Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gear Notes
Gear Notes
Uploaded by
Risira Erantha Kannangara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views17 pagesGear note
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGear note
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views17 pagesGear Notes
Gear Notes
Uploaded by
Risira Erantha KannangaraGear note
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
SPUR GEARS
GEARS
* toothed members used to transmit
rotary motion from one shaft to
another
* used for mechanical power
transmission
SPUR GEARS
axes of gears sre parallel
CONJUGATE GEAR.
ACTION
OTH
“As the gears rotate. the common
nomnal to the surfaces at the point of
contact must always intersect the line
of centres at the same point, P, which is
called the pitch point”
Line behwern gear
Cenbens
The most common gear shape that
satisfies this condition is called the
INVOLUTE gear profile
Fry
CONJUGATE GEAR-TOOTH
ACTION
“As the gears rotate, the common
normal to the surfaces at the point of
contact must always intersect the line
of centres at the same point, P, which is
called the pitch point”
The most common gear shape that
satisfies this condition is called the
INVOLUTE gear profile
th
MATING SPUR GEARS
Ww,
Pioien
Geuse as
* GEAR -the larger of the two gears
‘% PINION. the smaller of the two gears
% PITCH CIRCLE - locus of the
pitch points
-)
where:
‘g, = anguler velocity of the pinion (rad/s*)
‘,= angular velocity of the gear (rad/s.
4, pitch circle diameter of the pinion (m)
= pitch circle diameter of the gear (m)
Negative sign indicates that clockwise
rotation in one causes anti-clockwise
rotation in the other (and visa versa).
The distance between the centres of the
gears is
ee nx4s) 2 Q)
QTHER TERMINOLOGY
Pitch point, P
Circular pitch, p
Pitch circle diameter, d
Number of teeth, N
Module (m) = d (mm) +)
N
‘ny is inmm per tooth
The module is fixed for a given set of
mating gears (gear train)
mranges from 0.2 to~6
mm (um per:
‘tooth)
4 6.35
3 5.08
10
15
20
40
80
The contact force between two mating
gears is always at the same angle, This
is known as the pressure angle, 9.
“Involute profile maintains a
constant pressure angle as the gears
rotate”
Pressure angle, = 20° for UK, Europe
and Asia.
Vener Cert t
GEAR FORCE ANALYSIS
an
ren fa
Dewen
A tangential force, F;, is transmitted to
the mating gear due to the torque:
where F, = T/(d/2) wf)
Also, a radial force, F,, is generated due
to the angle of contact between the
mating gears (j.¢. pressure angle):
where F, =F, tan > 6)
F, acts towards the centre of the mating
gear and is reacted by the shaft
supporting the gear.
Torque, power and speed are related
by:
POWER (W) = TORQUE (Nm) x
ANGULAR VELOCITY (rad/s)
P=To 6)
where o=22S$
60
+7)
(Sinrpm)
EXAMPLE — THREE MATING SPUR GEARS
EXAMPLE — THREE MATING SPER GEASS
mS ay,
Eews
Gea A
On = Mex NA = 2x20 = 4O mm
UW = Looe xtx + 104-92 rdf
60
Powe = Tow
7. Ta = 28,000 = 238.22 Nm
POD
we Fe = Ta = 28833 = 1/23G6N
(ay) 302
- = ied EN
f= Fe tend = IAI x Fon 20°
f= 434 4N
We = - S236 male (is opponte
Geac C
Merman Baas
SO mw
We = ~ da ay
de
Wes = 9 *(- 5240)
We t+ 83628 wl Ao
B
Te = Fe * (4)
= ABE ~ (288) New Fe
2
= Z9R HL Nim
Force axeced ear Bon tts shaft
ey
Power = Te We
= 29R42 x 83+F% 19
a
Forces in kN
We
DOVELE REDUCTION GEA TANS
- Gud
M
heh
Few fozet > tet) “Trereal*[
WACK
Abel
ag, ay
Fe = 23-02 Ky
Nobe
An equal and opposite Lome 15
Septied, by the shatt on the “idler
jer,
nm
View from dirction Y Agplied Mahe Beye.
— eee
(4/2)
Driver OY
8 a ae Th =F (de
Dever (&A) (i)
Hance ~
Feceas on Counter hat 7 Ao the beénonal planet
Faram g
Fe
Rar Rua Fe
€
md Raw Rae by Taking momante
2 Tn Phe verlest planers
7
Fetund
a S
Ru
Aso Fink Ry, and Ruy By Foley monet
Fe tong
s
Rua
3, Toke) Dear radial loads c—
Zant ary CAN) toads
R £
he
Rar Rue
14
BUGLE KEWCTION _ Genegox SAMPLE
ee SAKES
For the Previous
cont puntbion t=
M = Me = 2 > memes 3
Na = Lo Nos 1S
Ne =20 Na = 20
R= Skv @ 800 «pes
BC = bom | = 200
Caleta = Taper % Oubpet reqne
% adicl fort so beans
Aisin te pover losses.
