Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ralph Joseph Sandoval FIN 111-0 AY01
Ralph Joseph Sandoval FIN 111-0 AY01
Uploaded by
raprapOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ralph Joseph Sandoval FIN 111-0 AY01
Ralph Joseph Sandoval FIN 111-0 AY01
Uploaded by
raprapCopyright:
Available Formats
Ralph Joseph Sandoval
FIN 111-0 AY01
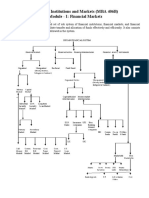
Types of Financial Markets
1. Capital Market - Is one in which individuals and institutions trade financial securities.
Organizations and institutions in the public and private sectors also often sell
securities on the capital markets in order to raise funds. Thus, this type of market is
composed of both the primary and secondary markets.
2. Stock Market - allow investors to buy and sell shares in publicly traded companies.
3. Bond Market/Debt Market - is the market where debt instruments are traded. Debt
instruments are assets that require a fixed payment to the holder, usually with
interest. Examples of debt instruments include bonds (government or corporate) and
mortgages.
4. Money Market - Is a segment of the financial market in which financial instruments
with high liquidity and very short maturities are traded. The money market is used by
participants as a means for borrowing and lending in the short term, from several days
to just under a year.
5. Cash Market - is a public financial market in which financial instruments or
commodities are traded for immediate delivery.
6. Derivatives Market - Is the financial market for derivatives, financial instruments like
futures contracts or options, which are derived from other forms of assets. The market
can be divided into two, that for exchange-traded derivatives and that for over-thecounter derivatives.
7. Over the Counter Market - A decentralized market, without a central physical location,
where market participants trade with one another through various communication
modes such as the telephone, email and proprietary electronic trading systems. An
over-the-counter (OTC) market and an exchange market are the two basic ways of
organizing financial markets.
You might also like
- Global Finance and Electronic BankingDocument16 pagesGlobal Finance and Electronic BankingKrishaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finacial Markets Final With Refence To CDSLDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Finacial Markets Final With Refence To CDSLShoumi Mahapatra100% (1)
- Chapter 1 (Role of Financial Markets and Institutions)Document25 pagesChapter 1 (Role of Financial Markets and Institutions)Momenul Islam Mridha Murad100% (2)
- Intro To Fin MarketsDocument3 pagesIntro To Fin Markets65xykwtn8rNo ratings yet
- Financial Market TopicDocument31 pagesFinancial Market TopicGautam MahtoNo ratings yet
- A Quanittative Study of Nepalese Stock ExchangeDocument87 pagesA Quanittative Study of Nepalese Stock ExchangenirajNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction of Financial MarketDocument5 pages1.1 Introduction of Financial MarketAbdul NomanNo ratings yet
- Module 04 Financial Markets and InstrumentsDocument13 pagesModule 04 Financial Markets and InstrumentsGovindNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Financial Markets and Instruments Group 1 FM7Document23 pagesModule 2 Financial Markets and Instruments Group 1 FM7hikunanaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document5 pagesTopic 2Jeffrey RiveraNo ratings yet
- FMI NotesDocument93 pagesFMI Notesjain_ashish_19888651No ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Institutionschap 2Document8 pagesFinancial Markets and Institutionschap 2Ini IchiiiNo ratings yet
- Minute Paper - Philippine Financial MarketDocument1 pageMinute Paper - Philippine Financial MarketIan Paul CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- International Financial MarketDocument36 pagesInternational Financial MarketSmitaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document7 pagesTopic 1Jeffrey RiveraNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument2 pagesFinancial MarketsSaira Ishfaq 84-FMS/PHDFIN/F16No ratings yet
- Financial Market & InstrumentDocument73 pagesFinancial Market & InstrumentSoumya ShettyNo ratings yet
- Copy of SS-BF-II-12 WEEK 3 Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesCopy of SS-BF-II-12 WEEK 3 Lecture NotesSheanne GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Raja Shekar ReddyDocument42 pagesRaja Shekar ReddypavithrajiNo ratings yet
- Big Picture in Focus: Ulob. Differentiate The Types of Financial MarketsDocument10 pagesBig Picture in Focus: Ulob. Differentiate The Types of Financial MarketsJohn Stephen PendonNo ratings yet
- Classification of Financial MarketsDocument12 pagesClassification of Financial Marketsvijaybhaskarreddymee67% (6)
- FMDocument7 pagesFMA.K.S.PNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Their Role in EconomyDocument6 pagesFinancial Markets and Their Role in EconomyMuzammil ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Financial/ Securities Markets Notes: For Sebi Grade A & Rbi Grade BDocument10 pagesFinancial/ Securities Markets Notes: For Sebi Grade A & Rbi Grade BAadeesh JainNo ratings yet
