Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I.V Cheat Sheet!
Uploaded by
Audrey LeonarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
I.V Cheat Sheet!
Uploaded by
Audrey LeonarCopyright:
Available Formats
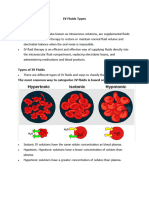
IV Solution Cheat Sheet
A quick reference guide on the different intravenous solutions.
Type
Normal Saline (NS)
0.9% NaCl in
Water
Crystalloid
Solution
Isotonic (308
mOsm)
1/2 Normal Saline
(1/2 NS)
0.45% NaCl in
Water
Crystalloid
Solution
Hypotonic (154
mOsm)
Lactated Ringers
(LR)
Use
Normal saline
with electrolytes
and buffer
Isotonic (275
mOsm)
Increases circulating plasma
volume when red cells are
adequate
Shock
Fluid replacement in patients
with diabetic ketoacidosis
Hyponatremia
Blood transfusions
Resuscitation
Metabolic Alkalosis
Hypercalcemia
Water replacement
Raises total fluid volume
DKA after initial normal
saline solution and before
dextrose infusion
Hypertonic dehydration
Sodium and chloride
depletion
Gastric fluid loss from
nasogastric suctioning or
vomiting.
Replaces fluid and buffers
pH
Hypovolemia due to thirdspace shifting.
Dehydration
Burns
Lower GI tract fluid loss
Acute blood loss
Special Considerations
Do not use in patients with heart failure,
edema, or hypernatremia, because NSS
replaces extracellular fluid and can lead to
fluid overload.
Replaces losses without altering fluid
concentrations.
Helpful for Na+ replacement
Use cautiously; may cause cardiovascular
collapse or increase in intracranial
pressure.
Dont use in patients with liver disease,
trauma, or burns.
Useful for daily maintenance of body fluid,
but is of less value for replacement of
NaCl deficit.
Helpful for establishing renal function.
Fluid replacement for clients who dont
need extra glucose (diabetics)
Has similar electrolyte content with serum
but doesnt contain magnesium.
Has potassium therefore dont use to
patients with renal failure as it can cause
hyperkalemia
Dont use in liver disease because the
patient cant metabolize lactate; a
functional liver converts it to bicarbonate;
dont give if patients pH > 75.
Normal saline with K+, Ca++, and lactate
(buffer)
Often seen with surgery
D5 W
Dextrose 5% in
water Crystalloid
solution
Isotonic (in the
bag)
*Physiologically
hypotonic (260
mOsm)
Raises total fluid volume.
Helpful in rehydrating and
excretory purposes.
Fluid loss and dehydration
Hypernatremia
D5NS
Dextrose 5% in
0.9% saline
Hypertonic (560
mOsm)
D5 1/2 NS
Dextrose 5% in
0.45% saline
Hypertonic (406
mOsm)
D5LR
Dextrose 5% in
Lactated Ringers
Hypertonic (575
mOsm)
Normosol-R
Normosol
Isotonic (295
mOsm)
Hypotonic dehydration
Replaces fluid sodium,
chloride, and calories.
Temporary treatment of
circulatory insufficiency and
shock if plasma expanders
arent available
SIADH (or use 3% sodium
chloride).
Addisonian crisis
DKA after initial treatment
with normal saline solution
and half-normal saline
solution prevents
hypoglycemia and cerebral
edema (occurs when serum
osmolality is reduced
rapidly).
Same as LR plus provides
about 180 calories per
1000ccs.
Indicated as a source of
water, electrolytes and
calories or as an alkalinizing
agent
Replaces fluid and buffers
pH
Indicated for replacement of
acute extracellular fluid
volume losses in surgery,
trauma, burns or shock.
Used as an adjunct to restore
a decrease in circulatory
volume in patients with
moderate blood loss
Solution is isotonic initially and becomes
hypotonic when dextrose is metabolized.
Not to be used for resuscitation; can
cause hyperglycemia
Use in caution to patients with renal or
cardiac disease, can cause fluid overload
Doesnt provide enough daily calories for
prolonged use; may cause eventual
breakdown of protein.
Provides 170-200 calories/1,000cc for
energy.
