Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wrist Injury
Uploaded by
mariyalqibtiyahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wrist Injury
Uploaded by
mariyalqibtiyahCopyright:
Available Formats
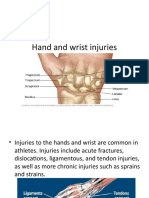
HAND AND WRIST
INJURIES
AOSSM SPORTS TIPS
With so many bones, ligaments, tendons,
and joints keeping hands and wrists
working, there is ample opportunity for
injury. In fact, injuries to the hand and
wrists are some of the most common
ailments facing athletes. If managed
properly, however, most athletes can
expect their injury to heal without any
significant long-term disability.
WHAT ARE THE MOST
COMMON SPORTS-RELATED
HAND AND WRIST INJURIES?
There are a number of injuries that
may occur in an athletes hands or
wrists. They can be classified into two
main categories: traumatic (acute)
and overuse (chronic).
Traumatic injuries are more likely to
occur in athletes who participate in
sports that require higher levels of contact (i.e., football, hockey, or wrestling),
whereas overuse injuries result in
athletes who participate in sports that
require them to overdo a particular
movement (i.e., baseball, tennis, or golf).
Some common traumatic injuries in
athletes include joint dislocations,
sprains, muscle strains, broken bones,
tendon inflammation, and ligament
tears. The most common fracture
injury in the athletic population occurs
in the fingers.
Overuse injuries are stress-induced
and include tendon inflammation and
dislocation, nerve injury, and over use
stress fractures. Long-term disability
is less likely to occur from overuse
injuries than from traumatic injuries.
However, if left untreated, an athletes
sports performance may be significantly
diminished. Surgical treatment may be
required if an injury persists.
WHAT SHOULD I DO IF I
INJURE MY HAND OR WRIST?
Should you sustain a hand or wrist injury
while participating in a game where an
attending team physician is not present,
seek immediate medical care if any of
the following symptoms are present:
Severe pain
Severe swelling
Numbness
Coldness or grayness in the
finger, hand, or wrist
Abnormal twisting or bending
of the finger or hand
A clicking, grating, or shifting
noise while moving your finger,
hand, or wrist
Bleeding that does not slow and
persists for more than 15 minutes.
Contact your physician during regular
practice hours if mild wrist pain, bruising, or swelling after an injury persists
and does not improve after two weeks.
For minor hand injuries, home treatment, including rest, ice, compression,
and elevation to the effected limb can
help relieve pain, swelling, and stiffness.
An anti-inflammatory medication such
as ibuprofen or naproxen may also
be taken to help with the pain and
inflammation.
WHAT TREATMENT OPTIONS
ARE AVAILABLE FOR HAND
AND WRIST INJURIES?
Treatment depends on the location,
type, duration, and severity of the
injury. While surgery is needed for
some injuries, such as ligament tears,
medication, buddy-taping (taping
the injured finger to a neighboring
one for support), splints, braces, casts,
or physical therapy may be used as
a treatment option. Your doctor will
determine the best option, taking into
consideration short and long-term
damage; deformities, and stiffness.
HOW CAN I PREVENT A
HAND OR WRIST INJURY?
Wearing wrist guards, gloves, and
stretching are just a few ways to help
prevent a traumatic hand or wrist
injury. You can prevent overuse injuries
by taking breaks to rest the hands
or wrists, using proper posture and
technique, and utilizing protective
equipment.
Expert Consultant
Dan Matthews, MD
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
American Physical Therapy Association
American Medical Society for Sports
Medicine
Sports Tips are brought to you by the American
Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine. They
provide general information only and are not
a substitute for your own good judgement or
consultation with a physician. To order multiple
copies of this fact sheet or learn more about
other orthopaedic sports medicine topics, please
visit www.sportsmed.org.
Copyright 2008. American Orthopaedic
Society for Sports Medicine. All rights reserved.
Multiple copy reproduction prohibited.