- Types of Financial MarketsDocument2 pagesTypes of Financial MarketsMher Edrolyn Cristine LlamasNo ratings yet
- Notes On Financial SystemsDocument62 pagesNotes On Financial SystemsamitNo ratings yet
- Financial System and MarketsDocument32 pagesFinancial System and Marketsmohamedsafwan0480No ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument5 pagesFinancial MarketRoxanne Jhoy Calangi VillaNo ratings yet
- MGT of Financial MKT & Instu CH-3Document7 pagesMGT of Financial MKT & Instu CH-3fitsumNo ratings yet
- Ifm WS 1Document6 pagesIfm WS 1singhai_sud3138No ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument25 pagesMoney Marketvicky_n007No ratings yet
- Financial Markerts: An OverviewDocument9 pagesFinancial Markerts: An OverviewArly Kurt TorresNo ratings yet
- 3.the Money Market Refers To A Segment of The Financial Market Where ShortDocument6 pages3.the Money Market Refers To A Segment of The Financial Market Where Shortkhageswarsingh865No ratings yet
- # Fin. Market Chapter 3Document5 pages# Fin. Market Chapter 3Kanbiro OrkaidoNo ratings yet
- Industry Profile: Financial MarketDocument17 pagesIndustry Profile: Financial MarketAprameya kowshikNo ratings yet
- Capital MarketDocument8 pagesCapital Marketkomal_studentNo ratings yet
- Capital MarketDocument34 pagesCapital MarketVaibhavRanjankarNo ratings yet
- 2.1 To 2.6 CONCEPT & FINANCIAL MARKET STRUCTURE IN INDIA PDFDocument30 pages2.1 To 2.6 CONCEPT & FINANCIAL MARKET STRUCTURE IN INDIA PDFImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Business EconomicsDocument9 pagesBusiness EconomicsSachin MethreeNo ratings yet
- BY: Osama Tariq. Sajawal. Adnan Shahzad. Shaikh Ahmed AliDocument36 pagesBY: Osama Tariq. Sajawal. Adnan Shahzad. Shaikh Ahmed Alishaikh ahmedNo ratings yet
- CH04 FimDocument4 pagesCH04 Fimfentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- GigiDocument2 pagesGigiAleko tamiruNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Reports From Group 1 6Document104 pagesCompilation of Reports From Group 1 6Kearn CercadoNo ratings yet
- Bba Notes 6Document53 pagesBba Notes 6RAJATNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial MarketDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Financial Marketmaria evangelistaNo ratings yet
- IFS Chapter 3Document26 pagesIFS Chapter 3riashahNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument5 pagesFinancial MarketSaif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document18 pagesChapter 8Marie Sheaneth BalitangNo ratings yet
- Capital Market Management: Mr. Abner A. AquinoDocument95 pagesCapital Market Management: Mr. Abner A. AquinoKizzandria BayotNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document10 pagesChapter 4Muhammed YismawNo ratings yet
- In The Primary MarketDocument5 pagesIn The Primary MarketDickson NsiimeNo ratings yet
- Fin MarketsDocument5 pagesFin MarketsDarra MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Final Blackbook by Sanju PDF VARSHADocument67 pagesFinal Blackbook by Sanju PDF VARSHAYukta SalviNo ratings yet
- GR12 Business Finance Module 3-4Document8 pagesGR12 Business Finance Module 3-4Jean Diane JoveloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 FM: Money MarketDocument4 pagesLesson 2 FM: Money MarketChristina MalaibaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Financial Markets and InstrumentsDocument61 pagesChapter Two Financial Markets and InstrumentsKume MezgebuNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument13 pagesFinancial MarketRajeswari KuttimaluNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Financial InstrumentsDocument80 pagesFinancial Markets and Financial Instrumentsabhijeit86100% (2)
- Types of Financial Markets Wihtin The Financial SystemDocument2 pagesTypes of Financial Markets Wihtin The Financial SystemRod'z Tan LongaresNo ratings yet
- Tool and Die Industry 01132015Document1 pageTool and Die Industry 01132015raprapNo ratings yet
- 3 Pages EssayDocument7 pages3 Pages EssayraprapNo ratings yet
- English 103 Basic Techniques in Technica PDFDocument8 pagesEnglish 103 Basic Techniques in Technica PDFraprapNo ratings yet
- Fin 110 Notes Chapter I: Introduction Concept of Risk Definition of RiskDocument10 pagesFin 110 Notes Chapter I: Introduction Concept of Risk Definition of RiskraprapNo ratings yet
- Written Act 1Document1 pageWritten Act 1raprapNo ratings yet
- Intellectual CapitalDocument2 pagesIntellectual CapitalraprapNo ratings yet
- Cost of Capital (REVIEWER)Document4 pagesCost of Capital (REVIEWER)raprapNo ratings yet
- Republic vs. GingoyonDocument65 pagesRepublic vs. GingoyonraprapNo ratings yet
- Ralph Joseph Sandoval TAX 001 - BY02: Brief BackgroundDocument2 pagesRalph Joseph Sandoval TAX 001 - BY02: Brief BackgroundraprapNo ratings yet
- HO3Document2 pagesHO3raprapNo ratings yet
- Managerial GraduateDocument8 pagesManagerial GraduateraprapNo ratings yet
- Development Across LifespanDocument6 pagesDevelopment Across Lifespanraprap100% (1)
- Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesInterview QuestionsraprapNo ratings yet