Professional Documents
Culture Documents
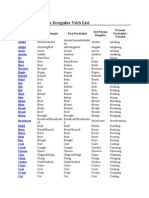
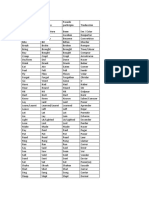
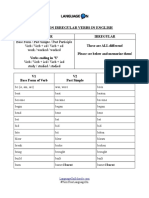
List of English Irregular Verbs
Uploaded by
Kiky Risxy AmeliaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
List of English Irregular Verbs
Uploaded by
Kiky Risxy AmeliaCopyright:
Available Formats
Home > Reference > Irregular Verbs
List of English Irregular Verbs
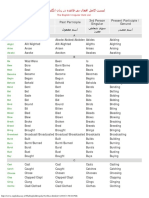
A list of 211 common English irregular verbs, including their base form, past
simple, past participle, 3rd person singular, and the present participle / gerund. Click
on a verb to view extended information about it.
Note: The full list of 620 irregular verbs, including 409 extra verbs, is only available to
members. Sign up for your free account now!
Common English Irregular Verb List
Search:
Search
Base Form
Past Simple
Past Participle
3rd Person
Singular
Present
Participle /
Gerund
Abide
Abode/Abided
Abode/Abided/Abidden
Abides
Abiding
Alight
Alit/Alighted
Alit/Alighted
Alights
Alighting
Arise
Arose
Arisen
Arises
Arising
Awake
Awoke
Awoken
Awakes
Awaking
Be
Was/Were
Been
Is
Being
Bear
Bore
Born/Borne
Bears
Bearing
Beat
Beat
Beaten
Beats
Beating
Become
Became
Become
Becomes
Becoming
Begin
Began
Begun
Begins
Beginning
Behold
Beheld
Beheld
Beholds
Beholding
Bend
Bent
Bent
Bends
Bending
Bet
Bet
Bet
Bets
Betting
Bid
Bade
Bidden
Bids
Bidding
Bid
Bid
Bid
Bids
Bidding
Bind
Bound
Bound
Binds
Binding
Bite
Bit
Bitten
Bites
Biting
Bleed
Bled
Bled
Bleeds
Bleeding
Blow
Blew
Blown
Blows
Blowing
Break
Broke
Broken
Breaks
Breaking
Breed
Bred
Bred
Breeds
Breeding
Bring
Brought
Brought
Brings
Bringing
Broadcast/Broadcasted
Broadcasts
Broadcasting
Broadcast
Broadcast/Broadcaste
d
Build
Built
Built
Builds
Building
Burn
Burnt/Burned
Burnt/Burned
Burns
Burning
Burst
Burst
Burst
Bursts
Bursting
Bust
Bust
Bust
Busts
Busting
Buy
Bought
Bought
Buys
Buying
Cast
Cast
Cast
Casts
Casting
Catch
Caught
Caught
Catches
Catching
Choose
Chose
Chosen
Chooses
Choosing
Clap
Clapped/Clapt
Clapped/Clapt
Claps
Clapping
Cling
Clung
Clung
Clings
Clinging
Clothe
Clad/Clothed
Clad/Clothed
Clothes
Clothing
Come
Came
Come
Comes
Coming
Cost
Cost
Cost
Costs
Costing
Creep
Crept
Crept
Creeps
Creeping
Cut
Cut
Cut
Cuts
Cutting
Dare
Dared/Durst
Dared
Dares
Daring
Deal
Dealt
Dealt
Deals
Dealing
Dig
Dug
Dug
Digs
Digging
Dive
Dived/Dove
Dived
Dives
Diving
Do
Did
Done
Does
Doing
Draw
Drew
Drawn
Draws
Drawing
Dream
Dreamt/Dreamed
Dreamt/Dreamed
Dreams
Dreaming
Drink
Drank
Drunk
Drinks
Drinking
Drive
Drove
Driven
Drives
Driving
Dwell
Dwelt
Dwelt
Dwells
Dwelling
Eat
Ate
Eaten
Eats
Eating
Fall
Fell
Fallen
Falls
Falling
Feed
Fed
Fed
Feeds
Feeding
Feel
Felt
Felt
Feels
Feeling
Fight
Fought
Fought
Fights
Fighting
Find
Found
Found
Finds
Finding
Fit
Fit/Fitted
Fit/Fitted
Fits
Fitting
Flee
Fled
Fled
Flees
Fleeing
Fling
Flung
Flung
Flings
Flinging
Fly
Flew
Flown
Flies
Flying
Forbid
Forbade/Forbad
Forbidden
Forbids
Forbidding
Forecast
Forecast/Forecasted
