Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Settlement Prediction Method PDF
Uploaded by
HRCOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Settlement Prediction Method PDF
Uploaded by
HRCCopyright:
Available Formats
Journal of the Faculty of Environmental Science and Technology.
Okayama University
Vol.1. No.1. pp.193-198. March 1996
Settlement Prediction Method Using Observed Settlement li?locity
Kiyoshi SHIMADA *, Sin-ichi NISHIMURA * and Hiroaki FUJII*
(Received January 16 . 1996)
Abstract
This paper presents a new method for prediction of consolidation
settlements bf soft grounds. The method is based on the theoretical result which shows
that the settlement velocity of soft grounds non-improved or improved with sand drains
decreases exponentially with time. Final settlements can be easily derived from the
regression analysis for the relationship between the elapsed time and the observed
settlement velocity. The method has advantages of its simplicity and capability to give
the satisfactorily good estimate of the consolidation settlements, and also the support of
the theoretical background.
Key Words: consolidation, settlement prediction, soft ground, sand drains, one-
dimensional consolidation
1. INTRODUCTION
We sometimes fail to obtain the acceptable
estimate of consolidation settlements of soft
grounds even though adopting an elaborate
constitutive equation in finite element method.
The failure is probably due to uncertainty of
soil constants and boundary conditions, etc.
Accordingly, several methods to predict settlements using observed data have been proposed
and widely used. (Yoshikuni et al. 1981)
This paper presents a new method of settlement prediction using observed settlement
velocity. The method is based on the theoretical
result which shows that the settlement velocity
of soft grounds non-improved or improved
with sand drains decreases exponentially with
time. The final settlement can be easily derived
from the regression analysis for the relationship
between the elapsed time and the observed
settlement velocity.
2. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TIME
AND SETTLEMENT VELOCITY IN
SOFT GROUND IMPROVED WITH
SAND DRAINS
The approximate solution of Barron's
consolidation equation for a sand drain (Barron
1948, Richart 1957, and Yoshikuni 1979) is as
follows:
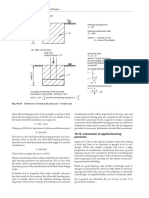
S(t)=Sj{ 1 - exp[at]}
(1)
where t is the time measured from the start of
consolidation, Set) the settlement at the time t,
* Department of Environmental Management Engineering
193
1. Fac. Environ. Sci. and Tech., Okayama Univ. 1 (1) 1996
194
instead of (dS Idt). Fig. 1 shows the calcula-
Sf the final settlement, and
-8 C h
a=-- -2
F(n)
n
F(n)=
where
Ch
tion procedure of the observed settlement
velocity. When we obtain observed data at
'
n -1
In(n) -
3n -1
4n2 '
Point A and B whose time and settlement are
de
n=-d
w
is the coefficient of consolidation, de
(ta, Sa)' (tb, Sb) respectively, we define the
observed settlement velocity at time t c with the
next equations:
is the equivalent effective diameter of a sand
AS / At =
drain, and d w the diameter of a sand drain.
The differentiation of Eq.( 1) with respect to
S -S
b
(6)
tb - ta
time (t) gives the settlement velocity (dSldt),
Applying the model to the relationship between
dS
dt = - aSf exp[ at] .
the elapsed time (t) and the observed settle(2)
ment velocity (I1S1I1t), we can find the regression parameters a 0, a 1. Then we can calculate
Eq.(2) can be rewritten as follows:
y =A o exp[ Al x]
(3)
Ao, Al and the final settlement Sf from Eq.(4)
as
where y = dSldt, x = t, and
A o =- aSf , Al = a
(4)
(7)
Transforming the variables as Y = In (y) and X
=x, we obtain the following linear regression
The settlement velocity during embankment
model.
(5)
where ao
and also the settlement curve from Eq.(l).
Eq.(l) can be held only with such an assump-
=InAo and al =AI-
Since settlement observations are usually
made in a certain interval, we cannot obtain the
derivative ( dS I dt) like a mathematical derivative of a continuous function. Then we define
the observed settlement velocity
should not be used in the analysis because
(tiS II1t)
Time, I
tion that all loads are applied simultaneously.
