand & Elasticity of Demand: Foundation Economics Bimtech June 2008Document16 pagesLaw of Demand & Elasticity of Demand: Foundation Economics Bimtech June 2008PrashantNo ratings yet
- Economics ProjectDocument11 pagesEconomics ProjectKeertana MuraliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2vinit sahooNo ratings yet
- Me - Unit 2Document20 pagesMe - Unit 2Lalitha KonduriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Ten Principles of Economics Chapter 2: Thinking Like An EconomistDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Ten Principles of Economics Chapter 2: Thinking Like An EconomistMAPNo ratings yet
- Application of Demand and SupplyDocument25 pagesApplication of Demand and SupplyThriztan Andrei BaluyutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Application of Supply and DemandDocument4 pagesChapter 2 - Application of Supply and Demandleah_may6No ratings yet
- Recuenco, Ass4, Basic MacroeconomicsDocument3 pagesRecuenco, Ass4, Basic Macroeconomicskyle RecuencoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four 4. Demand and Demand Forecasting: 4.1 Definition of Market DemandDocument16 pagesChapter Four 4. Demand and Demand Forecasting: 4.1 Definition of Market DemandKaleab EnyewNo ratings yet
- +2 Commerce Economics Notes Chapter Demand and Law of DemandDocument8 pages+2 Commerce Economics Notes Chapter Demand and Law of DemandBerryNo ratings yet
- TOPIC TWO-DD and SSDocument20 pagesTOPIC TWO-DD and SS444 geminiNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 EconomicsDocument34 pagesUnit-2 Economicsrakshit konchadaNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics Awais BakshyDocument10 pagesMicro Economics Awais BakshyAwais BakshyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledCKEC-CSE IVNo ratings yet
- Micro 2 - Demand and SupplyDocument13 pagesMicro 2 - Demand and SupplyNelson Toh100% (3)
- Lecture-3, Topic-Demand, Chapter 3-Demand and SupplyDocument19 pagesLecture-3, Topic-Demand, Chapter 3-Demand and Supplyrashiqul rijveNo ratings yet
- Economy Study Material - 636Document12 pagesEconomy Study Material - 636PARAMITA DUTTANo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document14 pagesChapter 13dongsara2006No ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour and Utility MaximizationDocument8 pagesConsumer Behaviour and Utility MaximizationJagmohan KalsiNo ratings yet
- Vi Mô True False V1Document10 pagesVi Mô True False V1minhhieu034No ratings yet
- Applied EconomicsDocument3 pagesApplied EconomicsShaB TorresNo ratings yet
- Unit III - Demand AnalysisDocument52 pagesUnit III - Demand AnalysisAmita GandhiNo ratings yet
- 2017 WVMEA Conference Honor Show Choir ApplicationDocument1 page2017 WVMEA Conference Honor Show Choir ApplicationAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Protocals For HallwayDocument1 pagePioneer Protocals For HallwayAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Protocals For ClassroomDocument1 pagePioneer Protocals For ClassroomAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- On The 1st Day, God Said, "Let There Be Light."Document1 pageOn The 1st Day, God Said, "Let There Be Light."Alli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Pioneer ProtocalsDocument1 pagePioneer ProtocalsAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Creation Day 1Document1 pageCreation Day 1Alli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Clinical Intern Rehearsal Observation Form: University of Dayton Department of MusicDocument5 pagesClinical Intern Rehearsal Observation Form: University of Dayton Department of MusicAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- pp2-129847Document20 pagespp2-129847Alli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Appendix 004Document5 pagesAppendix 004Alli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Concert EtiquetteDocument2 pagesConcert EtiquetteAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- ELA Mid-Term EvaluationDocument5 pagesELA Mid-Term EvaluationAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Health Supplemental Evaluation LiveTextDocument6 pagesHealth Supplemental Evaluation LiveTextAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- 3126380Document10 pages3126380Alli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Prelude and EnergicoDocument1 pagePrelude and EnergicoAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Band Method Book DissertationDocument213 pagesBand Method Book DissertationAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Welcome Back Pikeview Panthers!!: Choir & General Music Pikeview Middle SchoolDocument1 pageWelcome Back Pikeview Panthers!!: Choir & General Music Pikeview Middle SchoolAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet
- Practice SetDocument39 pagesPractice SetAlli WhitenerNo ratings yet