Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllogism: How To Use These Syllogism Rules To Solve Questions?
Syllogism: How To Use These Syllogism Rules To Solve Questions?
Uploaded by
Sourav Mishra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageSyllogism
Original Title
Syllogism
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSyllogism
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageSyllogism: How To Use These Syllogism Rules To Solve Questions?
Syllogism: How To Use These Syllogism Rules To Solve Questions?
Uploaded by
Sourav MishraSyllogism
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
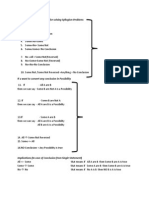
SYLLOGISM
First and foremost have a quick glance at the Main rules to solve Syllogism Problems...
1st 2nd sntnc
ALL
SOME
NO
ALL
ALL
NO
SOME
SOME
SOME NOT
NO
SOME NOT REVERSED
SOME NOT REVERSED
If the conclusion is in Possibility case then these rules must be applied.
If All A are B then we can say - Some B are Not A is a Possibility
If Some B are Not A then we can say - All A are B is a Possibility
If Some A are B then we can say - All A are B is a Possibility All B are A is a Possibility
That is
All <=> Some Not Reversed
Some => All
NO Conclusion = Any Possibility is true
When it is implemented (In case of Conclusion from Single Statement)
1. All => Some that means if All A are B then Some B are A is true.
2. Some <=> Some that means if Some A are B then Some B are A is true.
3. No <=> No that means if No A is B then NO B is A is true
How to use these Syllogism Rules to solve questions?
Inorder to solve Syllogism there are two types:
1. Cross Cancellation
2. Vertical Cancellation
Statements:
1. All Cows are Parrots
2. All Parrots are Birds
with cross cancellation STATEMENT 1 is considered as 1st sentence and STATEMENT 2 is considered as 2nd
sentence. so Conclusion is ALL+All= ALL.
All parrots are birds.
Statements:
1. Some Mails are Messages
2. All Updates are Messages
with vertical cancellation, STATEMENT 2 is considered as 1st sentence and STATEMENT 1 is considered as 2nd
sentence. so Conclusion is ALL+SOME= NO CONCLUSION . Here SOME+ALL=SOME conclusion will be
incorrect.
You might also like
- Logic Mat101Document32 pagesLogic Mat1017CsNo ratings yet
- Logical ReasoningDocument39 pagesLogical ReasoningayjnihhhNo ratings yet
- LAE Reviewer TrackerDocument8 pagesLAE Reviewer Trackerjen quiambao0% (1)
- Logical ReasoningDocument39 pagesLogical ReasoningRohan SharmaNo ratings yet
- SphygmomanometerDocument13 pagesSphygmomanometerSourav MishraNo ratings yet
- Basic Number TheoryDocument68 pagesBasic Number TheoryPercy Khan100% (1)
- Golden Rules For SyllogismDocument4 pagesGolden Rules For Syllogismshivanishah100% (1)
- Syllogism - Gr8AmbitionZDocument3 pagesSyllogism - Gr8AmbitionZAmit Bharti100% (1)
- 1 An Example and Some Terminology: Facts About SyllogismsDocument22 pages1 An Example and Some Terminology: Facts About SyllogismsRama NathanNo ratings yet
- (Reasoning) Syllogism (All Cats Are Dogs) - Method, Approach, Techniques, Shortcuts Explained For IBPS, SSC, CSAT and CAT - Mrunal PDFDocument43 pages(Reasoning) Syllogism (All Cats Are Dogs) - Method, Approach, Techniques, Shortcuts Explained For IBPS, SSC, CSAT and CAT - Mrunal PDFsathish1990100% (1)
- Logic Atty MirasDocument5 pagesLogic Atty MirasAijeleth Shahar Gunay AwacayNo ratings yet
- Latin Legal MaximsDocument34 pagesLatin Legal MaximsZeaweaNo ratings yet
- To Solve Syllogism Questions With The Help of RulesDocument11 pagesTo Solve Syllogism Questions With The Help of Rulesrichard anishNo ratings yet
- Syllogism 2Document54 pagesSyllogism 2saurabhNo ratings yet
- To Solve Syllogism Questions With The Help of RulesDocument4 pagesTo Solve Syllogism Questions With The Help of RulessantoshkumarNo ratings yet
- SyllolismDocument22 pagesSyllolismRajiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Syllogism 1Document60 pagesSyllogism 1Smiley HarishNo ratings yet
- Syllogism Rules: Case 1 Allaareb - AllbarecDocument1 pageSyllogism Rules: Case 1 Allaareb - AllbarecqswerNo ratings yet
- (Reasoning) Logical Connectives (If, Unless, Either Or) For CSAT, CAT Shortcuts Formulas Approach Explained MrunalDocument11 pages(Reasoning) Logical Connectives (If, Unless, Either Or) For CSAT, CAT Shortcuts Formulas Approach Explained MrunalMohit AryaNo ratings yet
- Syllogism Concepts Part IDocument7 pagesSyllogism Concepts Part IShiba Narayan SahuNo ratings yet
- RBI Grade B 2023: ReasoningDocument45 pagesRBI Grade B 2023: ReasoningpsNo ratings yet
- Syllogism - Solved ExamplesDocument9 pagesSyllogism - Solved Examplesamank114No ratings yet
- Syllogism 100 50 Rule No Venn Diagram With MCQsDocument183 pagesSyllogism 100 50 Rule No Venn Diagram With MCQsnotesnotes078No ratings yet
- Mission IBPS: Syllogisms Concepts: I.E. All A's Are B'sDocument6 pagesMission IBPS: Syllogisms Concepts: I.E. All A's Are B'sMahakNo ratings yet
- 15.053 February 22, 2007: Introduction To The Simplex AlgorithmDocument62 pages15.053 February 22, 2007: Introduction To The Simplex AlgorithmEhsan SpencerNo ratings yet