Hence it is necessary to introduce a new coordinate system (t', S') whose origin is located at
(t= to, S= So) on the settlement curve Eq.(l).
We then obtain the following equation.
S'(t')=Si{ 1 - exp[at']}
(8)
where S(t) = So + S'(t') and Sf= So+ Sf.
Applying the same procedure to the relation-
--
ship between the elapsed time (t') and the
observed settlement velocity (11.5'll1t') , we
cCI):
E
CI)
can obtain the final settlement Sf from the
regression parameters A '0, A'1 on Eq.(7) as
(J)
A'
S'f = - Y0 '
1
Fig. 1 Calculation of observed settlement
velocity (ASI AI)
and also the total settlement S as
(9)
K. SHIMADA et al. / Settlement Prediction Method Using Observed Settlement Velocity
S=So+S.r{ 1 - exp[at'
n.
(10)
3.
DIFFERENCE
BETWEEN
ANALYTICAL AND APPROXIMATE
SOLUTIONS OF BARRON'S CONSOLIDATION EQUATION
The relationships between the time factor
(Th) and the settlement velocity ( dUldTh) for
the different values of the diameter ratio (n ) are
shown in Fig. 2. The solid lines represent
analytical solutions and the open circles the
-
Analytical
0 Approximate
195
approximate solutions of Barron's consolidation equation. We notice that there are slight
differences between the approximate solutions
and the analytical solutions in the region of
small Th.
Fig. 3 shows the relationship between the
real time (t) and the real settlement velocity
( dSI dt) calculated with the soil constants of
KASAOKA-Bay clay (Fujii et al. 1991). The
differences appear only in the initial stage of
consolidation. Those differences are therefore
practically negligible.
10 . . . . - - - - - - . . . - - - - - - - - ,
4. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TIME
AND SETTLEMENT VELOCITY IN
NON-IMPROVED SOFT GROUND
Asaoka (1978) shows that the following
equation is identical to Mikasa's consolidation
equation for non-improved soft grounds.
.r:.
I-
::!:2
:> 8
'0
>.
130 6
~
l ::
CI)
CI)
ECI) 2
...
C/)
(n)
S+c1S+cZS+ ... +cnS
0
0.01
0.1
Time factor, Th
where
Ct,
cz ...
+ ",=Sf (11)
en are constants, and dots
refer to the differentiation with respect to time.
Fig. 2 Analytical and approximate relationships
between time factor (Th) and settlement
velocity (dU/dTh)
Approximate
He also proposed a graphical settlement
prediction method based on the following
equation which is the first order approximation
of Eq.(l1).
>:
2 w------.---...,......--.------r-----,
as
(12)
Analytical
::!:2
';: 1.5 1-\----+----+--+---+---1
::!:2
C/)
'0
~1
The differential equation (12) can be easily
solved as follows:
t
Set) = Sf { 1 - exp[ - - ] }
c1
1i 0.5
E
CI)
~ 0 L_--l._~~~;;;;;;;;t;g;=d..o()o-J
100
200
300
400
500
Time, t (days)
Fig. 3 Analytical and approximate relationships
between time (t) and settlement velocity (dS/dt)
(13)
Eq.(13) takes the same form as that of
Eq.(1) for the settlement of the soft grounds
improved with sand drains. The method previously proposed for improved soft grounds is
therefore applicable to the settlement prediction
of non-improved soft grounds.
J. Fac. Environ. Sci. and Tech.. Okayama Univ. I (1) 1996
196
Atkinson and Bransby (1978) obtained an
approximate solution of Terzaghi's consolidation equation for non-improved soft grounds.
They approximate the isochrones with parabolas. The solution has the same form as that of
Eq.(13), and accordingly the settlement velocity decreases exponentially with time.
5. PREDICTED SETTLEMENTS OF
SOFf GROUNDS IMPROVED WITH
PACKED SAND DRAINS
The proposed method is applied to the
settlement prediction of the soft grounds in
o Observed
KASAOKA-Bay reclaimed land, OKAYAMA.
The ground had been improved with packed
sand drains and preloading embankments (Fujii
et al. 1991, Shimada et al. 1992).
