Professional Documents
Culture Documents
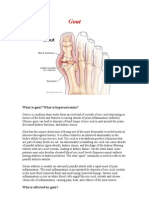
Gout (Also Known As Podagra When It Involves The Joint at The Base of The Big
Uploaded by
dian5christiani5malaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gout (Also Known As Podagra When It Involves The Joint at The Base of The Big
Uploaded by
dian5christiani5malaCopyright:
Available Formats
Gout (also known as podagra when it involves the joint at the base of the big toe)[4] is usually
characterized by recurrent attacks of inflammatory arthritisa red, tender, hot, and swollen joint.
[5]
Pain typically comes on rapidly in less than twelve hours.[6] The joint at the base of the big toe
is affected in about half of cases.[7] It may also result in tophi, kidney stones, or urate
nephropathy.[6]
The cause is a combination of diet and genetic factors. It occurs more commonly in those who
eat a lot of meat, drink a lot of beer, or are overweight. The underlying mechanisms involves
elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. When the uric acid crystallizes, and the crystals deposit
in joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues an attack of gout occurs. Diagnosis may be confirmed
by seeing the characteristic crystals in joint fluid or tophus. Blood uric acid levels may be normal
during an attack.[6]
Treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), steroids, or colchicine improves
symptoms. Once the acute attack subsides, levels of uric acid are usually lowered via lifestyle
changes, and in those with frequent attacks, allopurinol or probenecid provides long-term
prevention.[6] Taking vitamin C and eating a diet high in low fat dairy products may be
preventative.[8]
Gout affects about 1 to 2% of the Western population at some point in their lives. It has become
more common in recent decades which is believed to be due to increasing risk factors in the
population, such as metabolic syndrome, longer life expectancy, and changes in diet. Older
males are most commonly affected.[6] Gout was historically known as "the disease of kings" or
"rich man's disease".[6][9] It has been recognized at least since the time of the ancient Egyptians.[6]
You might also like
- GoutDocument6 pagesGoutNader Smadi100% (1)
- Drug Treatment Options for GoutDocument21 pagesDrug Treatment Options for GoutAlbertoBeltránRojasNo ratings yet
- ASP Strategy Automatic Stop OrdersDocument9 pagesASP Strategy Automatic Stop OrdersTamil SelvaNo ratings yet
- Gouty PowerpointDocument14 pagesGouty PowerpointBSN4ANo ratings yet
- Gouty ArthritisDocument5 pagesGouty ArthritisLorebell100% (3)
- GoutDocument10 pagesGoutAmberNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument5 pagesGoutTeslim RajiNo ratings yet
- Gout Is Usually Characterized by Recurrent Attacks ofDocument15 pagesGout Is Usually Characterized by Recurrent Attacks ofJimmy KusumaNo ratings yet
- Gout Is Usually Characterized by Recurrent Attacks ofDocument14 pagesGout Is Usually Characterized by Recurrent Attacks ofJimmy KusumaNo ratings yet
- Gout Is Usually Characterized by Recurrent Attacks ofDocument17 pagesGout Is Usually Characterized by Recurrent Attacks ofJimmy KusumaNo ratings yet
- Classification and External Resources: Icd 10 Icd 9 Omim Diseasesdb Medlineplus 000422 Emedicine Patient Uk MeshDocument9 pagesClassification and External Resources: Icd 10 Icd 9 Omim Diseasesdb Medlineplus 000422 Emedicine Patient Uk MeshBecky NekesaNo ratings yet
- Gout (Also Known As Podagra When It Involves The Big ToeDocument54 pagesGout (Also Known As Podagra When It Involves The Big ToearunshreerajendranNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: LifestyleDocument12 pagesSigns and Symptoms: LifestyleJimmy KusumaNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle: SLC2A9 SLC22A12 Abcg2Document11 pagesLifestyle: SLC2A9 SLC22A12 Abcg2Jimmy KusumaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Introduction BDocument5 pagesPart 1 Introduction BGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Gouty Arthritis: Presented By: Petit Ivy Mae B. NacarioDocument21 pagesGouty Arthritis: Presented By: Petit Ivy Mae B. NacarioMarivic DianoNo ratings yet