Forecast/Forecasted
Forecasts
Forecasting
Foresee
Foresaw
Foreseen
Foresees
Foreseeing
Foretell
Foretold
Foretold
Foretells
Foretelling
Forget
Forgot
Forgotten
Forgets
Foregetting
Forgive
Forgave
Forgiven
Forgives
Forgiving
Forsake
Forsook
Forsaken
Forsakes
Forsaking
Freeze
Froze
Frozen
Freezes
Freezing
Frostbite
Frostbit
Frostbitten
Frostbites
Frostbiting
Get
Got
Got/Gotten
Gets
Getting
Give
Gave
Given
Gives
Giving
Go
Went
Gone/Been
Goes
Going
Grind
Ground
Ground
Grinds
Grinding
Grow
Grew
Grown
Grows
Growing
Handwrite
Handwrote
Handwritten
Handwrites
Handwriting
Hang
Hung/Hanged
Hung/Hanged
Hangs
Hanging
Have
Had
Had
Has
Having
Hear
Heard
Heard
Hears
Hearing
Hide
Hid
Hidden
Hides
Hiding
Hit
Hit
Hit
Hits
Hitting
Hold
Held
Held
Holds
Holding
Hurt
Hurt
Hurt
Hurts
Hurting
Inlay
Inlaid
Inlaid
Inlays
Inlaying
Input
Input/Inputted
Input/Inputted
Inputs
Inputting
Interlay
Interlaid
Interlaid
Interlays
Interlaying
Keep
Kept
Kept
Keeps
Keeping
Kneel
Knelt/Kneeled
Knelt/Kneeled
Kneels
Kneeling
Knit
Knit/Knitted
Knit/Knitted
Knits
Knitting
Know
Knew
Known
Knows
Knowing
Lay
Laid
Laid
Lays
laying
Lead
Led
Led
Leads
Leading
Lean
Leant/Leaned
Leant/Leaned
Leans
Leaning
Leap
Leapt/Leaped
Leapt/Leaped
Leaps
Leaping
Learn
Learnt/Learned
Learnt/Learned
Learns
Learning
Leave
Left
Left
Leaves
Leaving
Lend
Lent
Lent
Lends
Lending
Let
Let
Let
Lets
Letting
Lie
Lay
Lain
Lies
Lying
Light
Lit
Lit
Lights
Lighting
Lose
Lost
Lost
Loses
Losing
Make
Made
Made
Makes
Making
Mean
Meant
Meant
Means
Meaning
Meet
Met
Met
Meets
Meeting
Melt
Melted
Molten/Melted
Melts
Melting
Mislead
Misled
Misled
Misleads
Misleading
Mistake
Mistook
Mistaken
Mistakes
Mistaking
Misunderstand
Misunderstood
Misunderstood
Misunderstands
Misunderstanding
Miswed
Miswed/Miswedded
Miswed/Miswedded
Misweds
Miswedding
Mow
Mowed
Mown
Mows
Mowing
Overdraw
Overdrew
Overdrawn
Overdraws
Overdrawing
Overhear
Overheard
Overheard
Overhears
Overhearing
Overtake
Overtook
Overtaken
Overtakes
Overtaking
Pay
Paid
Paid
Pays
Paying
Preset
Preset
Preset
Presets
Presetting
Prove
Proved
Proven/Proved
Proves
Proving
Put
Put
Put
Puts
Putting
Quit
Quit
Quit
Quits
Quitting
Re-prove
Re-proved
Re-proven/Re-proved
Re-proves
Re-proving
Read
Read
Read
Reads
Reading
Rid
Rid/Ridded
Rid/Ridded
Rids
Ridding
Ride
Rode
Ridden
Rides
Riding
Ring
Rang
Rung
Rings
Ringing
Rise
Rose
Risen
Rises
Rising
Rive
Rived
Riven/Rived
Rives
Riving
Run
Ran
Run
Runs
Running
Saw
Sawed
Sawn/Sawed
Saws
Sawing
Say
Said
Said
Says
Saying
See
Saw
Seen
Sees
Seeing
Seek
Sought
Sought
Seeks
Seeking
Sell
Sold
Sold
Sells
Selling
Send
Sent
Sent
Sends
Sending
Set
Set
Set
Sets
Setting
Sew
Sewed
Sewn/Sewed
Sews
Sewing
Shake
Shook
Shaken
Shakes
Shaking
Shave
Shaved
Shaven/Shaved
Shaves
Shaving
Shear
Shore/Sheared
Shorn/Sheared
Shears
Shearing
Shed
Shed
Shed
Sheds
Shedding
Shine
Shone
Shone
Shines
Shining
Shoe
Shod
Shod
Shoes
Shoeing
Shoot
Shot
Shot
Shoots
Shooting
Show
Showed
Shown
Shows
Showing
Shrink
Shrank
Shrunk
Shrinks
Shrinking
Shut
Shut
Shut
Shuts
Shutting
Sing
Sang
Sung