Figs. 4 and 5 show the relationships
between time (t') and the settlement velocity (
/i,S'/ !i.t') for Point H in the field No.4 and
No.7, respectively. The time of the completion
of embankment is adopted as the origin of (t',
S') coordinate system. The open circles show
the observed settlement velocities, The exponentially decaying lines are the result of the regression analysis with the least square method. The
-==
o Observed
Regression line
~1.5
Regression line
....
~
en
"'C
1'=0 to t'=91 days
t'=Oto t'=190 days
all data
~ 1
en
"'C
~
o
~ 0.5 I--~~--+--_+---+--_____j
'0
Q)
E
Q)
en
t'=O to t'=60 days
t'=O to t'=114 days
all data
~
(,)
o
~ 0.5
'E
Q)
E
l ::
....
L...-_--'-_ _...L--_----L.....u.~~
_
100
200
300
Time,
r (days)
400
__'
500
~ 0 L_..L_--.l_-=~~~~~
en
200
300
400
200
300
r (days)
400
500
Fig. 5 Relationship between time (t') and settlement
velocity (dS'/dt') of Point H in field NO.7
Time (days)
Time (days)
100
100
Time,
Fig. 4 Relationship between time (t') and settlement
velocity (dS'/dt') of Point H in field No.4
Q)
500
600
100
200
300
400
500
600
O~-....----.----r-----r----r----,
O~.---.,....--...,.---,--....,...----r-----,
t'=O
_
50
I--~~-+---+---+--_+-_____j
_ 50
E
'E
l ::
~ 100
Q)
E
Q)
Q)
~
en 150
EQ)
en 150
o Observed
-
Predicted
100
all data
200
Fig. 6 Settlement prediction for Point H in field NO.4
o Observed
Predicted
all data
200
Fig. 7 Settlement prediction for Point H in field NO.7
K. SHIMADA et al. / Settlement Prediction Method Using Observed Settlement Velocity
thin solid lines are derived from all observed
data. The thick solid lines are derived from the
data observed from t' =0 to t' =91 days, 190
days in Fig. 4, and t'=O to t'=60 days, 114
days in Fig. 5, respectively.
Fig. 6 shows the results of the settlement
prediction for Point H in the field No.4. The
open circles represent observed settlements.
Three solid lines are settlement curves predicted
at t'=91 days, 190 days and predicted with all
observed data, respectively. The prediction is
also applied to the Point H in the field No.7
and results are shown in Fig. 7. Three settlement curves are predicted at t' = 60 days, 144
days and predicted with all observed data,
respectively.
These figures show that the observed settlements can be expressed successfully when all
observed data are used, i.e., the settlement of
soft grounds improved with sand drains can be
calculated with Eq.(1). It is also clear from the
figures that the prediction accuracy becomes
improved more with the longer elapsed time
from the completion of embankment.
The prediction accuracy is presented in Fig.
_
4H
6C
197
8 as the relationship between V' and R s . These
parameters are defined with the following
equations by Yoshikuni et a1. (1981).
V' = Observed settlement at the time of prediction
Last observed settlement
Predicted settlement for the time of last observation
Last observed settlement
(14)
where V' refers to the equivalent degree of
consolidation at the time of prediction. R s
shows the accuracy of prediction. When there
is no error in prediction, R s becomes unity.
Yoshikuni et a1. (1981) compared the
accuracies of several prediction methods with
their observed data. Their results are summarized in Table 1 which shows V' at some levels
of R s The smaller value of V' at the same level
of R s indicates good prediction.
The result of the proposed method with the
data of KASAOKA-Bay reclaimed land is also
presented in the table. The method gives the
satisfactorily good estimate of settlements.