HAND AND WRIST INJURIES
COMMON HAND AND WRIST INJURIES
INJURY
CAUSES/DESCRIPTION
SYMPTOMS
TREATMENT
RETURN TO PLAY
Jammed Finger
Striking the end of the finger
while fully extended
Pain, swelling at the joint,
difficult to bend, tenderness
over the joint
Ice, rest, buddy tape
to adjacent finger
As tolerated with
buddy tape
Finger Fracture
Force of contact overwhelms
strength of bone (ball, ground,
helmet)
Pain, tenderness over the bone,
deformity may be present
Ice, splint, doctor
evaluation, X-rays
Only after proper evaluation,
realignment from a physician,
and wearing appropriate
protection until healed
Mallet Finger
Impact on tip of finger
leads to rupture of tendon
that holds finger tip straight
Unable to hold small joint
at finger tip out straight,
tender just behind nail
Doctor evaluation,
splinting finger in
full extension 8 weeks
May return as tolerated in
splint which must be worn
at all times for 8 weeks
Nail Bed Injury
Impact or crushing injury
on top of nail
Blood under nail, tender
may represent tear in
nailbed under nail
If blood covers >50% of
nail, need doctor evaluation
may need repair of nail bed
As tolerated
Finger
Dislocation
Force on finger overwhelms
ligaments and joint displaces
Most common at middle
joint of finger, with visible
displacement
Relocation of joint best
performed by doctor, may
require local anesthesia
and X-ray evaluation. May
require surgery.
After proper evaluation,
use buddy tape or splint
as determined by physician
Tendon Tear
Jersey Finger
Force of grasp with object
(jersey) pulling away,
ruptures tendon
Most commonly seen in
ring finger, unable to flex
the joint at finger tip
Needs medical evaluation
within 2448 hours,
requires surgery, possibly
within 10 days
Only after surgical repair
is fully healed. Early RTP
places the athlete at risk
of long-term problems with
finger function and motion
Wrist Bone
Fracture
Scaphoid
Fall on outstretched hand
Pain with wrist motion,
tenderness in wrist at
the base of thumb
Needs doctor evaluation
may require special X-ray
(CT scan). May require
surgery.
Not allowed until thorough
evaluation by physician. If
fracture present may be able
to return with proper protection (cast) which is worn
until healed.
Wrist Ligament
Tear
Impaction or twisting
injury of wrist
Pain in wrist with gripping
rotation of wrist
Needs physician evaluation,
X-rays, possible MRI
Not allowed until thorough
evaluation by physician.
Evaluation and early treatment
can prevent long-term problems.
Ulnar Collateral
Ligament Tear
Skiers Thumb
Tear of ligament that
stabilizes the thumb
with grasping
Pain and instability of thumb
with grasping objects
Needs physician evaluation,
X-rays, may need surgery
or casting
May return to play in
cast protection.