TH He eleven, af ead gear pate ik
FSD, calalke He nas reqs ok gene
EPICYCLIC (PLANETARY) GEAR TRAINS
PLANET
ARM
Son
RING
eg. 3 planet gear system
2i
EPICYCLIC (PLANETARY) GEAR TRAINS
» ARM is not attached to SUN gear
> Generally 2 or more PLANET gears equally spaced
> Increase in torque and power capacity
> Used in automatic gearboxes (c.g. cars)
3 MODES OF OPERATION
1. With the ARM fixed
simple gear train, SUN and RING rotate in the opposite
direction (c.g. reverse gear)
2. With the RING fixed
SUN and ARM rotate in the same direction
3. With the SUN fixed
RING and ARM rotate in the same direction but with a
different speed ratio to Option 2.
ite. These three members have three functions, depending on the.mode of
operation:-
> INPUT
>» OUTPUT
> FIXED REACTION MEMBER
A clutch is used to lock any two of the SUN, ARM or RING together.
Under these conditions, the whole system rotates as a single unit.
ANALYSIS OF FORCES
In this analysis ,the SUN is fixcd (ic. SUN is reaction member)
To
ANALYSIS OF FORCES
a
Lek
Oe
an
as
de
= RAG dvamber
= ROM NY amater
= Sow diamtee
= RAweT diameter
a
(AeA)
"
W
a
26
hema i~ dy = de sae
2
Br Safes Ti) (deed
3 &A
¢
Te = (de +ds) T,
de
To “(' + o\T
de
Se
Exampic
‘The Figure shows an cpicyclic gear train im which the wheel A
is helt seationary and the arm j= rotated at 300 rpm. The
compound planet B & C rotates freely on a pin carried by the
arm. The number of teeth are:
ASse, B= 20, C30 and D—30 tecth, Find the speed and
rection of wheel D?.
Mo E
c zs
|_-4
ae 1
> “a
T= S0testh | Te 20, to=0 | Ta=30 | ARM
x BC B E
= Rote whole gear
[eonin tram. +m =m. Sm om
2 Fie ARM
rotate. Bie crm | -zovsay 9 +m, Lmaorz0y o
Aaa eS ears) =o pa =
Since Wheel A is held stationary ==> art(z/Sya- O .(1)
& Arm rotmes at 300 rpm >>>> m~300 xpm .-.(2)
From (1) >> n= (5/2)m or n= (5/2) 300+ 750 rpm
Hence, Gear D= m-(4/3) n= 300 - (4/3) 750= -700 rom
You might also like
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- BS Gear StrandedDocument66 pagesBS Gear StrandedRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ISO Tolerance Part 1 PDFDocument34 pagesISO Tolerance Part 1 PDFRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Pre Assessment Questionnaire-EnmsDocument21 pagesPre Assessment Questionnaire-EnmsRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University: Material, Design & Analysis of A Bicycle FrameDocument28 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University: Material, Design & Analysis of A Bicycle FrameRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Drawing of GearboxDocument1 pageDrawing of GearboxRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Design of A Drone With A Robotic End-EffectorDocument8 pagesDesign of A Drone With A Robotic End-EffectorRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Lease Agreement 6976Document5 pagesLease Agreement 6976Risira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Bq76Pl455Evm: Designator Quantity Value Description Packagereference Partnumber ManufacturerDocument3 pagesBq76Pl455Evm: Designator Quantity Value Description Packagereference Partnumber ManufacturerRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Car Component: Product NameDocument4 pagesCar Component: Product NameRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
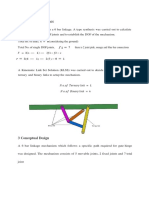
- Mechanism Syntheses: 3 Conceptual DesignDocument9 pagesMechanism Syntheses: 3 Conceptual DesignRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- CFRP 25 KDocument4 pagesCFRP 25 KRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- TOC For Global and China Power Battery Management System (BMS) Industry Report, 2014-2017 at China Market Research ReportsDocument4 pagesTOC For Global and China Power Battery Management System (BMS) Industry Report, 2014-2017 at China Market Research ReportsRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- 2938Document8 pages2938Risira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Catalouge Data Sheet A100Document9 pagesCatalouge Data Sheet A100Risira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Key Shot 6 Whats NewDocument22 pagesKey Shot 6 Whats NewRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Essential Notes PDFDocument11 pagesEssential Notes PDFRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Material Structure Solid WorksDocument10 pagesMaterial Structure Solid WorksRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- A Posteriori Modelling of The Growth Phase of Dalmarnock Fire Test OneDocument9 pagesA Posteriori Modelling of The Growth Phase of Dalmarnock Fire Test OneRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Assignment: .:K.A.Y.L. Harischandra: 090172H:Intellectual PropertyDocument5 pagesAssignment: .:K.A.Y.L. Harischandra: 090172H:Intellectual PropertyRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet
- Value EngineeringDocument24 pagesValue EngineeringRisira Erantha KannangaraNo ratings yet