Physiologically hypotonic -the dextrose is
metabolized quickly so that only water
remains - a hypotonic fluid
Do not use in patients with cardiac or
renal failure because of danger of heart
failure and pulmonary edema.
Watch for fluid volume overload
In DKA, use only when glucose falls < 250
mg/dl
Most common postoperative fluid
Useful for daily maintenance of body
fluids and nutrition, and for rehydration.
Contraindicated in newborns ( 28 days of
age), even if separate infusion lines are
used (risk of fatal ceftriaxone-calcium salt
precipitation in the neonates
bloodstream).
Contraindicated in patients with a known
hypersensitivity to sodium lactate.
Not intended to supplant transfusion of
whole blood or packed red cells in the
presence of uncontrolled hemorrhage or
severe reductions of red cell volume
You might also like
- Equine Fluid TherapyFrom EverandEquine Fluid TherapyC. Langdon FieldingNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia, (Low Blood Sodium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyponatremia, (Low Blood Sodium) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte TherapyDocument6 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Therapygilpogs100% (1)
- Types of Intravenous FluidsDocument4 pagesTypes of Intravenous FluidsMhaye Ruiz Genturalez RN100% (2)
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsMehdi SabeiNo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- IV Cheatsheet Bgnocolor PDFDocument2 pagesIV Cheatsheet Bgnocolor PDFHermiie Joii Galang MaglaquiiNo ratings yet
- IV CheatsheetDocument2 pagesIV CheatsheetDWIGHT LESTER O. MANGILANo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsEsarpy (Nana)No ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- IV Cheatsheet Monochrome PDFDocument2 pagesIV Cheatsheet Monochrome PDFElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsJamil KhanNo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsDocument2 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheet: A Quick Reference Guide On The Different Intravenous SolutionsNicole Xyza JunsayNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy - NCM 106Document8 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Therapy - NCM 106Hana CyrilNo ratings yet
- IV FluidsDocument3 pagesIV FluidsJohn Daniel IbatNo ratings yet
- Intravena Fluid HTRDocument30 pagesIntravena Fluid HTRFera CuthikNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid/Solution Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesIV Fluid/Solution Quick Reference GuideCin DyNo ratings yet
- Pocket Card - IV Fluids - December 2023Document6 pagesPocket Card - IV Fluids - December 2023Evieta CallysthaNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids and Solutions Quick Reference Guide Cheat Sheet - NurseslabsDocument7 pagesIV Fluids and Solutions Quick Reference Guide Cheat Sheet - Nurseslabsபிரேம் குமார் ராஜாமணி100% (1)
- IV Solution Cheat SheetDocument1 pageIV Solution Cheat Sheet'Jessie' Poquiz100% (2)
- IV Fluid CommonDocument1 pageIV Fluid CommonmydewyboyNo ratings yet
- pdfDocument2 pagespdfbebeNo ratings yet
- Fluid TherapyDocument36 pagesFluid TherapyAmin MasromNo ratings yet
- IV Solutions GuideDocument8 pagesIV Solutions GuideNhietz SeraNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids: CrystalloidsDocument6 pagesIV Fluids: CrystalloidsGlaiza BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Lots of Salt Causes Retention of WaterDocument8 pagesLots of Salt Causes Retention of WaterMarchant Lowry BleyNo ratings yet
- Hary-Fluid Management Part 1Document49 pagesHary-Fluid Management Part 1Keta PatelNo ratings yet
- IV FluidsDocument6 pagesIV FluidsAr-jay PorrasNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids - January 2019Document6 pagesIV Fluids - January 2019Benjamin NgNo ratings yet
- HyponatremiaDocument21 pagesHyponatremiaselma100% (1)
- Hypernatremia: Marielle Adey R. Magcawas BSN-3CDocument28 pagesHypernatremia: Marielle Adey R. Magcawas BSN-3CMarielle Adey Magcawas RNNo ratings yet
- IVF Table of Commonly Used IV SolutionsDocument3 pagesIVF Table of Commonly Used IV SolutionsKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- DR Omar Kamal Ansari Dept of AnaesthesiologyDocument46 pagesDR Omar Kamal Ansari Dept of Anaesthesiologyvvb_frndNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte DisordersDocument10 pagesElectrolyte DisordersSlavicaNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids TheoryDocument13 pagesIV Fluids TheoryFRESY TRI SUGIANTONo ratings yet
- IV Solution Cheat SheetDocument1 pageIV Solution Cheat Sheetlauramphs79No ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy For 2nd Year ConceptDocument83 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy For 2nd Year ConceptMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Flluid and ElectDocument107 pagesFlluid and ElectHassan SalamehNo ratings yet
- Dehydration 4Document73 pagesDehydration 4Ali YousefNo ratings yet
- Digital Scrapbook by Jacela BunayogDocument31 pagesDigital Scrapbook by Jacela BunayogJacela Annsyle J. BunayogNo ratings yet
- Pocket Card - IV Fluids - September 2021Document6 pagesPocket Card - IV Fluids - September 2021NeweeJoonYowNo ratings yet
- Major Intra and Extracellular IonsDocument29 pagesMajor Intra and Extracellular IonsRasel IslamNo ratings yet
- Fluid Resuscitation NewDocument32 pagesFluid Resuscitation Newffattimu667No ratings yet
- IV Fluid Lecturette for Nursing StudentsDocument16 pagesIV Fluid Lecturette for Nursing StudentsbabiNo ratings yet
- Hypernatremia: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument16 pagesHypernatremia: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentBlessyNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid TherapyDocument28 pagesIV Fluid Therapyansuh2250% (2)
- Fluid ManagementDocument10 pagesFluid ManagementdradaadNo ratings yet
- Review: Diagnostic and Treatment of Electrolyte DisturbancesDocument31 pagesReview: Diagnostic and Treatment of Electrolyte DisturbancesalvyandaniNo ratings yet
- PALS Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument32 pagesPALS Fluids and ElectrolytesZi SongNo ratings yet
- Na, K ImbalanceDocument42 pagesNa, K ImbalanceDr. Ammar KhalilNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids ExplainedDocument5 pagesIV Fluids ExplainedRegine Mae Encinada100% (1)
- Intravenous Fluid Therapy GuideDocument68 pagesIntravenous Fluid Therapy GuideMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte - 2022Document147 pagesFluid and Electrolyte - 2022Lacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy FinalDocument3 pagesFluid Therapy Finallaureeate100% (1)
- Fluid & Electrolyte Management & Acid Base Disorders: Alice Augustin Amina S Anagha P RDocument47 pagesFluid & Electrolyte Management & Acid Base Disorders: Alice Augustin Amina S Anagha P RAsif AbbasNo ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceDocument157 pagesFluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceManisha Shakya0% (1)
- Acid-Base and Electrolyte Handbook for Veterinary TechniciansFrom EverandAcid-Base and Electrolyte Handbook for Veterinary TechniciansAngela Randels-ThorpNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- How Much Water To Drink When Fasting - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Eric Berg: Ensuring Proper Water Consumption While FastingFrom EverandHow Much Water To Drink When Fasting - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Eric Berg: Ensuring Proper Water Consumption While FastingNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading t2dmDocument11 pagesJournal Reading t2dmAudrey LeonarNo ratings yet
- Types of Anesthesia ExplainedDocument3 pagesTypes of Anesthesia ExplainedAudrey LeonarNo ratings yet
- Funda BulletsDocument17 pagesFunda BulletsAudrey LeonarNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing Bullets (Nle & Nclex)Document21 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Bullets (Nle & Nclex)Richard Ines Valino100% (24)
- Understanding HypokalemiaDocument4 pagesUnderstanding HypokalemiaAudrey Leonar100% (1)
- Types of Anesthesia ExplainedDocument3 pagesTypes of Anesthesia ExplainedAudrey LeonarNo ratings yet
- Rare Skin Disorder Stevens-Johnson SyndromeDocument6 pagesRare Skin Disorder Stevens-Johnson SyndromeAudrey LeonarNo ratings yet
- The Complete List of NANDA Nursing Diagnosis For 2012Document4 pagesThe Complete List of NANDA Nursing Diagnosis For 2012annNo ratings yet