Sings
Singing
Sink
Sank
Sunk
Sinks
Sinking
Sit
Sat
Sat
Sits
Sitting
Slay
Slew
Slain
Slays
Slaying
Sleep
Slept
Slept
Sleeps
Sleeping
Slide
Slid
Slid/Slidden
Slides
Sliding
Sling
Slung
Slung
Slings
Slinging
Slink
Slunk
Slunk
Slinks
Slinking
Slit
Slit
Slit
Slits
Slitting
Smell
Smelt/Smelled
Smelt/Smelled
Smells
Smelling
Sneak
Sneaked/Snuck
Sneaked/Snuck
Sneaks
Sneaking
Soothsay
Soothsaid
Soothsaid
Soothsays
Soothsaying
Sow
Sowed
Sown
Sows
Sowing
Speak
Spoke
Spoken
Speaks
Speaking
Speed
Sped/Speeded
Sped/Speeded
Speeds
Speeding
Spell
Spelt/Spelled
Spelt/Spelled
Spells
Spelling
Spend
Spent
Spent
Spends
Spending
Spill
Spilt/Spilled
Spilt/Spilled
Spills
Spilling
Spin
Span/Spun
Spun
Spins
Spinning
Spit
Spat/Spit
Spat/Spit
Spits
Spitting
Split
Split
Split
Splits
Splitting
Spoil
Spoilt/Spoiled
Spoilt/Spoiled
Spoils
Spoiling
Spread
Spread
Spread
Spreads
Spreading
Spring
Sprang
Sprung
Springs
Springing
Stand
Stood
Stood
Stands
Standing
Steal
Stole
Stolen
Steals
Stealing
Stick
Stuck
Stuck
Sticks
Sticking
Sting
Stung
Stung
Stings
Stinging
Stink
Stank
Stunk
Stinks
Stinking
Stride
Strode/Strided
Stridden
Strides
Striding
Strike
Struck
Struck/Stricken
Strikes
Striking
String
Strung
Strung
Strings
Stringing
Strip
Stript/Stripped
Stript/Stripped
Strips
Stripping
Strive
Strove
Striven
Strives
Striving
Sublet
Sublet
Sublet
Sublets
Subletting
Sunburn
Sunburned/Sunburnt
Sunburned/Sunburnt
Sunburns
Sunburning
Swear
Swore
Sworn
Swears
Swearing
Sweat
Sweat/Sweated
Sweat/Sweated
Sweats
Sweating
Sweep
Swept/Sweeped
Swept/Sweeped
Sweeps
Sweeping
Swell
Swelled
Swollen
Swells
Swelling
Swim
Swam
Swum
Swims
Swimming
Swing
Swung
Swung
Swings
Swinging
Take
Took
Taken
Takes
Taking
Teach
Taught
Taught
Teaches
Teaching
Tear
Tore
Torn
Tears
Tearing
Tell
Told
Told
Tells
Telling
Think
Thought
Thought
Thinks
Thinking
Thrive
Throve/Thrived
Thriven/Thrived
Thrives
Thriving
Throw
Threw
Thrown
Throws
Throwing
Thrust
Thrust
Thrust
Thrusts
Thrusting
Tread
Trod
Trodden
Treads
Treading
Undergo
Underwent
Undergone
Undergoes
Undergoing
Understand
Understood
Understood
Understands
Understanding
Undertake
Undertook
Undertaken
Undertakes
Undertaking
Upset
Upset
Upset
Upsets
Upsetting
Vex
Vext/Vexed
Vext/Vexed
Vexes
Vexing
Wake
Woke
Woken
Wakes
Waking
Wear
Wore
Worn
Wears
Wearing
Weave
Wove
Woven
Weaves
Weaving
Wed
Wed/Wedded
Wed/Wedded
Weds
Wedding
Weep
Wept
Wept
Weeps
Weeping
Wend
Wended/Went
Wended/Went
Wends
Wending
Wet
Wet/Wetted
Wet/Wetted
Wets
Wetting
Win
Won
Won
Wins
Winning
Wind
Wound
Wound
Winds
Winding
Withdraw
Withdrew
Withdrawn
Withdraws
Withdrawing
Withhold
Withheld
Withheld
Withholds
Withholding
Withstand
Withstood
Withstood
Withstands
Withstanding
Wring
Wrung
Wrung
Wrings
Wringing
Write
Wrote
Written
Writes
Writing
Zinc
Zinced/Zincked
Zinced/Zincked
Zincs/Zincks
Zincking
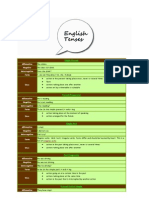
1. Simple Past Tense
Simple Past Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau peristiwa yang
telah terjadi pada waktu lampau dan tidak ada hubungannya dengan masa sekarang.