Tendonitis
Repetitive activity of one
specific movement
Tenderness over the tendon
may feel grading over tendon
with finger or wrist motion
Rest, ice, limitation of
repetitive motion, NSAIDS
As tolerated
Stress Fractures
Repetitive activity overcomes
strength of bones and leads to
small fractures
Pain with activity, most
commonly in lower
extremities (running,
jumping)
Physician evaluation, X-rays,
bone scans, may need casting,
surgery, must have rest,
nutritional evaluation
Must rest and cease
offending activity until fully
healed. May need bone growth
stimulator, casting, surgery
Growth Plate
Stress
Over stressing bone of still
growing children, most commonly
seen in gymnastics (wrist bone),
baseball pitchers(shoulder, elbow)
Persistent pain, tenderness
swelling over growing bone,
bone pain/tenderness
Physician evaluation rest,
ice, must cease offending
activity
Athlete cannot return to
play until fully healed as
growing problems can have
long-term problems
You might also like
- Jocko Willink Workout GuideDocument3 pagesJocko Willink Workout GuideJulius Adams77% (13)
- Medical Student HandbookDocument36 pagesMedical Student HandbookJulius AdamsNo ratings yet
- Diamond-Cut Abs, How To Engineer The Ultimate Six-PackDocument244 pagesDiamond-Cut Abs, How To Engineer The Ultimate Six-PackJulius Adams80% (5)
- Brooks Kubik - Dinosaur DietDocument22 pagesBrooks Kubik - Dinosaur Dietjacksparrow291% (11)
- All About Arthritis- Find Updated Causes, Symptoms, Diagnostic Tests, New Alternative Treatments, Cures and BreakthroughsFrom EverandAll About Arthritis- Find Updated Causes, Symptoms, Diagnostic Tests, New Alternative Treatments, Cures and BreakthroughsNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal TraumaDocument103 pagesMusculoskeletal TraumaJona Kristin EnclunaNo ratings yet
- Atlas of TitanDocument380 pagesAtlas of TitanJulius Adams86% (22)
- Typical Shoulder TroublesDocument7 pagesTypical Shoulder TroublesLev KalikaNo ratings yet
- B JJ ManifestoDocument42 pagesB JJ ManifestoJulius AdamsNo ratings yet
- Professor Atilla's Five Pound Dumb-Bell ExerciseDocument76 pagesProfessor Atilla's Five Pound Dumb-Bell ExerciseCullen O'Gorman87% (23)
- Hand and Wrist InjuriesDocument25 pagesHand and Wrist InjuriesMAMA LALA100% (2)
- Euphoria 2021 F K Anyone Whos Not A Sea Blob Part 2 Jules Script Teleplay Written by Sam Levinson and Hunter SchaferDocument40 pagesEuphoria 2021 F K Anyone Whos Not A Sea Blob Part 2 Jules Script Teleplay Written by Sam Levinson and Hunter SchaferMadalena Duarte7No ratings yet
- 50 Greyskull ConditioningDocument66 pages50 Greyskull ConditioningVicente Ambrosio Torres83% (6)
- Tennis Elbow RehabDocument8 pagesTennis Elbow RehabDarren Willis100% (2)
- Knee Pain: Treating Knee Pain: Preventing Knee Pain: Natural Remedies, Medical Solutions, Along With Exercises And Rehab For Knee Pain ReliefFrom EverandKnee Pain: Treating Knee Pain: Preventing Knee Pain: Natural Remedies, Medical Solutions, Along With Exercises And Rehab For Knee Pain ReliefRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Wrist PainDocument8 pagesWrist PainLev KalikaNo ratings yet
- Occlusal Considerations in Implant Therapy Clinical Guidelines With Biomechanical Rationale PDFDocument10 pagesOcclusal Considerations in Implant Therapy Clinical Guidelines With Biomechanical Rationale PDFSoares MirandaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Tennis ElbowDocument5 pagesJurnal Tennis ElbowMuhamad Fahrizal RilahiNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide For City PhotographyDocument48 pagesThe Ultimate Guide For City Photographygbhat62No ratings yet
- Tennis Elbow or Lateral Epicondylitis: Key PointsDocument10 pagesTennis Elbow or Lateral Epicondylitis: Key PointsMarliani AfriastutiNo ratings yet
