Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power Interruption Tester For Restart Circuit
Uploaded by
JulietaEric0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThe document describes a power interruption tester that was designed to test the operation of restart circuits in compressors. The tester uses a 555 timer circuit to create a variable width pulse that turns off a triac, interrupting power to the compressor under test for 20 to 50 milliseconds. By simulating brief power interruptions, the tester can determine if a restart circuit is needed to prevent the compressor from stalling under load. It has been used to characterize different pumps and identify which ones require a restart circuit to operate reliably after a power glitch.
Original Description:
Circuit who uses a Triac
Original Title
Power Interruption Tester for Restart Circuit
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes a power interruption tester that was designed to test the operation of restart circuits in compressors. The tester uses a 555 timer circuit to create a variable width pulse that turns off a triac, interrupting power to the compressor under test for 20 to 50 milliseconds. By simulating brief power interruptions, the tester can determine if a restart circuit is needed to prevent the compressor from stalling under load. It has been used to characterize different pumps and identify which ones require a restart circuit to operate reliably after a power glitch.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesPower Interruption Tester For Restart Circuit
Uploaded by
JulietaEricThe document describes a power interruption tester that was designed to test the operation of restart circuits in compressors. The tester uses a 555 timer circuit to create a variable width pulse that turns off a triac, interrupting power to the compressor under test for 20 to 50 milliseconds. By simulating brief power interruptions, the tester can determine if a restart circuit is needed to prevent the compressor from stalling under load. It has been used to characterize different pumps and identify which ones require a restart circuit to operate reliably after a power glitch.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
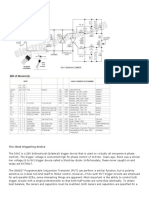
Power interruption tester for restart circuit
Electronic Design
Contributing Author
Contributing Author
Fri, 1998-05-01 (All day)
Compressors are susceptible to brief power interruptions as short as 30 ms or 2 cycles of ac
power. Even these short glitches may cause a pump to stall when its under load. To
alleviate this potential hazard, a restart circuit was designed. It controls a valve that opens
momentarily to relieve the load after the power interruption. The powerinterruption tester
presented here was designed to test the operation of the restart circuit. It also has been
used to characterize pumps and determine which ones require a restart circuit.
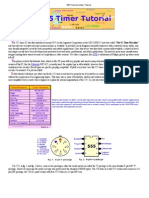
The power interruption circuit uses a 555 timer to create the variable width pulse that
momentarily turns off a triac. The triac functions as an electronic switch supplying ac power
to the pump under test. The circuit is activated by pressing a momentary contact switch.
This supplies a ground to the positive end of C2, which has been charged to +5 V. By setting
the value of C2 to 1 F, the contacts of the switch are debounced and wont retrigger the 555
one shot. The leading edge of the pulse is transferred to the trigger in-put of the one shot.
The 555 timer circuit is configured as the standard one-shot design. C3 is the timing
capacitor and chosen to be 1 F, while R3 is a variable 50k potentiometer. Having it in
series with R5, a 33k resistor, allows the pulse duration to vary from 20 to 50 ms. Changing
these values can easily provide alternative pulse widths and adjustment ranges.
The pulse is coupled to the optoisolator through R4. Resistor R6 assists in wave-shaping the
pulse. The output of the one shot is low until it fires. This condition maintains the isolator
and the triac in the conducting state. When the one shot fires, the output switches to 5 V,
which causes the isolator to remove the drive signal to the output triac. The triac remains
open or off for the duration of the pulse.
The triac chosen for this application is a 2N6071. This part provides plenty of current
capability for the largest motors that were tested. The 800-V breakdown voltage offers
plenty of margin if the tester is to be used on 230-V motors. It was mounted on a heat sink
to assure that the load of larger motors didnt cause the triac to overheat. Using the power
interruption tester makes it convenient to simulate the effect of power-line glitches that can
occur with momentary failures due to storms or maintenance operations.