Rumus :
( + ) S + V2
( - ) S + did not + V1
( ? ) Did + S + V1
Example :
( + ) I went to Campus yesterday.
(Saya pergi ke Kampus kemarin.)
( - ) I did not go to Campus yesterday.
(Saya tidak pergi ke Kampus kemarin.)
( ? ) Did you go to Campus yesterday?
(Apakah kamu pergi ke Kampus kemarin?)
2. Past Continuous Tense
Past Continuous Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau peristiwa
yang sedang beralangsung pada waktu lampau ketika kejadian lain terjadi.
Rumus :
( + ) S + was/were + Ving
( - ) S + was/were + not + Ving
( ? ) Was/were + S + Ving
Example :
( + ) I was listening to radio when the telephone rang
(Saya sedang mengdengarkan radio ketika telepon berbunyi.)
( - ) I wasnt watching TV when you phoned me.
(Saya tidak sedang menonton TV ketika anda menelpon saya.)
( ? ) Were you Watching TV when I called you?
(Apakah kamu sedang menonton TV ketika saya menelpon kamu?)
3. Past Perfect Tense
Past Perfect Tense digunakan untuk menerangkan suatu perbuatan atau peristiwa yang
sudah selesai dilakukan pada waktu lampau.
Rumus :
( + ) S + had + V3
( - ) S + had + not + V3
( ? ) Had + S + V3
Example :
( + ) I had gone when He arrived at my Home.
(Saya pergi ketika dia tiba di rumah saya.)
( - ) She hadnt been at home.
(Dia tidak ada di rumah.)
( ? ) Had you studied English when your father come here?
(Apakah kamu telah belajar Bahasa Inggris ketika ayahmu ke sini?)
4. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Perfect Continuous Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau
peristiwa yang sudah dimulai pada waktu lampau dan masih berlangsung terus hingga
pada waktu yang lampau pula.
Rumus :
( + ) S + had + been + Ving
( - ) S + had + not + been + Ving
( ? ) Had + S + been + Ving
Example :
( + ) He had been living in here before he moved to Semarang.
(Dia telah tinggal di sini, sebelum dia pindah ke Semarang.)
( - ) They had not been sleeping until I can me to meet him.
(Mereke belum sedang tidur hingga saya menemui mereka.)
( ? ) Had she been finishing her duty before her leader inspected it?
(Apakah dia sudah menyelesaikan tugas-tugasnya sebelum pimpinannya
memeriksanya?)
5. Simple Present Tense
Simple Present Tense adalah suatu bentuk kalimat yang menyatakan suatu perbuatan
atau peristiwa yang terjadi pada saat sekarang atau kejadian yang merupakan
kebiasaan sehari-hari.
Rumus :
( + ) S + V1 (s/es)
( - ) S + do/does + not + V1
( ? ) Do/does + S + V1
Example :
( + ) I drink coffee.
(Saya minum kopi.)
( - ) I dont coffee
(Saya tidak minum kopi.)
( ? ) Do you drink coffee?
(Apakah kamu minum kopi?)
6. Present Continuous Tense
Present Continuous Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau peristiwa
yang sedang berlangsung atau sedang dikerjakan, dan belum selesai di waktu
sekarang.
Rumus :
( + ) S + to be + Ving
( - ) S + to be + not + Ving
( ? ) to be + S + Ving
Example :
( + ) I am waiting a letter now
(Saya sedang menulis surat sekarang.)
( - ) They are not speaking English
(Mereka tidak sedang berbicara Bahasa Inggris.)
( ? ) Is he watching TV now?
(Apakah dia sedang nonton TV sekarang?)
7. Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tenses digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau
persitiwa yang sedang terjadi pada waktu lampau dan masih ada hubungannya dengan
saat sekarang.
Rumus :
( + ) S + have/has + V3
( - ) S + have/has + Not + V3
( ? ) Have/has + S + V3
Example :
( + ) He has lived there for two years ago.
(Dia telah tinggal di sana selama dua tahun.)
( - ) They havent come here yet.
(Mereka belum datang kemari.)
( ? ) Have you eaten your brea?
(Apakah kamu sudah makan rotimu?)
8. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau
peristiwa yang dimulai dari waktu lampau dan masin terus berlangsung hingga waktu
sekarang
Rumus :
( + ) S + have/has + been + Ving
( - ) S + have/has + not + been + Ving
( ? ) Have/has + S been + Ving
Example :
( + ) I have been studying English for over nine years.