- Gout Gout (Also Known As Podagra When It Involves The Big Toe) Is ADocument5 pagesGout Gout (Also Known As Podagra When It Involves The Big Toe) Is AJoanna Erika TanNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument32 pagesGoutEren YooNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: For Other Uses, SeeDocument27 pagesDiarrhea: For Other Uses, SeeCrimzonic ShadeNo ratings yet
- All About Gout: A Patient Guide To Managing GoutDocument8 pagesAll About Gout: A Patient Guide To Managing Goutmath_mallikarjun_sapNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument15 pagesGoutRatih PurwaningsihNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Gout EnglishDocument8 pagesJurnal Gout EnglishPutri ArtikaNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument12 pagesGoutEarle Jimenez Niervo RN100% (1)
- Case Study ScriptDocument5 pagesCase Study ScriptTRECHIA DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Akram Et AlDocument3 pagesAkram Et AlElok IzawatiNo ratings yet
- Osh State UniversityDocument14 pagesOsh State Universitykhuzaima9No ratings yet
- Clinpharm M4 ReviewerDocument10 pagesClinpharm M4 ReviewerCHARLES RONALD GENATONo ratings yet
- Understanding KwashiorkorDocument7 pagesUnderstanding KwashiorkorpraneethNo ratings yet
- Preview: Originally Published in Therapeutic Guidelines: Rheumatology, Version 2, 2010Document2 pagesPreview: Originally Published in Therapeutic Guidelines: Rheumatology, Version 2, 2010Hannah CoNo ratings yet
- Agis Mira Dewi, S.kedDocument35 pagesAgis Mira Dewi, S.kedAgiish EMdeNo ratings yet
- Pseudogout Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument6 pagesPseudogout Diagnosis and TreatmentAl TaMiraNo ratings yet
- Gout Management: Understanding The Science, Causes, And Treatment Options For Gout ReliefFrom EverandGout Management: Understanding The Science, Causes, And Treatment Options For Gout ReliefNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Nutritional Status of The Patients Suffering From Gout in KashmirDocument12 pagesAssessment of Nutritional Status of The Patients Suffering From Gout in KashmirTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Lect # 2 Care of Patients With Gout and Paget's DiseaseDocument21 pagesLect # 2 Care of Patients With Gout and Paget's DiseaseShayan ShayanNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases and Epidemics: PolioDocument7 pagesCommon Diseases and Epidemics: PolioTheAwein ChannelNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Avian Renal Disease: Christal Pollock, DVM, DABVP-AvianDocument22 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Avian Renal Disease: Christal Pollock, DVM, DABVP-AvianjudithNo ratings yet
- CaseDocument66 pagesCaseJustin HannahNo ratings yet
- Gout - Anusha V HDocument11 pagesGout - Anusha V HAnusha VhNo ratings yet
- Name: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859Document12 pagesName: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859drng48No ratings yet
- CholestasisDocument8 pagesCholestasisCrina LupuNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis - (Arthrose in Europe) how to Prevent and Treat This Disease AccordinglyFrom EverandOsteoarthritis - (Arthrose in Europe) how to Prevent and Treat This Disease AccordinglyNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY- MEDCOREDocument4 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY- MEDCORELady Jean Milan ColataNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis in Adults and Older Children: EpidemiologyDocument4 pagesGastroenteritis in Adults and Older Children: Epidemiologyjotq19No ratings yet
- Gout An Old Disease in New Perspective - A ReviewDocument75 pagesGout An Old Disease in New Perspective - A ReviewdimasNo ratings yet
- Liver DiseasesDocument335 pagesLiver DiseasesdipakrussiaNo ratings yet
- Gout Term PaperDocument8 pagesGout Term Paperafmzubkeaydllz100% (1)
- MonuzDocument22 pagesMonuzH.M. AriyanNo ratings yet
- Dimension of Development:: Health AwarenessDocument28 pagesDimension of Development:: Health AwarenessMelNo ratings yet
- What Is GoutDocument11 pagesWhat Is GoutProser Faith TabaculdeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacy Aspects of Some DiseasesDocument67 pagesClinical Pharmacy Aspects of Some Diseasessurya tejaNo ratings yet
- Go To:: NtroductionDocument7 pagesGo To:: Ntroductionputri dirgahayuNo ratings yet
- FSN 315 Research PaperDocument15 pagesFSN 315 Research Paperapi-637701165No ratings yet