- Uma Lesson 3Document0 pagesUma Lesson 3Julius Adams100% (1)
- Lumbar Spine ExamDocument2 pagesLumbar Spine ExamJulius AdamsNo ratings yet
- Melbourne ACL Rehabilitation Guide - Gabriel Bala PDFDocument32 pagesMelbourne ACL Rehabilitation Guide - Gabriel Bala PDFgabi balaNo ratings yet
- The Nine Success Principles of Japan's Greatest Swordsman, Musashi Miyamoto PDFDocument42 pagesThe Nine Success Principles of Japan's Greatest Swordsman, Musashi Miyamoto PDFDiana RiveraNo ratings yet
- A Flowering Tree NotesDocument4 pagesA Flowering Tree Notesparidhi50% (4)
- Tactical Booklet 5-5-11Document24 pagesTactical Booklet 5-5-11Raul Guerrero100% (1)
- Nanotechnology in Civil EngineeringDocument22 pagesNanotechnology in Civil EngineeringNehad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)Document8 pagesLateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)Rusu AdrianNo ratings yet
- Ghost Hawk ExcerptDocument48 pagesGhost Hawk ExcerptSimon and SchusterNo ratings yet
- Guide To HandstandDocument23 pagesGuide To HandstandmargaritassNo ratings yet
- Ankle and Foot InjuriesDocument42 pagesAnkle and Foot InjuriesJulius Adams100% (1)
- Hand Injuries: by LakshmiprabhaDocument50 pagesHand Injuries: by LakshmiprabhaLakshmiprabha KalyanaramanNo ratings yet
- Sprains and StrainsDocument15 pagesSprains and StrainsPutri ClaraNo ratings yet
- SPRAINS: Overstretching or Tearing The Ligaments Results in A Sprain. Ligaments Are The Bands ofDocument7 pagesSPRAINS: Overstretching or Tearing The Ligaments Results in A Sprain. Ligaments Are The Bands ofPriyanshu KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Sports Injuries in Wrist & Hand.Document72 pagesSports Injuries in Wrist & Hand.salmankhan09215No ratings yet
- Cotul Reumatic EnglezaDocument7 pagesCotul Reumatic EnglezaElena GaneaNo ratings yet
- Tendonitis Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsDocument6 pagesTendonitis Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsSylvia GraceNo ratings yet
- Patellar Tendonitis TreatmentDocument7 pagesPatellar Tendonitis TreatmentRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Types of Knee InjuriesDocument6 pagesTypes of Knee InjuriesSagarNo ratings yet
- Surgery WorkDocument9 pagesSurgery WorkHigh TechNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between An Acute Injury and A Chronic Injury?Document10 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between An Acute Injury and A Chronic Injury?Tafadzwa PiyoNo ratings yet
- KneeDocument3 pagesKneedoos1No ratings yet
- Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer's Elbow) What Is Medial Epicondylitis?Document4 pagesMedial Epicondylitis (Golfer's Elbow) What Is Medial Epicondylitis?Kalamegam RamasamiNo ratings yet
- Sprain: P P P PDocument4 pagesSprain: P P P PJc RocuyanNo ratings yet
- PE 2 Midterm ModulesDocument20 pagesPE 2 Midterm ModulesEsra May AngadNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis PocDocument4 pagesOsteoarthritis PocIrene Joy GomezNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Applied Medicine BY: Dr. Kinza IftikharDocument16 pagesOsteoarthritis: Applied Medicine BY: Dr. Kinza IftikharsabaamjadNo ratings yet
- 04 Wrist and Hand Injuries in Sport Acute Soft Tissue InjuriesDocument65 pages04 Wrist and Hand Injuries in Sport Acute Soft Tissue InjuriesKhushboo IkramNo ratings yet
- PIP Joint InjuryDocument4 pagesPIP Joint InjurySAYEM AHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- The Common Sports: Fashion GeneralDocument17 pagesThe Common Sports: Fashion GeneralShiela Jane Langga SanghidNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: T Person's of Developing Osteoarthritis. It IncludesDocument5 pagesOsteoarthritis: T Person's of Developing Osteoarthritis. It IncludesLove Shery SabrosoNo ratings yet