(Saya telah belajar bahasa inggris selama lebih dari Sembilan tahun.)
( - ) They havent been swimming since January .
(Mereka belum berenang lagi sejak bulan January.)
( ? ) Has she been studying English for two year?
(Apakah dia teleh mempelajari bahsa Inggris selama dua tahun?)
9. Future Tense
Future Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau peristiwa yang terjadi
atau dilakukan pada waktu yang akan datang. Ciri penandanya misalnya terdapat kata
tomorrow, next month, next year, next saturday, dan sebagainya.
Rumus :
( + ) S + will + V1
( - ) S + will + not + V1
( ? ) Will + S + V1
Example :
( + ) I will do to Jakarta next week.
(Saya akan ke Jakarta minggu depan.)
( - ) They will not sail to the sea.
(Mereka tidak akan berlayar ke lautan.)
( ? ) What will she do then?
(Apa yang akan dia lakukan selanjutnya?)
10. Future Continuous Tense
Future Continuous Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau peristiwa
yang akan sedang terjadi pada waktu yang akan datang
Rumus :
( + ) S + will + be + Ving
( - ) S + will + not + be + Ving
( ? ) Will + S + be + Ving
Example :
( + ) My mother will be teaching math at oclock next week.
(Ibu saya akan (sedang) mengajar matematika jam delapan minggu depan.)
( - ) We shall not be working at 7 p.m.
(Kita tidak akan (sedang) bekerja pada jam tujuh malam besok.)
( ? ) Will you be going out if she comes here to night?
(Akan Anda akan (sedang) keluar, jika dia datang ke sini nanti malam?)
11. Future Perfect Tense
Future Perfect Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau peristiwa
yang sudah dimulai pada waktu lampau dan segera selesai pada waktu yang akan
datang.
Rumus :
( + ) S + will + have + V3
( - ) S + will + not have + V3
( ? ) Will + S + have + V3
Example :
( + ) She will have been at home.
(Dia akan telah berada di rumah.)
( - ) The wild cat will not have been here for a year by next month.
(Kucing liar itu belum akan sudah di sini selama setahun setahun menjelang bulan ini.)
( ? ) Will you have been a doctor by next year?
(Akan Anda sudah menjado dokter tahun depan?)
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Future Perfect Continuous Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau
peristiwa yang sudah dimulai pada waktu lapau tetapi mungkin akan berlangsung pada
waktu yang berlainan di masa mendatang.
Rumus :
( + ) S + will + have + been + Ving
( - ) S + will + not + have + been + Ving
( ? ) Will + S + have + been + Ving
Example :
( + ) By next new year I shall have been teaching at this SMU for three years.
(Menjelang tahun baru mendatang, (berarti) tiga tahun saya mengajar di SMU ini.)
( - ) I shall not have been staying here for five years by the end by month.
(Saya belum akan sudah tinggal di sini selama lima tahun menjelang akhir bulan ini.)
( ? ) Will she have been leaving the town for two years by end of this year?
(Apakah kamu akan sudah meninggalkan kota ini menjelang akhir tahun ini?)
13. Past Future Tense
Past Future Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbutan atau peristiwa yang
akan terjadi pada waktu lampau.
Rumus :
( + ) S + should/would + V1
( - ) S + should/would + not + V1
( ? ) should/would + S + V1
Example :
( + ) I would be there the week before.
(Saya mestinya berada di sana minggu sebelumnya.)
( - ) I should not give money if you to my shop.
(Saya tidak akan member uang jika kau datang ke tokoku.)
( ? ) Would he buy a shoes last month ?
(Akankan ia membeli sepatu bulan lalu?)
14. Past Future Continuous Tense
Past Future Continuous Tenses ialah bentuk waktu untuk menyatakan perbuatan atau
peristiwa yang akan sedang dilaksanakan dimasa lampau.
Rumus :
( + ) S + would + be + Ving
( - ) S + would + not + be + Ving
( ? ) Would + S + be + Ving
Example :
( + ) I should be beginning an examination at this time following day.
(Saya akan sedang memulai ujian pada jam ini di hari berikutnya.)
( - ) We couldnt be playing at six oclock yesterday moorning.
(Pukul enam kemarin pagi kita tidak akan sedang bermain.)
( ? ) Would you be playing a chess at three oclock yesterday?
(Apakah kamu akan sedang bermain catur pada jam tiga kemarin?)
15. Past Future Perfect Tense
Past Future Perfect Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan atau peristiwa
yang akan sudah selasai pada waktu lampau atau menyatakan pengandaian yang tidak
mungkin terjadi karena syaratnya sudah pasti tidak akan terpenuhi.