- Particularly Unpasteurised CheesesDocument4 pagesParticularly Unpasteurised Cheeseskarenkaren09No ratings yet
- Hyperuricemia Mohammed Ismail Abdul Samad Ismail Hegazy 2254 Mohamed18378@fvtm - Bu.eg 01277952085Document8 pagesHyperuricemia Mohammed Ismail Abdul Samad Ismail Hegazy 2254 Mohamed18378@fvtm - Bu.eg 01277952085Mohammed Ismail HegazyNo ratings yet
- Non Communicable Disease Grade 7Document4 pagesNon Communicable Disease Grade 7Joshua RamirezNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) : Group A Beta Hemolytic StretococcusDocument3 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) : Group A Beta Hemolytic StretococcusKristine Danielle DejeloNo ratings yet
- Gouty ArthritisDocument12 pagesGouty ArthritisArman IntacNo ratings yet
- Gastritis: Signs and SymptomsDocument11 pagesGastritis: Signs and SymptomsSher KhanNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument3 pagesGoutashylajaraniNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument6 pagesGoutNhoydaleen SandovalNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea InformationDocument6 pagesDiarrhea InformationGanesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Lee Se YoungDocument4 pagesLee Se Youngdian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Is A Class of Diseases That Involve TheDocument1 pageCardiovascular Disease (CVD) Is A Class of Diseases That Involve Thedian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- AntihistaminDocument1 pageAntihistamindian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- HG: Severe Nausea and Vomiting of PregnancyDocument1 pageHG: Severe Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancydian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Is A Class of Diseases That Involve TheDocument1 pageCardiovascular Disease (CVD) Is A Class of Diseases That Involve Thedian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- ECG Records the Heart's Electrical ActivityDocument1 pageECG Records the Heart's Electrical Activitydian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Central Venous PressureDocument1 pageCentral Venous Pressuredian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Is A Class of Diseases That Involve TheDocument1 pageCardiovascular Disease (CVD) Is A Class of Diseases That Involve Thedian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- InsomniaDocument1 pageInsomniadian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Is A Class of Diseases That Involve TheDocument1 pageCardiovascular Disease (CVD) Is A Class of Diseases That Involve Thedian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Phalanx Bone: TechnicalDocument2 pagesPhalanx Bone: Technicaldian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Neoplasm: de Stijl Tumor (Comics)Document1 pageNeoplasm: de Stijl Tumor (Comics)dian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumoniadian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Meningitis (From: Méninx, "Membrane"Document3 pagesMeningitis (From: Méninx, "Membrane"dian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- HEPES (4 - (2-Hydroxyethyl) - 1-Piperazineethanesulfonic Acid) Is ADocument1 pageHEPES (4 - (2-Hydroxyethyl) - 1-Piperazineethanesulfonic Acid) Is Adian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- SinusitisDocument1 pageSinusitisdian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Vertigo Is When A Person Feels As If They or The Objects Around Them Are Moving When They AreDocument1 pageVertigo Is When A Person Feels As If They or The Objects Around Them Are Moving When They Aredian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- hēpar (παρ, root hepat-, πατ-)Document1 pagehēpar (παρ, root hepat-, πατ-)dian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Types and Treatment of DiabetesDocument1 pageTypes and Treatment of Diabetesdian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Cancer, Also Known As A: Malignant Tumor NeoplasmDocument1 pageCancer, Also Known As A: Malignant Tumor Neoplasmdian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Ketrampilan InggrisDocument3 pagesKetrampilan Inggrisdian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet
- Ketrampilan InggrisDocument3 pagesKetrampilan Inggrisdian5christiani5malaNo ratings yet