- Degeneracy in Linear Programming: Reverend Jerry FalwellDocument16 pagesDegeneracy in Linear Programming: Reverend Jerry FalwellJohanna Martinne CanlasNo ratings yet
- Session 2 (Control Flow)Document37 pagesSession 2 (Control Flow)LukaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Introductory To Elementary Logic (Part 2)Document27 pages2.3 Introductory To Elementary Logic (Part 2)Ken Justine RapistaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Simplex AlgorithmDocument62 pagesIntroduction To The Simplex AlgorithmKarim CHERIFINo ratings yet
- TMP 6992 Inequality Tricks 577536331Document19 pagesTMP 6992 Inequality Tricks 577536331Uday kiranNo ratings yet
- Upsc Job: Syllogisms - A Nightmare SolvedDocument3 pagesUpsc Job: Syllogisms - A Nightmare Solvedakumar_277No ratings yet
- Introduction To SyllogismDocument27 pagesIntroduction To SyllogismrerereNo ratings yet
- (Reasoning) Logical Connectives (If, Unless, Either Or) For CSAT, CAT Shortcuts Formulas Approach Explained MrunalDocument15 pages(Reasoning) Logical Connectives (If, Unless, Either Or) For CSAT, CAT Shortcuts Formulas Approach Explained MrunalPooja Basu0% (2)
- Logic Chapter 2 Rules of SyllogismDocument23 pagesLogic Chapter 2 Rules of SyllogismNISHITA ACHREKARNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument41 pagesConditional Sentencesgaby.grunge95No ratings yet
- Problems With OLSDocument8 pagesProblems With OLSHarshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Finite Element Analysis Prof. R. Krishnakumar Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 9Document24 pagesAdvanced Finite Element Analysis Prof. R. Krishnakumar Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 9abimanaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Break Gs 1 Art and CultureDocument19 pagesSyllabus Break Gs 1 Art and CulturePriyanshi AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Control Flow Structure - CsDocument44 pagesChapter4 Control Flow Structure - Cskemal BerisoNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document11 pagesBook 2Mohamed SaleemNo ratings yet
- Logical Reasoning NotesDocument60 pagesLogical Reasoning NotesGyaani GuptaNo ratings yet
- AU Chapter 3Document14 pagesAU Chapter 3Daaniyyee AbdiisaaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 10variables Sequence BooleanLogic SelectionDocument65 pagesLecture 9 10variables Sequence BooleanLogic SelectionSurya KotamrajaNo ratings yet
- Syllogisms Tricks With Examples Complete ExplanationDocument30 pagesSyllogisms Tricks With Examples Complete ExplanationSachin SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Equations and InequalitiesDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Equations and InequalitiesLeonessa CortesNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry (Full Version)Document23 pagesTrigonometry (Full Version)Leng Kien YuenNo ratings yet
- Lecture OneDocument11 pagesLecture Onebrightnanor19No ratings yet
- All Cats Are DogsDocument42 pagesAll Cats Are Dogspoo235No ratings yet
- Syllogism Made EasyDocument12 pagesSyllogism Made EasySatish YadavNo ratings yet
- Matematical InductionDocument9 pagesMatematical InductionMatthewNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finite Element Method Dr. R. Krishnakumar Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 4Document25 pagesIntroduction To Finite Element Method Dr. R. Krishnakumar Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 4mahendranNo ratings yet
- Syllogism Part 3 31690565552911Document50 pagesSyllogism Part 3 31690565552911be happyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument20 pagesAdvanced Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madrasammar sangeNo ratings yet
- Syllogism Winter Winning Camp BE 2024Document25 pagesSyllogism Winter Winning Camp BE 2024Utkarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- SyllogismDocument23 pagesSyllogismkuntal854uNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - ReducibilityDocument10 pagesLecture 9 - ReducibilityAgha KazimNo ratings yet
- English VII Academic Consulting Session 02 August 2021Document9 pagesEnglish VII Academic Consulting Session 02 August 2021Zoilita Altamirano LeonNo ratings yet
- Mrunal PDFDocument8 pagesMrunal PDFPradeepa SadhviNo ratings yet
- QA - SyllolismDocument11 pagesQA - SyllolismfihonasinghNo ratings yet
- Syllogism (All Cats Are Dogs) - Method, Approach, Techniques, Shortcuts ExplainedDocument24 pagesSyllogism (All Cats Are Dogs) - Method, Approach, Techniques, Shortcuts ExplainedJagan RockzzNo ratings yet
- Syllogisms Tricks With Examples Complete Explanation (How To Solve)Document1 pageSyllogisms Tricks With Examples Complete Explanation (How To Solve)JagadishNo ratings yet
- Term Paper SubratDocument8 pagesTerm Paper SubratSourav MishraNo ratings yet
- BIP Assignment 1Document3 pagesBIP Assignment 1Sourav MishraNo ratings yet
- GOD Answers in 3 WaysDocument2 pagesGOD Answers in 3 WaysSourav MishraNo ratings yet
- Pulley QuestionDocument2 pagesPulley QuestionSourav MishraNo ratings yet