Rumus :
( + ) S + would + have + V3
( - ) S + would + not + have + be + V3
( ? ) Would + S + have + V3
Example :
( + ) I should have been at home if you had invited me
(Saya akan sudah berada di rumah jika kamu telah mengundanku.)
( - ) He would not have graduated if he hadnt studied hard.
(Dia tidak akan lulus seandainya dia tidak belajar dengan giat.)
( ? ) Would your aunt have wedded with my uncle if my father had been agreed?
(Apakah bibimu akan sudah menikah dengan pamanku, seandainya ayahku sudah
menyetujuinya?)
16. Past Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Past Future Perfect Continuous Tense digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu perbuatan
atau peristiwa yang akan sudah sedang akan berlangsung pada waktu lampau.
Rumus :
( + ) S + would + have + been + Ving
( - ) S + would + not + have + been + Ving
( ? ) Would + S + have + been + Ving
Example :
( + ) We should have been teaching English at SMP for three years by the end of last
year.
(Kami akan sudah sedang mengajar bahasa inggris di SMP selama tiga tahun menjelang
tahun lalu.)
( - ) You would not have been studying mathematics for two month, by the end of
lastmonth
(Kamu belum akan sudah belajar matematika selama dua bulan menjelang akhir bulan
lalu.)
( ? ) Would they have been waiting for me for three hours by Last Sunday?
(Apakah mereka akan sudah sedang menungguku selama tiga jam menjelang
hariminggu lalu?)
You might also like
- Irregular Verb Forms PDFDocument5 pagesIrregular Verb Forms PDFKoteswaraRao Bandla100% (2)
- Drow Dictionary PDFDocument25 pagesDrow Dictionary PDFDavid WhaleyNo ratings yet
- 70 Common Irregular Verbs: Pre-Intermediate Learners: Verb (Infinitive) Past Simple Form Past ParticipleDocument4 pages70 Common Irregular Verbs: Pre-Intermediate Learners: Verb (Infinitive) Past Simple Form Past Participlejanansaya100% (1)
- لیست کامل افعال بی قاعده در زبان انگلیسی PDFDocument6 pagesلیست کامل افعال بی قاعده در زبان انگلیسی PDFm_seyedNo ratings yet
- English Irregular VerbsDocument15 pagesEnglish Irregular VerbsChico JuniorNo ratings yet
- Affirmative Negative Interrogative Form: Simple PresentDocument4 pagesAffirmative Negative Interrogative Form: Simple PresentIvana PlenčaNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs ListDocument2 pagesIrregular Verbs ListingewscNo ratings yet
- The Prespresent Perfect ActivitiesDocument8 pagesThe Prespresent Perfect ActivitiesBarba MintaNo ratings yet
- Common English Irregular Verb ListDocument7 pagesCommon English Irregular Verb ListIwanttolearnbritish English100% (1)
- Learn Irregular Verbs EffectivelyDocument4 pagesLearn Irregular Verbs EffectivelyPolyna Polina100% (1)
- English Grammar, Learn English Verbs, Learn English Verb Forms, Verb List, FormDocument6 pagesEnglish Grammar, Learn English Verbs, Learn English Verb Forms, Verb List, FormAshish Singh0% (1)
- List of Past Participle PDFDocument3 pagesList of Past Participle PDFali100% (2)
- Easy Learning English Spelling: Your essential guide to accurate EnglishFrom EverandEasy Learning English Spelling: Your essential guide to accurate EnglishRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- 300 Verbos en Ingles.Document13 pages300 Verbos en Ingles.andreaNo ratings yet
- Ticket To EnglishDocument333 pagesTicket To EnglishLahcen Ayoub79% (306)
- Demonstration Lesson Plan in English, Second Quarter: Columbus Elementary SchoolDocument16 pagesDemonstration Lesson Plan in English, Second Quarter: Columbus Elementary SchoolBENITO LUMANAONo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple+exercisesDocument20 pagesPresent Perfect Simple+exercisesroxxi89No ratings yet
- Essential Grammar in Use 4th Edition by R. Murphy-Páginas-243-244Document2 pagesEssential Grammar in Use 4th Edition by R. Murphy-Páginas-243-244BrunaNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verb ListDocument10 pagesIrregular Verb ListIbnu HaritsahNo ratings yet
- Verbos Irregulares en InglésDocument8 pagesVerbos Irregulares en Inglésparedes1818No ratings yet
- Irregular Verb ListDocument4 pagesIrregular Verb ListBesimNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verb ListDocument5 pagesIrregular Verb ListNandu BoseNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Irregulares Del InglesDocument8 pagesLista de Verbos Irregulares Del Inglesmuseo_comunitarioNo ratings yet