- Knucle JointDocument2 pagesKnucle Joint12ranjNo ratings yet
- G11 - Pe 2 - Module 1Document7 pagesG11 - Pe 2 - Module 1John Lois VanNo ratings yet
- Stress FracturesDocument11 pagesStress FracturesSURWEZ'SNo ratings yet
- Distal Radius Fractures (Broken Wrist) - OrthoInfo - AAOSDocument4 pagesDistal Radius Fractures (Broken Wrist) - OrthoInfo - AAOSmuhammad iqbal mahfuzhNo ratings yet
- Word To PDFDocument119 pagesWord To PDFshravaniNo ratings yet
- Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) - OrthoInfo - AAOSDocument8 pagesTennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) - OrthoInfo - AAOSnoony 98No ratings yet
- Sprains, Strains and Other Soft-Tissue Injuries: CauseDocument5 pagesSprains, Strains and Other Soft-Tissue Injuries: CauseYosef OxinioNo ratings yet
- Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College Physiotherapy Department Study Year 2020-2021Document13 pagesErbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College Physiotherapy Department Study Year 2020-2021Muhamad SdeqNo ratings yet
- Lateral and Medial Epicondylitis-1Document21 pagesLateral and Medial Epicondylitis-1Jalil AhmadNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder ProblemsDocument14 pagesShoulder Pain and Common Shoulder ProblemsRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Elbow Tendinopathy (Tennis and Golf Elbow)Document5 pagesElbow Tendinopathy (Tennis and Golf Elbow)Siddharth PillaiNo ratings yet
- What Causes Osteoarthritis?Document9 pagesWhat Causes Osteoarthritis?jajabsNo ratings yet
- Tendonitis - Harvard HealthDocument3 pagesTendonitis - Harvard Healthroadwhiz.infoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Submitted To DR Iqra Naz 70063678 Habiba Jameel DPT 10 Semester. Topic: ArthritisDocument10 pagesAssignment Submitted To DR Iqra Naz 70063678 Habiba Jameel DPT 10 Semester. Topic: ArthritisMuiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- Wrist Tendonitis - What Is Wrist Tendonitis?: CausesDocument1 pageWrist Tendonitis - What Is Wrist Tendonitis?: CausesenadNo ratings yet
- InjuryDocument34 pagesInjuryenajejohn9No ratings yet
- Common Sports InjuriesDocument24 pagesCommon Sports InjuriesChris PatlingraoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Jonaidi T, SPKFR Instalasi Rehabilitasi Medik Rsud Dr. Soedarso, PontianakDocument29 pagesDr. Jonaidi T, SPKFR Instalasi Rehabilitasi Medik Rsud Dr. Soedarso, PontianakHerlam SyahNo ratings yet
- Ankle SprainDocument4 pagesAnkle SprainSakthi Annamalai.cNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis EssayDocument8 pagesOsteoarthritis EssayMeysha PNo ratings yet
- Trigger Finger: AnatomyDocument4 pagesTrigger Finger: AnatomyAlfun IqbalNo ratings yet
- Wrist Injury at SiteDocument10 pagesWrist Injury at SiteClark Angelo JuanNo ratings yet
- Sports TreatmentDocument84 pagesSports TreatmentBASAVARAJNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders Part 7 Sports InjuriesDocument67 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders Part 7 Sports InjuriesCarmela Lacsa DomocmatNo ratings yet
- Sprains and Strains FFDocument4 pagesSprains and Strains FFBryan De HopeNo ratings yet
- Common Injuries and First Aid TreatmentDocument22 pagesCommon Injuries and First Aid TreatmentebullientcynosureNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument38 pagesFinalKeanna Marie MarfilNo ratings yet
- Different Sports InjuriesDocument11 pagesDifferent Sports InjuriesregineNo ratings yet
- How To Identify and Treat Inner Knee PainDocument6 pagesHow To Identify and Treat Inner Knee PainRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument63 pagesOsteoarthritisDuaa BalochNo ratings yet
