Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy Storage: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013
Energy Storage: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013
Uploaded by
gthulasi7871260 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesEnergy
Original Title
Energy-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnergy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesEnergy Storage: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013
Energy Storage: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013
Uploaded by
gthulasi787126Energy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Energy Storage
Energy is stored to use it at a different time than when it
was generated.
The process of converting the energy to storable form
means that some energy is lost.
Additional energy is lost when the energy is released or
recovered.
Ideally, storage is avoided to have a more efficient process.
Renewable energy, however, is often intermittent (like wind
and sun), and storage allows use at a convenient time.
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
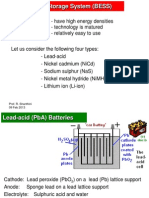
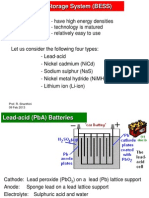
Types of Energy Storage
Electricity can be stored by converting it into another form
such as potential, kinetic or chemical energy.
Electrical energy storage technologies include the following
types of storage media:
- Battery electric storage system (BESS)
- Flow batteries
- Fuel cells
- Flywheel energy storage (FES)
- Superconducting magnetic energy storage (SMES)
- Super capacitor energy storage (SCES)
- Compressed air energy storage (CAES)
- Pumped hydro energy storage (PHES)
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
Energy and Buildings 42 (2010) 21242130
Pumped Hydro Energy Storage (PHES)
Electricity is produced from this 27-billion gallon reservoir using six
turbines that drive electric generators. The same turbines double as
giant water pumps to fill the reservoir with water from Lake Michigan.
Real-life example:
1872 MW generating capacity
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
www.consumersenergy.com/content.aspx?id=1830
Pumped Hydro Energy Storage (PHES)
Reversible pump-turbine can spin an alternator to generate
electricity.
It also can act as a pump to pump water uphill using electricity.
This reversibility allows excess electrical energy to be used to
pump water to a higher storage reservoir to be used as an
energy source later.
PHES is the most widespread high-energy storage
technique.
PHES provides rapid response (<1 minute) to support
intermittent renewable generation.
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
Pumped Hydro Energy Storage (PHES)
The energy used to pump a water volume (V) to a height (h)
with a specific pumping efficiency (p) is given by:
Epumping =
ghV
p
The energy supplied to the electrical network by a generator
of efficiency (g) can be obtained by:
Egenerator = g h V g
Overall efficiency of the energy storage system
= Egenerator / Epumping
Prof. R. Shanthini
09 Feb 2013
http://www.sc.ehu.es/sbweb/energias-renovables/temas/almacenamiento/almacenamiento.html
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 2.5 Field Of A Sheet Of Charge: Adding the effects of all the strips; dy' ρDocument5 pages2.5 Field Of A Sheet Of Charge: Adding the effects of all the strips; dy' ρgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- 01maxwells Equations5Document5 pages01maxwells Equations5gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of ChargesDocument7 pagesMaxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of Chargesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Electromagnetics 1 PDFDocument4 pagesElectromagnetics 1 PDFgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of ChargesDocument3 pagesMaxwell's Equations (SI Units) Differential Form: Density of Chargesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
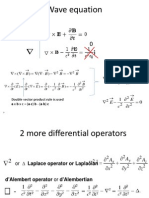
- Differential Operators: A A A A X y ZDocument3 pagesDifferential Operators: A A A A X y Zgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Displacement Current & Maxwell's EquationsDocument4 pagesDisplacement Current & Maxwell's Equationsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic Fields and UnitsDocument3 pagesElectric and Magnetic Fields and Unitsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell - Equations 2Document6 pagesMaxwell - Equations 2gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- With This Terminology, We Can Say That:: Line Integrals of Conservative Vector Fields Are Independent of PathDocument6 pagesWith This Terminology, We Can Say That:: Line Integrals of Conservative Vector Fields Are Independent of Pathgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Engine Sealing, Gaskets, and Fastener Torque: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument5 pagesEngine Sealing, Gaskets, and Fastener Torque: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learninggthulasi787126No ratings yet
- The Following Theorem Says That The Only Vector Fields That Are Independent of Path Are ConservativeDocument4 pagesThe Following Theorem Says That The Only Vector Fields That Are Independent of Path Are Conservativegthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Maxwell - Equations 1Document5 pagesMaxwell - Equations 1gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Choose Any Point (X, Y) in The Disk With X X.: Conservative Vector FieldDocument4 pagesChoose Any Point (X, Y) in The Disk With X X.: Conservative Vector Fieldgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- As Is Independent of Path, It Does Not Matter Which Path C From (A, B) To (X, Y) Is Used To Evaluate F (X, Y)Document5 pagesAs Is Independent of Path, It Does Not Matter Which Path C From (A, B) To (X, Y) Is Used To Evaluate F (X, Y)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Lithium Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013Document5 pagesLithium Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- We Assume That D Is Open - Which Means That, For Every Point P in D, There Is A Disk With Center P That Lies Entirely in DDocument4 pagesWe Assume That D Is Open - Which Means That, For Every Point P in D, There Is A Disk With Center P That Lies Entirely in Dgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Most Computer Algebra Systems (CAS) Have Commands That Compute The Curl and Divergence of Vector FieldsDocument5 pagesMost Computer Algebra Systems (CAS) Have Commands That Compute The Curl and Divergence of Vector Fieldsgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Notice The Similarity To What We Know From Section 12.4:: A X A 0 For Every Three-Dimensional (3-D)Document5 pagesNotice The Similarity To What We Know From Section 12.4:: A X A 0 For Every Three-Dimensional (3-D)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- F I J K: X y Z P Q R R Q P R Q P y Z Z X X yDocument6 pagesF I J K: X y Z P Q R R Q P R Q P y Z Z X X ygthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Nickel Metal Hydride (Nimh) Batteries: H) 2 / 1 (Oh E 2 MM O HDocument3 pagesNickel Metal Hydride (Nimh) Batteries: H) 2 / 1 (Oh E 2 MM O Hgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Nickel Cadmium (Nicd) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013Document5 pagesNickel Cadmium (Nicd) Batteries: Prof. R. Shanthini 09 Feb 2013gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Sodium Sulphur (Nas) BatteriesDocument4 pagesSodium Sulphur (Nas) Batteriesgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Vector CalculusDocument6 pagesVector Calculusgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Lead-Acid (Pba) Batteries: DrawbacksDocument5 pagesLead-Acid (Pba) Batteries: Drawbacksgthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Energy Storage 5Document5 pagesEnergy Storage 5gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Battery Electric Storage System (BESS) : - Have High Energy Densities - Technology Is Matured - Relatively Easy To UseDocument6 pagesBattery Electric Storage System (BESS) : - Have High Energy Densities - Technology Is Matured - Relatively Easy To Usegthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Energy Storage 2Document4 pagesEnergy Storage 2gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)Document6 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage (FES)gthulasi787126No ratings yet
- Mechanical Energy Storage-1Document4 pagesMechanical Energy Storage-1gthulasi787126No ratings yet