Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Noise Suppression by Low-Pass Filters 3.11. Understanding Ferrite Bead Inductors
Noise Suppression by Low-Pass Filters 3.11. Understanding Ferrite Bead Inductors
Uploaded by
Nattanapong KongtrakulOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Noise Suppression by Low-Pass Filters 3.11. Understanding Ferrite Bead Inductors
Noise Suppression by Low-Pass Filters 3.11. Understanding Ferrite Bead Inductors
Uploaded by
Nattanapong KongtrakulCopyright:
Available Formats
This is the PDF file of text No.TE04EA-1.
No.TE04EA-1.pdf 98.3.20
3. Noise Suppression by Low-pass Filters
3.11. Understanding Ferrite Bead Inductors
Understanding Ferrite Bead
Inductors
23
At high frequencies, ferrite bead inductors work like resistors instead of inductors.
Equivalent circuit
L(f)
In a low-frequency range
R(f)
as frequency increases
In a high-frequency range
The inductance (L) is
dominant.
The resistance (R) is
dominant.
Examples of impedance characteristic
Ferrite bead inductor
Reference: Coil for high-frequency filter circuits
(Air-core coil)
100k
1k
Impedance ()
Impedance ()
10k
100
Z
R
10
1k
Z
100
10
1
1
10
50 100
500 1000
10
50 100
500 1000
Frequency (MHz)
Frequency (MHz)
Resistance is small.
(The loss is low, i.e. Q is high.)
Resistance is dominant.
(The loss is high.)
In addition to small stray capacitance, ferrite bead inductors have
another excellent feature. At high frequencies, this type of inductor
works not as an inductor but as a resistor, and dissipates noise in
the form of heat.
The above graphs show examples of the impedance curves
exhibited by a ferrite bead inductor and coil for high-frequency
filter circuits. Z shows the impedance and R shows the
resistance. The R is high in the ferrite bead inductor.
23
[Notes]
This is the PDF file of text No.TE04EA-1.
No.TE04EA-1.pdf 98.3.20
3. Noise Suppression by Low-pass Filters
3.12. Structure of Chip Ferrite Bead Inductors
Structure of Chip Ferrite Bead
Inductors
24
Structure of chip ferrite bead inductors
Input and Output terminal
Input and Output terminal
(b) Winding electrode type
(a) Straight electrode type
Electrode pattern
Electrode pattern
The above drawings show the structure of chip ferrite bead
inductors. An electrode pattern, which forms a feedthrough
electrode, is printed on ferrite sheets. These sheets are stacked to
form a chip inductor. When larger impedance is required, the
electrode pattern on each sheet in connected through the via-holes
to form a winding electrode type chip inductor.
Unlike general inductors, both chip types are designed so that
stray capacitance is small.
24
[Notes]
This is the PDF file of text No.TE04EA-1.
No.TE04EA-1.pdf 98.3.20
3. Noise Suppression by Low-pass Filters
3.13. Impedance Characteristic
Impedance Characteristic
25
Example of different impedance characteristic
1500
Sample B
Impedance ()
1200
900
600
Sample A
300
10
100
Frequency (MHz)
1000
Examples of measured signal waveforms (10 MHz)
No filter
Sample A
Sample B
With ferrite bead inductors, the impedance characteristic varies depending on the material and
structure. The signal waveform and noise suppression effect vary depending on the impedance.
With ferrite bead inductors the impedance varies depending upon
the material and internal structure. The above graphs show
examples of signal waveforms varying with impedance. The signal
frequency is 10 MHz. When selecting a ferrite bead inductor, it is
necessary to consider the impedance in the noise band and also
the impedance gradient.
25
[Notes]
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Amanda Tremblay at Citrine Software SolutionsDocument3 pagesOn Amanda Tremblay at Citrine Software SolutionssanjaanNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Lions Mane Ultimate Guide 00Document1 pageLions Mane Ultimate Guide 00János JuhászNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Gl-300 Gps Tracker User Manual Rev2Document28 pagesGl-300 Gps Tracker User Manual Rev2ravelsteinNo ratings yet
- BACnet Aplication GuideDocument502 pagesBACnet Aplication GuideLaercio Marques100% (3)
- Leonard Schiff Quantum MechanicsDocument563 pagesLeonard Schiff Quantum Mechanicssxydxt100% (5)
- Lesson 1 Checklist and Rating ScalesDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Checklist and Rating ScalesCivlerf Naej DaZo SetnobNo ratings yet
- Sices - Gc315 - Modbus Map - Eaas0575-Xa (Editado)Document169 pagesSices - Gc315 - Modbus Map - Eaas0575-Xa (Editado)Laercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- FREE Advance ManualDocument188 pagesFREE Advance ManualLaercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- Hot BitDocument1 pageHot BitLaercio Marques100% (1)
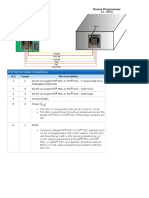
- Flow-Based Programming: J.Paul Morrison J.P. Morrison Enterprises LTDDocument28 pagesFlow-Based Programming: J.Paul Morrison J.P. Morrison Enterprises LTDLaercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- Motorola - Regulator Switching MC34063ADocument12 pagesMotorola - Regulator Switching MC34063ALaercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- !!! ReadMe !!!from - Evgeny972Document2 pages!!! ReadMe !!!from - Evgeny972Laercio Marques0% (2)