- Path Demanding Volume 1 PDFDocument224 pagesPath Demanding Volume 1 PDFJulius AdamsNo ratings yet
- WHM 20 Day Cold Shower Challenge2018pdf PDFDocument1 pageWHM 20 Day Cold Shower Challenge2018pdf PDFJulius AdamsNo ratings yet
- Working Agile EightCCSMDocument2 pagesWorking Agile EightCCSMJulius AdamsNo ratings yet
- Australian Science Teachers Journal Sep 2000 46, 3 Education ModuleDocument7 pagesAustralian Science Teachers Journal Sep 2000 46, 3 Education ModuleJulius AdamsNo ratings yet
- FMS AppendicesDocument16 pagesFMS AppendicesJulius AdamsNo ratings yet
- Examination of The KneeDocument5 pagesExamination of The KneeJulius AdamsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Sports TrainingDocument155 pagesFundamentals of Sports TrainingJulius AdamsNo ratings yet
- 3.6-6kva Battery Cabinet: 1600Xp/1600Xpi SeriesDocument22 pages3.6-6kva Battery Cabinet: 1600Xp/1600Xpi SeriesIsraelNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 1 Class X Social Science Time 3 Hrs. M.M 80 General InstructionsDocument6 pagesPractice Paper 1 Class X Social Science Time 3 Hrs. M.M 80 General Instructionsvvs .b.s1453No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Reco ScriptDocument2 pagesGrade 11 Reco ScriptCecill Nicanor LabininayNo ratings yet
- Job Offer Electrical EngineerDocument3 pagesJob Offer Electrical EngineerAbner ZaldivarNo ratings yet
- Tan Shuy v. MaulawinDocument10 pagesTan Shuy v. MaulawinheyoooNo ratings yet
- East Coast Yacht's Expansion Plans-06!02!2008 v2Document3 pagesEast Coast Yacht's Expansion Plans-06!02!2008 v2percyNo ratings yet
- Healthy Boundaries Healthy MinistryDocument5 pagesHealthy Boundaries Healthy MinistryMailey GanNo ratings yet
- Music For BandDocument143 pagesMusic For BandTedTerroux604No ratings yet
- IFAS - Presentation - S2Document21 pagesIFAS - Presentation - S2Abinash BiswalNo ratings yet
- Baughman Don Marianne 1977 NigeriaDocument11 pagesBaughman Don Marianne 1977 Nigeriathe missions networkNo ratings yet
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument9 pagesIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDaniella mae ElipNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 2 June 2001Document11 pagesMaths Paper 2 June 2001Shelin FarmerNo ratings yet
- Marxist - Political Science IGNOUDocument15 pagesMarxist - Political Science IGNOUDesi Boy100% (2)
- Regulations ON Academic Matters: Tezpur UniversityDocument21 pagesRegulations ON Academic Matters: Tezpur UniversitybishalNo ratings yet
- ACT 1, SCENE 7: Macbeth's CastleDocument3 pagesACT 1, SCENE 7: Macbeth's CastleViranthi CoorayNo ratings yet
- Please DocuSign Youssef ADMISSIONS FORM W ATDocument5 pagesPlease DocuSign Youssef ADMISSIONS FORM W ATyoussefkhalfaoui30No ratings yet
- SC9 Vocab GHI - Buddhism - ClozeDocument2 pagesSC9 Vocab GHI - Buddhism - ClozeBeakerika shortsNo ratings yet
- IOM - Recovery Through Lok Adalat - HODocument5 pagesIOM - Recovery Through Lok Adalat - HOAbhishek BarwalNo ratings yet
- List of Affilited CollegesDocument28 pagesList of Affilited Collegesuzma nisarNo ratings yet
- Setup Venture Basic Rigging Training EnglishDocument34 pagesSetup Venture Basic Rigging Training EnglishAhmad LuqmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Marks: 30: InstructionsDocument2 pagesAssignment Marks: 30: InstructionsbishtamitdipNo ratings yet
- From St. Francis To Dante-Translations From The Chronicle of The Franciscan Salimbene, 1221-1288Document489 pagesFrom St. Francis To Dante-Translations From The Chronicle of The Franciscan Salimbene, 1221-1288Jake SalNo ratings yet
- Milkfish Tilapia TunaDocument5 pagesMilkfish Tilapia Tunatonbar000No ratings yet
- Pengembangan Transferable Skills Dalam PembelajaraDocument12 pagesPengembangan Transferable Skills Dalam PembelajaraKesat RiyanNo ratings yet