- Abide: Base Form Past Simple Past Participle 3rd Person Singular Present Participle / GerundDocument10 pagesAbide: Base Form Past Simple Past Participle 3rd Person Singular Present Participle / GerundDarundiyo Pandupitoyo, S. Sos.No ratings yet
- English Irregular Verbs - Using EnglishDocument7 pagesEnglish Irregular Verbs - Using EnglishDavid SebastianNo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument7 pagesIrregular VerbsDiego RochaNo ratings yet
- Common English Irregular Verb ListDocument7 pagesCommon English Irregular Verb ListJuliana DNo ratings yet
- Liste Verbes Irreguliers AnglaisDocument6 pagesListe Verbes Irreguliers AnglaisAladin IjijrNo ratings yet
- List of Irregular VerbsDocument5 pagesList of Irregular VerbsSun SunthaNo ratings yet
- Extended Irregular Verbs ListDocument25 pagesExtended Irregular Verbs ListminsandiNo ratings yet
- Abide: Base Form Past Simple Past Participle 3rd Person Singular Present Participle / GerundDocument16 pagesAbide: Base Form Past Simple Past Participle 3rd Person Singular Present Participle / GerundCYti WaWaNo ratings yet
- English Irregular Verbs - UsingEnglishDocument7 pagesEnglish Irregular Verbs - UsingEnglishdai_anef100% (1)
- Abide Alight Arise Awake Be Bear Beat Become Begin Behold Bend Bet Bid Bid Bind Bite Bleed Blow Break Breed BringDocument10 pagesAbide Alight Arise Awake Be Bear Beat Become Begin Behold Bend Bet Bid Bid Bind Bite Bleed Blow Break Breed BringShan KhingNo ratings yet
- Verbos Irregulares/Irregular Verbs (A-B)Document1 pageVerbos Irregulares/Irregular Verbs (A-B)naomysayenNo ratings yet
- Base Form Simple Past Past ParticipleDocument4 pagesBase Form Simple Past Past Participleben harold cortesNo ratings yet
- Hay 158 Verbos Irregulares en La Base de DatosDocument7 pagesHay 158 Verbos Irregulares en La Base de DatosDavid PortilloNo ratings yet
- Regular Dan IrregularDocument3 pagesRegular Dan Irregularاحمداولى النهىNo ratings yet
- First, I Had Abode To Yerson's 10 Grade B. Lista de Verbos Irregulares Del InglesDocument2 pagesFirst, I Had Abode To Yerson's 10 Grade B. Lista de Verbos Irregulares Del InglesJenny RinconNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.inggris TalaDocument8 pagesTugas B.inggris TalaTamara Anindhya PutriNo ratings yet
- Irregular - Verbs - List For University StudentsDocument14 pagesIrregular - Verbs - List For University Studentstxepa232No ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument7 pagesIrregular VerbsSyifaa' NajibNo ratings yet
- Evres Common Irregular VerbsDocument3 pagesEvres Common Irregular VerbsCristina DanNo ratings yet
- List of Irregular Verbs Ab-Do: Base Form - Past Simple - Past ParticipleDocument1 pageList of Irregular Verbs Ab-Do: Base Form - Past Simple - Past ParticipleDragana AnticNo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument6 pagesIrregular VerbsVinoth SenthilNo ratings yet
- Irregular and Regular VerbsDocument13 pagesIrregular and Regular VerbsHyoyeon MagandaNo ratings yet
- Common Irregular Verb List Present Participle / GerundDocument4 pagesCommon Irregular Verb List Present Participle / GerundCristianGaunaNo ratings yet
- Prepositions ListDocument4 pagesPrepositions ListAlec MonteroNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary in EnglishDocument8 pagesVocabulary in EnglishalexNo ratings yet
- Common English Irregular Verb List: Base Form Past Simple Past Participle 3rd Person Singular Present Participle / GerundDocument5 pagesCommon English Irregular Verb List: Base Form Past Simple Past Participle 3rd Person Singular Present Participle / GerundAdelinaHocaNo ratings yet
- Aprende para Siempre Los 148 Verbos Irregulares Más Usados Y Espectacularmente Útiles Del InglésDocument5 pagesAprende para Siempre Los 148 Verbos Irregulares Más Usados Y Espectacularmente Útiles Del Inglésresurrectionem6No ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs List FullDocument5 pagesIrregular Verbs List FullAle QuiliNo ratings yet
- Roots, Bases and StemsDocument25 pagesRoots, Bases and Stemsjana ahmedNo ratings yet
- Verbs IrregularDocument8 pagesVerbs IrregularTun LinNo ratings yet
- Lista de Los Verbos Irregulares en InglésDocument4 pagesLista de Los Verbos Irregulares en InglésgonzalosanferNo ratings yet
- Verbos Irregulares EN InglesDocument4 pagesVerbos Irregulares EN InglesPatricia Salazar HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Base Form Simple Paste Past Participle Meaning Base Form Simple Paste Past Participle MeaningDocument1 pageBase Form Simple Paste Past Participle Meaning Base Form Simple Paste Past Participle MeaningKevin CuéllarNo ratings yet