You might also like
- DC DC Converter BOMDocument1 pageDC DC Converter BOMFady HachemNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Protection For Single Phasing, Overvoltage and Over TemperatureDocument13 pagesInduction Motor Protection For Single Phasing, Overvoltage and Over Temperatureصدام حسینNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Triac ControlDocument6 pagesTriac ControlSyaiful BakhriNo ratings yet
- Circuits Controlling Relays PageDocument5 pagesCircuits Controlling Relays PageBenjamin DoverNo ratings yet
- Parallel Operation of Transformers With Non-Identical TapsDocument13 pagesParallel Operation of Transformers With Non-Identical TapsRohini DesaiNo ratings yet
- Varius and Explanation PDFDocument7 pagesVarius and Explanation PDFnormangNo ratings yet
- AN1060 Flyback L6561Document12 pagesAN1060 Flyback L6561Armando SánchezNo ratings yet
- Cyclic On - Off Timer For Cooler PumpDocument2 pagesCyclic On - Off Timer For Cooler PumpPrabhat SagarNo ratings yet
- Power Transfer and Circuit Breaker TypesDocument15 pagesPower Transfer and Circuit Breaker TypesHimanshu Soni100% (1)
- AppNote03 Uc3842Document14 pagesAppNote03 Uc3842Heriberto Flores AmpieNo ratings yet
- Aplicacion Uc3842Document15 pagesAplicacion Uc3842Gian Mejia100% (1)
- Slua 143Document15 pagesSlua 143Tonia KataNo ratings yet
- Flyback Converters With The L6561 PFC Controller: AN1060 Application NoteDocument11 pagesFlyback Converters With The L6561 PFC Controller: AN1060 Application NotegrittinjamesNo ratings yet
- Transient Over Voltage Due To Switching Operation of Industrial Motor by Vacuum Circuit Breaker and Suppression of SurgesDocument4 pagesTransient Over Voltage Due To Switching Operation of Industrial Motor by Vacuum Circuit Breaker and Suppression of SurgesHo Jun XianNo ratings yet
- Single Phasing EffectsDocument41 pagesSingle Phasing EffectsdiljithNo ratings yet
- Report MosfetDocument13 pagesReport MosfetaiswaryaNo ratings yet
- Testing A MOSFETDocument5 pagesTesting A MOSFETinter2176No ratings yet
- Basler BE1-60 DatasheetDocument8 pagesBasler BE1-60 DatasheetstuartsjgNo ratings yet
- 1mrk508002-Ben B en Time Relays RXKL 1 and RXKM 2hDocument8 pages1mrk508002-Ben B en Time Relays RXKL 1 and RXKM 2hDave ChaudhuryNo ratings yet
- Controlled Switching of High-Voltage Circuit-BreakersDocument8 pagesControlled Switching of High-Voltage Circuit-BreakersBaris GurbuzNo ratings yet
- SYNCHRONOUS SWITCHING OF CIRCUIT-BREAKERSDocument5 pagesSYNCHRONOUS SWITCHING OF CIRCUIT-BREAKERSFaridahmad AziziNo ratings yet
- RTCCDocument9 pagesRTCCer_ashutosh87No ratings yet
- Elec SMPS2Document4 pagesElec SMPS2Victor D'souzaNo ratings yet
- O & M of Sub-Station Equipment: Narender Kumar Me Mba MieDocument31 pagesO & M of Sub-Station Equipment: Narender Kumar Me Mba MiewaleedalzaidiNo ratings yet
- Put As An SCR Triggering CKTDocument6 pagesPut As An SCR Triggering CKTGeorgieDominguezAtienza100% (1)
- AUTO CONTROLLER FOR PETROL (Revised)Document25 pagesAUTO CONTROLLER FOR PETROL (Revised)Hamed RazaNo ratings yet
- Light Dimmer Circuit: The Ideal Triggering DeviceDocument4 pagesLight Dimmer Circuit: The Ideal Triggering DeviceEmmanuel MiguelNo ratings yet
- MFAC14 Application GuidanceDocument22 pagesMFAC14 Application GuidanceleedodsonNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current TransformersDocument27 pagesVoltage and Current TransformersRebekah Powell100% (1)
- Lab 6 Kawalan MotorDocument20 pagesLab 6 Kawalan MotorMohd FiqrieNo ratings yet
- Piezo Power Drive EPEDocument7 pagesPiezo Power Drive EPEShubhamJainNo ratings yet
- 41Document11 pages41Evgeniy IvkoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Modern Power Electronics Components and SystemsDocument16 pagesIntroduction to Modern Power Electronics Components and SystemsdanimannyNo ratings yet
- Protection Systems TransformerDocument14 pagesProtection Systems Transformerrajabharath12No ratings yet
- Automated Unified System For LPG UsingDocument84 pagesAutomated Unified System For LPG UsingVirat KaliNo ratings yet
- asHU NEWDocument38 pagesasHU NEWDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- ABB-RADSB UserAs Guide Transformer Differential Protection RADSBDocument52 pagesABB-RADSB UserAs Guide Transformer Differential Protection RADSBmentong100% (1)
- 555 Timer - Oscillator TutorialDocument14 pages555 Timer - Oscillator TutorialfgaluppoNo ratings yet
- Review - Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset For Temporary Fault and Trip For Permanent FaultDocument4 pagesReview - Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset For Temporary Fault and Trip For Permanent FaultMukeshNo ratings yet
- 220kV Transmission Substation PresentationDocument17 pages220kV Transmission Substation PresentationadarshNo ratings yet
- Static Excitation SystemDocument44 pagesStatic Excitation Systemgigelu79No ratings yet
- 2001jun15 Amd An2015Document8 pages2001jun15 Amd An2015Saurabh BhiseNo ratings yet
- ABB MCB CatalogDocument16 pagesABB MCB CatalogkarthiknmanuNo ratings yet
- Siemens SFU CATALOGUEDocument24 pagesSiemens SFU CATALOGUEMadhan Kumar92% (13)
- Project On Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset On Temporary Fault and Permanent Trip OtherwiseDocument34 pagesProject On Three Phase Fault Analysis With Auto Reset On Temporary Fault and Permanent Trip OtherwiseAkashPratap2100% (21)
- Document Mini Project No 1.117Document8 pagesDocument Mini Project No 1.117rahmat100% (1)
- Tap Changer: Voltage ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesTap Changer: Voltage Considerations1balamanianNo ratings yet
- Contactor de Estado SolidoDocument3 pagesContactor de Estado SolidoCruz RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaFrom EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)