Table 1 Prediction methods and their accuracies
(From Yoshikuni et al.(1981))
--[]- 7H
Rs
R s =O.7
R s =O.8
R s =O.9
R s =O.95
Hyperbolic
Monden
Hoshino
Asaoka
U'=O.4
U'=O.6
U'=O.4
U'=O.5
U'=O.6
U'=O.7
U'=O.5
U'=O.65
U'=O.7
U'=O.8
U'=O.6
U'=O.8
U'=O.8
U'=O.9
U'=O.7
U'=O.9
'E
Proposed
5E
--+-
Methods
7G
cr.'" 0.9
~ 0.8
~ 0.7
I U'=O.5 I U'=O.55 I U'=O.7 I U'=O.8
Q)
0.6
0.5
0.2
0.4
0.6
U'
0.8
Fig. 8 Predicting accuracy in Kasaoka-bay
reclaimed land
6. PREDICTED SETTLEMENTS OF
NON-IMPROVED SOFf GROUND
Fig. 9 shows the relationships between time
(t') and the settlement velocity (/lS'/!i.t') for a
non-improved soft ground. The observed data
1. Fac. Environ. Sci. and Tech.. Okayama Univ. 1 0) 1996
198
is published by Aboshi (1969) and cited by
Asaoka (1978). The time of the completion of
embankment is adopted as the origin of ( t', S')
coordinate system. The open circles show the
observed settlement velocities. The exponentially decaying lines are the result of the regression
analysis with the least square method. The thin
solid line is derived from all observed data. The
thick solid line is derived from the data
observed from t'=O to t'=550 days.
Fig. 10 shows the results of the settlement
prediction. The open circles represent observed
settlements. Two solid lines are the settlement
o Observed
~0.15
Regression line
curves predicted at t' = 550 days and predicted
with all observed data, respectively. The time
of the completion of embankment is shown as
t' =0 in the figure. The proposed method has
demonstrated its capability to predict the
settlements satisfactorily.
7. CONCLUSIONS
A settlement prediction method using the
settlement velocity is proposed for soft grounds
non-improved and improved with sand drains.
The method has the advantages of its simplicity
and capability to give satisfactorily good estimates of the consolidation settlements, and also
the support of the theoretical background.
:l:2
E
~
(J)
0.1
t'=O to t'=550 days
all data
"t:l
;i-
'0
~0.05
E
Q)
E
Q)
(J)
500
1000
1500
Time, f (days)
2000
Fig. 9 Relationship between time (t') and settlement
velocity (dS'/dt') of non-improved soft ground
o
50
Eo
<t>
0
c:
(I)
::;-100
~
150
t'=O
Observed
Predicted
'I
c Po..
(J)
"Q
tL550dlys -
\..
200
all data/'
250
500
1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
Time (days)
Fig. 10 Settlement prediction for non-improved
soft ground
References
Aboshi, T. (1969) : Soil Mechanics (Edited by T.
Mogami), Gihodo-shuppan, Tokyo, 464-465 (in
Japanese).
Asaoka, A. (1978) : Observational procedure of
settlement prediction, Soils and Foundations, 18(4),
87-101.
Atkinson, J.H. and Bransby, P.L. (1978) : The
mechanics of soils, McGraw-Hill, London.
Barron, R.A. (1948) : Consolidation of fine-grained
soils by drain wells, Trans of ASCE, 113, 718-754.
Fujii, H., Shimada, K., Nishimura, S. and Tajiri, N.
(1991) : Determination of soil parameters with
standard consolidation tests and its application to
ftnite element analysis, Trans. of JSIDRE, 154, 116 (in Japanese).
Richart, F.E.Jr. (1957) : A review of the theories for
sand drains, Proc. of ASCE, 83(SM3), 1301-1 1301-38.
Shimada, K., Fujii, H., Nishimura, S. and Tajiri, N.
(1992) : Plane strain ftnite element analysis for
consolidation settlement in soft ground improved
with packed sand drains, Trans. of JSIDRE, 162, 1-7
(in Japanese).
Yoshikuni, H., Inoue, T., Sumioka, N., Hara, H.
(1981) : On the characteristics of settlement
prediction methods by monitoring, Tsuchi-to-kiso,
29(8),7-13 (in Japanese).
Yoshikuni, H. (1979) : Design and perfonnance
management for vertical drains, Gihodo-shuppan,
Tokyo (in Japanese).