- IrregularesDocument4 pagesIrregularesidania machadoNo ratings yet
- List of English Irregular VerbsDocument6 pagesList of English Irregular VerbsAthalia ThaliaNo ratings yet
- Reg.-Irreg Verbs PDFDocument39 pagesReg.-Irreg Verbs PDFFredy Carrasco VillalbaNo ratings yet
- Irregular and Regular VerbsDocument3 pagesIrregular and Regular VerbsJackie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- List of English Irregular VerbsDocument6 pagesList of English Irregular VerbsWagner L MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Verbas Irregulares: Infinitivo Pasado Simple Participio PasadoDocument6 pagesVerbas Irregulares: Infinitivo Pasado Simple Participio PasadoAndrés FrancoNo ratings yet
- Simple Past FormsDocument14 pagesSimple Past FormsWillian SerpasNo ratings yet
- Lista Verbelor Neregulate in Limba EnglezaDocument3 pagesLista Verbelor Neregulate in Limba EnglezaAlexandra Osiceanu MaiducNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verb ListDocument4 pagesIrregular Verb ListJayson TayabanNo ratings yet
- Verbos IrregularesDocument14 pagesVerbos IrregularesPaola Olvera SolisNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs List: Base Form Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument2 pagesIrregular Verbs List: Base Form Past Simple Past ParticipleMarcelo FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Aprende Todo Sobre Los Verbos Irregulares en Inglés ConDocument5 pagesAprende Todo Sobre Los Verbos Irregulares en Inglés ConJosé RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Lista de Los Verbos Irregulares en InglésDocument23 pagesLista de Los Verbos Irregulares en InglésRAFAEL TORTOSANo ratings yet
- DOSSIER First Intermediate B1Document60 pagesDOSSIER First Intermediate B1Agustin Vega LobatoNo ratings yet
- English For Business: Unit 1: CompaniesDocument17 pagesEnglish For Business: Unit 1: CompaniesDevan BoyesNo ratings yet
- Concept Map The-Past-Simple ADocument10 pagesConcept Map The-Past-Simple AjuankylaflakNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense PDFDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect Tense PDFDebojani BorahNo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument6 pagesIrregular VerbsNelaNo ratings yet
- Give 10 Irregular Verbs Write Their Past Tense and Past Perticiple of The Verbs - Google SearchDocument1 pageGive 10 Irregular Verbs Write Their Past Tense and Past Perticiple of The Verbs - Google SearchMiacyrine MercadoNo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbsDocument6 pagesIrregular VerbsVinoth SenthilNo ratings yet
- Institucion Tecnologica Colegio Mayor de Bolivar Itcmb: The Past TenseDocument9 pagesInstitucion Tecnologica Colegio Mayor de Bolivar Itcmb: The Past TenseAusencia SentimentalNo ratings yet
- Language On Schools - English Irregular Verbs List PDFDocument5 pagesLanguage On Schools - English Irregular Verbs List PDFLarissa Costa da MataNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs TestDocument10 pagesIrregular Verbs TestsilviaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - LanguageDocument17 pagesUnit 4 - LanguageMai Thị Bích LợiNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs Bingo 1Document4 pagesIrregular Verbs Bingo 1Natalia KravtsivNo ratings yet
- Lista de Verbos Irregulares Mas UsadosDocument9 pagesLista de Verbos Irregulares Mas UsadosAnonymous 0rDFlZN8ANo ratings yet
- L4 Book v0203Document62 pagesL4 Book v0203angel cervantesNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs 1 - LösungenDocument4 pagesIrregular Verbs 1 - Lösungenсергей кабакNo ratings yet
- FEG04 Chapter 02 RevDocument83 pagesFEG04 Chapter 02 Revjavicho2006No ratings yet
- Simple Past Vs Present Perfect WorksheetDocument6 pagesSimple Past Vs Present Perfect WorksheetSantos MateusNo ratings yet
- 15questions in The Present PerfectDocument9 pages15questions in The Present PerfectCristian González ChávezNo ratings yet
- Review of English Tenses: Affirmative Negative Interrogative FormDocument4 pagesReview of English Tenses: Affirmative Negative Interrogative FormSujeevan TharmakulasingamNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs: Begin Began Begun EmpezarDocument4 pagesIrregular Verbs: Begin Began Begun EmpezarGOMEZ ROJAS PENELOPENo ratings yet