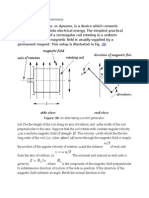
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Telecommunications
Uploaded by
Try Lang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pagetelecom2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenttelecom2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageTelecommunications
Uploaded by
Try Langtelecom2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Telecommunication occurs when the exchange of information between two entities
(communication) includes the use of technology. Communication technology uses channels to
transmit information (as electrical signals), either over a physical medium (such as signal
cables), or in the form of electromagnetic waves.[1][2][3][4][5][6] The word is often used in its plural
form, telecommunications, because it involves many different technologies.
Early means of communicating over a distance included visual signals, such as beacons, smoke
signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs.[7] Other examples of premodern long-distance communication included audio messages such as coded drumbeats, lungblown horns, and loud whistles. Modern technologies for long-distance communication usually
involve electrical and electromagnetic technologies, such as telegraph, telephone, and teleprinter,
networks, radio, microwave transmission, fiber optics, and communications satellites.
A revolution in wireless communication began in the first decade of the 20th century with the
pioneering developments in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the Nobel
Prize in Physics in 1909. Other highly notable pioneering inventors and developers in the field of
electrical and electronic telecommunications include Charles Wheatstone and Samuel Morse
(telegraph), Alexander Graham Bell (telephone), Edwin Armstrong, and Lee de Forest (radio), as
well as John Logie Baird and Philo Farnsworth (television).
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- A Thyristor Is A SolidDocument1 pageA Thyristor Is A SolidTry LangNo ratings yet
- Analog Signals Digital Signals Analog Communication Digital CommunicationDocument1 pageAnalog Signals Digital Signals Analog Communication Digital CommunicationTry LangNo ratings yet
- A Basic Telecommunication System Consists of Three Primary Units That Are Always Present in Some FormDocument1 pageA Basic Telecommunication System Consists of Three Primary Units That Are Always Present in Some FormTry LangNo ratings yet
- N-Type P-Type: Structure On The Physical and Electronic Level, and The Thyristor SymbolDocument1 pageN-Type P-Type: Structure On The Physical and Electronic Level, and The Thyristor SymbolTry LangNo ratings yet
- Figure 38: An Alternating Current GeneratorDocument1 pageFigure 38: An Alternating Current GeneratorTry LangNo ratings yet
- Analog CircuitsDocument1 pageAnalog CircuitsTry LangNo ratings yet
- Electronics Is The Science of How To Control Electric Energy2Document1 pageElectronics Is The Science of How To Control Electric Energy2Try LangNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Mobile Phone Cellular NetworkDocument1 pageStructure of The Mobile Phone Cellular NetworkTry LangNo ratings yet
- Cellular Handover in Mobile Phone NetworksDocument1 pageCellular Handover in Mobile Phone NetworksTry LangNo ratings yet
- Free Space Path Loss Basics: Signal 1 Distance 2Document2 pagesFree Space Path Loss Basics: Signal 1 Distance 2Try LangNo ratings yet
- Cell Signal Encoding: Frequency Division Multiple Access Code Division Multiple AccessDocument1 pageCell Signal Encoding: Frequency Division Multiple Access Code Division Multiple AccessTry LangNo ratings yet
- Free Space Path Loss FormulaDocument1 pageFree Space Path Loss FormulaTry LangNo ratings yet
- Movement From Cell To Cell and HandoverDocument1 pageMovement From Cell To Cell and HandoverTry LangNo ratings yet
- Directional Antennas: Cellular Telephone Frequency Reuse Pattern. SeeDocument1 pageDirectional Antennas: Cellular Telephone Frequency Reuse Pattern. SeeTry LangNo ratings yet
- Broadcast Messages and PagingDocument1 pageBroadcast Messages and PagingTry LangNo ratings yet
- D H Ebcdic AsciiDocument6 pagesD H Ebcdic AsciiTry LangNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)