You might also like
- Piles - Geothermal Presentation PDFDocument17 pagesPiles - Geothermal Presentation PDFernestnsabimana74No ratings yet
- P-Y Criterion For Rock Mass: Robert Liang, M.ASCE Ke Yang, M.ASCE and Jamal Nusairat, M.ASCEDocument11 pagesP-Y Criterion For Rock Mass: Robert Liang, M.ASCE Ke Yang, M.ASCE and Jamal Nusairat, M.ASCEAltan ErdemNo ratings yet
- Powrie - Solutions Chs 6-11Document59 pagesPowrie - Solutions Chs 6-11Nestor Bendezu UrbayNo ratings yet
- Designing Singular Jet Grouting Column For Sandy Soils: Gulsah Nur Karahan Osman SivrikayaDocument11 pagesDesigning Singular Jet Grouting Column For Sandy Soils: Gulsah Nur Karahan Osman SivrikayaJose Alberto Duran BaqueroNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Road Embankments in Swampy Area-A Case Study of Uganda in East AfricaDocument14 pagesDesign and Construction of Road Embankments in Swampy Area-A Case Study of Uganda in East AfricaNancy NiolaNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity Calculation of Rock Foundation Based On Nonlinear Failure CriterionDocument7 pagesBearing Capacity Calculation of Rock Foundation Based On Nonlinear Failure CriterionSpasenNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Shear Wave Velocity Profile Using SPTDocument18 pagesEvaluation of Shear Wave Velocity Profile Using SPTJerry BeardNo ratings yet
- Failure Mechanism of Geosynthetic-Encased Stone Columns in Soft Soils Under EmbankmentDocument8 pagesFailure Mechanism of Geosynthetic-Encased Stone Columns in Soft Soils Under EmbankmentJianfeng XueNo ratings yet
- Characterising Engineering Properties of Undisturbed Sedimentary Rock MassesDocument9 pagesCharacterising Engineering Properties of Undisturbed Sedimentary Rock Massesecossich123100% (1)
- Ology, Its Principal (De Freitas)Document45 pagesOlogy, Its Principal (De Freitas)Nathan VincentNo ratings yet
- W6 ReadmeDocument15 pagesW6 ReadmewerewNo ratings yet
- UCS Soft RockDocument6 pagesUCS Soft RockReynaldiNo ratings yet
- Lateral Earth Pressure in Expansive Clay SoilsDocument14 pagesLateral Earth Pressure in Expansive Clay SoilsSamad Arabi100% (1)
- Undrained Fragility of Clean Sands, Silty Sands, and Sandy SiltsDocument11 pagesUndrained Fragility of Clean Sands, Silty Sands, and Sandy SiltsLuciana PradoNo ratings yet
- Kansai Airport Settlement ReportDocument8 pagesKansai Airport Settlement ReportBarbara CunhaNo ratings yet
- Estimating Ultimate Socket Friction for Rock-Socketed Micro PilesDocument8 pagesEstimating Ultimate Socket Friction for Rock-Socketed Micro PileskushaljpNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Design and Stability Analysis of Retaining StructuresDocument15 pagesGeotechnical Design and Stability Analysis of Retaining StructuresSanko Kosan100% (1)
- Prediction of The Axial Bearing Capacity of PilesDocument6 pagesPrediction of The Axial Bearing Capacity of PilesNicole CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations in Engineering Practice by S - by Civildatas - Blogspot.inDocument784 pagesPile Foundations in Engineering Practice by S - by Civildatas - Blogspot.inTatiana RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Bieniawaski Z. T.Document11 pagesBieniawaski Z. T.OlivinNo ratings yet
- Equations for the Soil-Water Characteristic CurveDocument12 pagesEquations for the Soil-Water Characteristic CurveburlandNo ratings yet
- Mono Pile in SandDocument21 pagesMono Pile in SandAHNo ratings yet
- Japan 02Document8 pagesJapan 02Truong Phuoc TriNo ratings yet
- 2 Numerical Analyses of Soft Soil Foundations Improved by PVDs and Vacuum PreloadingDocument40 pages2 Numerical Analyses of Soft Soil Foundations Improved by PVDs and Vacuum PreloadingH.A.I Công ty100% (1)
