Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Distance and Velocity Time Graphs
Uploaded by
Sara Jones0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageDistance and Velocity Time Graphs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDistance and Velocity Time Graphs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageDistance and Velocity Time Graphs
Uploaded by
Sara JonesDistance and Velocity Time Graphs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
27
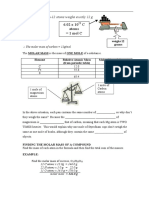
Distance-Time and Velocity-Time Graphs
Make sure you learn all these details real good. Make sure you can distinguish between the two, too.
Distance-Time Graphs Very Important Notes:
500
400
3004-
200
100
10 20 30 40 60 60 70 80 90 100 10 126
1) GRADIENT = PEED.
2) Flat cections are where its stopped.
8) The steeper the graph, the faster it's
going.
4) Downhill sections mean it's coming back |
toward its starting point.
5) Curves represent acceleration or
deceleration.
6) A stespening curve means it's
* speeding up {increasing gradient).
7) A levelling off curve means i's
slowing down (deoressing gradient).
50
40-
30:
20
10
10 20 30 40 60 60 70
Speed from a Dis e-Time Graph — it's just the Gradient
For example the speed of the return section of the graph is: Don't forget that you have to use
Speed = gradient = vertical = 500 = 16.7 m/s the soales of the axes ta work out
horizontal 80 the gradient. Don't measure in om.
| Velocity-Time Graphs | Very Important Notes:
i) 1) GRADIENT = ACCELERATION.
2) Flat sactions represent steady epeed.
8) The steeper the graph, the greater the
acceleration or deceleration.
4) Uphill eections (/) are acceleration.
Deceleration| 6) Downhill sections (\) — deceleration.
6) The area under ony section of he graph
{er all of it) fe equal to the
distance stavelied in that fime interval
7) A curve means changing agoeleration,
80 90 100 110 120
culating Acceleration,
eed and Distan elocity-time.Graph
1) The acceleration represented by the
‘Acceleration = gradient
8) the distance travelled in any fim
between
represent totally different kinds of
Understanding speed and stuff — it can be an uphill struggle...
The tricky thing about these fwo kinds of graph is that they can look pretty much the came but
then there's no substitute for simply learning all the numbered points for both types. Enjoy.
firat section of the graph is:
vertical = 30 = LS m/s?
horizontal 20
2) The speed at any point is simply found by reading the value off the speed axis.
nterval is equal to the area. For example, the distance travelled
80 and t = 100 is equal to the shaded area which is equal fo 1000m.
motion. If you want to be able to do them (in the Exam)
~ Section Two — Forces and Motion
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Psychology Units 1 & 2Document408 pagesPsychology Units 1 & 2Sara Jones100% (4)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Molar MassDocument3 pagesMolar MassSara Jones100% (1)
- Module 4 Further ReadingDocument13 pagesModule 4 Further ReadingSara JonesNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Further ReadingDocument3 pagesModule 3 Further ReadingSara JonesNo ratings yet
- Resultant Force and Terminal Velocity PDFDocument1 pageResultant Force and Terminal Velocity PDFSara JonesNo ratings yet
- Speed Velocity and AccelerationDocument1 pageSpeed Velocity and AccelerationSara JonesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Change Answers PDFDocument3 pagesChemical Change Answers PDFSara JonesNo ratings yet
- Super EssayDocument5 pagesSuper EssaySyed Arif AliNo ratings yet
- Evolution: Glossary: Define The Following TermsDocument2 pagesEvolution: Glossary: Define The Following TermsSara JonesNo ratings yet
- Writing A Literature Review AssignmentDocument2 pagesWriting A Literature Review AssignmentSara Jones100% (1)
- RMIT, Note Taking For LecturesDocument2 pagesRMIT, Note Taking For LecturesSara JonesNo ratings yet