- Motorola - Regulator Switching MC34063ADocument12 pagesMotorola - Regulator Switching MC34063ALaercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- ICD-S/U To Target ConnectionsDocument1 pageICD-S/U To Target ConnectionsLaercio Marques100% (1)
- 12v Ac DC mc34063 Led Buck Driver PDFDocument7 pages12v Ac DC mc34063 Led Buck Driver PDFLaercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- Vishay - VOM 3052Document7 pagesVishay - VOM 3052Laercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- IDTech - A SecuRED User ManualDocument40 pagesIDTech - A SecuRED User ManualLaercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- Daycounter Inc - Snubber Circuit Design CalculatorsDocument5 pagesDaycounter Inc - Snubber Circuit Design CalculatorsLaercio Marques100% (1)
- ED&C FloTHERM 12 Key Considerations in Enclosure Thermal Design A High-Level How To GuideDocument11 pagesED&C FloTHERM 12 Key Considerations in Enclosure Thermal Design A High-Level How To GuideLaercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- Prolon PL-RSC - EDocument3 pagesProlon PL-RSC - ELaercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- PIC18F45K22Document560 pagesPIC18F45K22Mauricio Rosas50% (2)
- Guidelines For Proper Wiring of An RS-485 Network - AN763Document11 pagesGuidelines For Proper Wiring of An RS-485 Network - AN763Laercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- BACnet Network Set Up and TroubleshootingDocument80 pagesBACnet Network Set Up and TroubleshootingLaercio Marques100% (1)
- Manual - ND 4600 5000 Operation ManualDocument9 pagesManual - ND 4600 5000 Operation ManualLaercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- RabbitCore RCM3700 (019-0136 - L)Document169 pagesRabbitCore RCM3700 (019-0136 - L)Laercio Marques67% (3)
- Noise Reduction Techniques For Supress Noise in Electronic SystemDocument224 pagesNoise Reduction Techniques For Supress Noise in Electronic SystemLaercio MarquesNo ratings yet
- TM 9 2320 280 20 2Document954 pagesTM 9 2320 280 20 2Angel Torres100% (2)
- 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) PDFDocument27 pages4 - Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) PDFmcclaink06No ratings yet
- Powerapps Design TemplatesDocument17 pagesPowerapps Design TemplatesMarino AbreuNo ratings yet
- 170 ArticleText 811 1 10 20191214 PDFDocument15 pages170 ArticleText 811 1 10 20191214 PDFMohammad KenigiNo ratings yet
- Turcon Varilip PDR: Trelleborg Se Aling SolutionsDocument41 pagesTurcon Varilip PDR: Trelleborg Se Aling SolutionsaceinsteinNo ratings yet
- ChartsOnly KV-2Document38 pagesChartsOnly KV-2BroooooNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Csa 8 SCDocument7 pagesJurnal Csa 8 SCPutri MinasariNo ratings yet
- Lua Introduction For New Programmers: Download Slides atDocument47 pagesLua Introduction For New Programmers: Download Slides atRandy MarmerNo ratings yet
- Everyday Dynamo: Practical Uses For BIM Managers: Session 3.1 & 3.2Document27 pagesEveryday Dynamo: Practical Uses For BIM Managers: Session 3.1 & 3.2Pablo Vega SilvaNo ratings yet
- How To Confirm A Delete in An ASPDocument10 pagesHow To Confirm A Delete in An ASPrenierolivaNo ratings yet
- Jinko 250WDocument1 pageJinko 250WCruz López MargaritoNo ratings yet
- Magic Lite Catalogue 2021Document136 pagesMagic Lite Catalogue 2021sandu scNo ratings yet
- Job Description - Vendor Development ManagerDocument3 pagesJob Description - Vendor Development ManagerPramod Kumar100% (2)
- PROSPECTUS 2021-22 FinalDocument36 pagesPROSPECTUS 2021-22 FinalAmitava BasuNo ratings yet
- BrixDocument5 pagesBrixAKSHAT TIWARINo ratings yet
- EsynDocument13 pagesEsynchanchalkNo ratings yet
- Samruddhi Thopate ViitDocument1 pageSamruddhi Thopate ViitROHANT NARANGNo ratings yet
- Road Transport BottlenecksDocument3 pagesRoad Transport BottlenecksmelodyNo ratings yet
- Creating A Custom HTML Theme - TumblrDocument16 pagesCreating A Custom HTML Theme - TumblrfluidreduxNo ratings yet
- Let Us Know Who You Are: Guest Details 1 Payment 2 ConfirmationDocument3 pagesLet Us Know Who You Are: Guest Details 1 Payment 2 ConfirmationFahrudin AlkhemiNo ratings yet
- ECA Clean Rooms HVAC Systems 2023 Live Online TrainingDocument4 pagesECA Clean Rooms HVAC Systems 2023 Live Online TrainingRahul RajNo ratings yet
- Airline Reservation SystemDocument81 pagesAirline Reservation SystemBanagiri AkhilNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Leisure Activities Lesson 6 Skills 2Document16 pagesUnit 1 Leisure Activities Lesson 6 Skills 2ScentCandleNo ratings yet
- Xcell Ammonia (NH) Sensor: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesXcell Ammonia (NH) Sensor: Technical Data SheetPaulo HeideckeNo ratings yet
- SG - Closed Sets in Topological Spaces: Pauline Mary Helen MDocument11 pagesSG - Closed Sets in Topological Spaces: Pauline Mary Helen MArnav GudduNo ratings yet