- The Plewes Method - A Word of CautionDocument10 pagesThe Plewes Method - A Word of CautionLuis Fernando Vergaray AstupiñaNo ratings yet
- Secondary Creek in Soft SoilsDocument9 pagesSecondary Creek in Soft Soilsgeo_unoNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Prefabricated Vertical Drains in Soft Clay and Evaluation of Their Effectiveness in PracticeDocument11 pagesModelling of Prefabricated Vertical Drains in Soft Clay and Evaluation of Their Effectiveness in PracticeHUGINo ratings yet
- Reul Randolph Geotechnique2003Document15 pagesReul Randolph Geotechnique2003YuryPasichnyNo ratings yet
- 07 Bond Design Embedded WallsDocument44 pages07 Bond Design Embedded WallsTae-kyun KimNo ratings yet
- Detailed Site Investigation PDFDocument303 pagesDetailed Site Investigation PDFAbdulrahman AlnagarNo ratings yet
- Retaining StructuresDocument15 pagesRetaining StructuresHarold TaylorNo ratings yet
- Optimal Deign of Pile FoundationDocument13 pagesOptimal Deign of Pile FoundationJustin Johnson100% (1)
- Applied Bearing Pressure For Spread Foundations - FormulaeDocument4 pagesApplied Bearing Pressure For Spread Foundations - Formulaealex_3_15No ratings yet
- PVD Case Study by Soham FoundationsDocument5 pagesPVD Case Study by Soham FoundationsJack DoverNo ratings yet
- CIVE1129 - Lecture Notes - Bearing Capacity PDFDocument14 pagesCIVE1129 - Lecture Notes - Bearing Capacity PDFLee Tin YanNo ratings yet
- Eathquake Hazard IraqDocument9 pagesEathquake Hazard IraqzementheadNo ratings yet
- Asadzadeh - Direct Shear Testing On A Rockfill MaterialDocument18 pagesAsadzadeh - Direct Shear Testing On A Rockfill MaterialDavid CastañoNo ratings yet
- RCK - Effect of Weathering On The Strength and Modulus of Basalt and Siltstone (Gu Et Al, 2008)Document8 pagesRCK - Effect of Weathering On The Strength and Modulus of Basalt and Siltstone (Gu Et Al, 2008)sandycastleNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Stability of Rock Slopes by The Slope StabilityDocument13 pagesAssessment of The Stability of Rock Slopes by The Slope StabilityArdi Alam JabirNo ratings yet
- The Compozer - A Method To Improve Characteristics of Soft Clays by Inclusion of Large Diameter Sand ColumnsDocument7 pagesThe Compozer - A Method To Improve Characteristics of Soft Clays by Inclusion of Large Diameter Sand ColumnsMohammed KhennoufNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Method For Prediction of Ultimate Primary Settlement of Clays Treated With Vertical DrainsDocument2 pagesHyperbolic Method For Prediction of Ultimate Primary Settlement of Clays Treated With Vertical DrainsSingDollarNo ratings yet
- Mayne & Kulhawy 1982a - K0-OCR Relationships in SoilDocument19 pagesMayne & Kulhawy 1982a - K0-OCR Relationships in SoiloamelodNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study of Ground Vibration Due To Impact Pile DrivingDocument12 pagesNumerical Study of Ground Vibration Due To Impact Pile DrivingmarcvenzNo ratings yet
- GeoMos 2010 SchweigerDocument13 pagesGeoMos 2010 SchweigerIancu-Bogdan TeodoruNo ratings yet
- A Numerical Analysis of Anchored Diaphragm Walls For A Deep Basement in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.Document6 pagesA Numerical Analysis of Anchored Diaphragm Walls For A Deep Basement in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.tangkokhongNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design and Construction in Hong KongDocument20 pagesFoundation Design and Construction in Hong KongXet Fat100% (1)
- Bridge bearing design specificationsDocument2 pagesBridge bearing design specificationsTariq HasanNo ratings yet
- Meet & Greet UK: Geotechnical EngineersDocument20 pagesMeet & Greet UK: Geotechnical EngineersBarney CoulsonNo ratings yet
- VibrofloatationDocument6 pagesVibrofloatationSelvemNo ratings yet
- Vertical DrainDocument15 pagesVertical DrainSyahbani EkaNo ratings yet
- Earth Pressure CoefficientsDocument8 pagesEarth Pressure Coefficientskabasy2015No ratings yet
- Modifications To The Geological Strength Index (GSI) and Their Applicibility To SlopesDocument18 pagesModifications To The Geological Strength Index (GSI) and Their Applicibility To Slopeskhanshahid1No ratings yet
- Design and Performance of Deep Excavations in Soft ClaysDocument27 pagesDesign and Performance of Deep Excavations in Soft Claysozdemir_bNo ratings yet
- Soil Maps and Materials Data Storage 1978Document36 pagesSoil Maps and Materials Data Storage 1978Lima PalaveNo ratings yet
- EN1997 5 Simpson Opt PDFDocument95 pagesEN1997 5 Simpson Opt PDFshykojcrsaNo ratings yet
- The Execution of Ground Anchor WorksDocument11 pagesThe Execution of Ground Anchor Worksغسان لو خماسيNo ratings yet
- GEO5 programs - Part 2Document66 pagesGEO5 programs - Part 2jasamnaj100% (1)
- Design of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsFrom EverandDesign of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsAlain PuechNo ratings yet
- Beach ChangeDocument10 pagesBeach ChangeHRCNo ratings yet
- Modeling Tombolos in GENESISDocument4 pagesModeling Tombolos in GENESISHRCNo ratings yet
- MarsDocument21 pagesMarsHRCNo ratings yet
- VTRANS Tech PaperDocument11 pagesVTRANS Tech PaperHRCNo ratings yet
- Submarine Pipes - FurgorDocument4 pagesSubmarine Pipes - FurgorHRCNo ratings yet
- Grids Rows and Columns in MathematicaDocument30 pagesGrids Rows and Columns in MathematicaHRCNo ratings yet
- MicroStation Training GuideDocument72 pagesMicroStation Training Guidekdj07No ratings yet
- TENAX - Reinforced Soil Slopes - Case StudyDocument1 pageTENAX - Reinforced Soil Slopes - Case StudyHRCNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Observation LogDocument1 pageAstronomy Observation LogHRCNo ratings yet
- Dyalog APL DotNet Interface GuideDocument222 pagesDyalog APL DotNet Interface GuideHRCNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Astronomy: Mike Swanson January 2005Document9 pagesIntroduction To Astronomy: Mike Swanson January 2005HRCNo ratings yet
- Dyalog APL Object ReferenceDocument612 pagesDyalog APL Object ReferenceHRCNo ratings yet
- ExoplanetsDocument10 pagesExoplanetsHRCNo ratings yet
- Astronomy SketchpadDocument1 pageAstronomy SketchpadHRCNo ratings yet
- Dyalog APL For UNIX Installation and User GuideDocument54 pagesDyalog APL For UNIX Installation and User GuideHRCNo ratings yet
- Dyalog APL Workspace Transfer GuideDocument24 pagesDyalog APL Workspace Transfer GuideHRCNo ratings yet
- Guide To The Code LibrariesDocument37 pagesGuide To The Code LibrariesHRCNo ratings yet
- User CommandsDocument42 pagesUser CommandsHRCNo ratings yet
- User GuideDocument222 pagesUser GuidePaolo MocellinNo ratings yet
- Dyalog APL DotNet Interface GuideDocument222 pagesDyalog APL DotNet Interface GuideHRCNo ratings yet
- Dyalog APL Programmer's Guide & Language ReferenceDocument766 pagesDyalog APL Programmer's Guide & Language ReferenceHRCNo ratings yet
- Tuning Applications Using The Profile User CommandDocument22 pagesTuning Applications Using The Profile User CommandHRCNo ratings yet
- Dyalog APL Interface GuideDocument334 pagesDyalog APL Interface GuideHRCNo ratings yet
- MarsDocument21 pagesMarsHRCNo ratings yet
- Israel Trains Route MapDocument2 pagesIsrael Trains Route MapHRCNo ratings yet
- SaturnDocument10 pagesSaturnHRCNo ratings yet
- Folding Protein StabilityDocument79 pagesFolding Protein StabilityEsaú E RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Dyalog APL Interface GuideDocument334 pagesDyalog APL Interface GuideHRCNo ratings yet
- FGC NetworkDocument2 pagesFGC NetworkbadmotorfingerNo ratings yet
- MarsDocument21 pagesMarsHRCNo ratings yet