Professional Documents
Culture Documents
06may CIM Grounding and DC Uptime
06may CIM Grounding and DC Uptime
Uploaded by
scribdkeliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
06may CIM Grounding and DC Uptime
06may CIM Grounding and DC Uptime
Uploaded by
scribdkeliCopyright:
Available Formats
design
Why grounding is critical to
data center uptime
ata centers need to
achieve unprecedented levels
of uptime to keep pace with
modern business demands To
achieve these uptime goals, data
center managers are paying increased attention to facility infrastructure issues, including
the network grounding system.
If youre a contractor, understanding network grounding can give you a competitive
edge by advising your customers on how to improve network
availability.
Proper grounding of data center equipment, often called network grounding or the data
center grounding infrastructure,
is dened by TIA/EIA-942 Telecommunications Infrastructure
Standard for Data Centers, and
goes beyond the requirements
of the National Electrical Code
(NEC) to protect equipment and
improve system reliability.
Grounding by tier
You can gain a competitive edge with your
customers by understanding and then offering
network grounding/bonding expertise.
Network grounding system in a data center
Telecommunications
grounding busbar
Equipment to
rack jumper
AC electrical panel
Paint piercing
hardware
Common bonding network to rack jumper
Source: Panduit
TIA-942 has adopted the tier denition provided by the
Uptime Institute (www.upsite.com). Tier I is the lowest
0605cidef1 informalevel, which allows 28.8 hours of site-caused
tion technology downtime per year. By contrast, Tier IV
data centers used within nancial institutions, Web
hosting organizations, healthcare and others with the
greatest need for critical uptime, have availability rates
of 99.995%. This requires the data center be designed to
experience only 0.4 hours of downtime annuallyless
TOM TURNER is business development manager at Panduit Corp.
(www.panduit.com).
This image of a TIA-942-compliant data center network grounding
system includes the AC electrical panel, which must be bonded by
an electrician. The electrician typically installs a busbar network,
including the telecommunications grounding busbar. Other
elements include the equipment-to-rack jumper, paint-piercing
hardware, and the common bonding network-to-rack jumper.
than 5 seconds per day (Industry Standard Tier Classications Dene Site Infrastructure Performance, authored by
W. Pitt Turner IV, John H. Seader, and Kenneth G. Brill
and available at: www.upsite.com/le_downloads/PDF/
Tier_Classications.pdf). Building data centers to meet
Reprinted with revisions to format, from the May 2006 edition of CABLING INSTALLATION & MAINTENANCE
Copyright 2006 by PennWell Corporation
tier requirements is a complex process, encompassing expertise
in a wide range of technical specialties, including architecture,
cabling infrastructure, electrical design, environmental control, and re protection. To make this task more manageable,
TIA-942 provides design guidelines to help meet the uptime requirements of each tier level.
For example, when designing a Tier I
data center, TIA-942 states, A data center
grounding infrastructure is not required, but
may be desirable as an economic method to
Grounding strips
satisfy equipment manufacturers grounding
for cabinet
requirements. At Tiers III and IV, the data
mounting rails
center infrastructure grounding system is absolutely required.
Contractors are ideally positioned to provide much of the network grounding system,
and those who understand these requirements can provide a value-added service
the expertise to help customers understand
and implement the necessary grounding system to improve their data center.
Network grounding design
additional damaged equipment.
5. All metallic components in the data center shall be bonded
to the grounding system. The goal is to have all conductive materials at the same electrical potential to minimize current ow.
Current ows when there is a dierence in potential between
components. If the current ows across a piece of equipment,
Kits engineered for network grounding
Paint piercing
hardware
Grounding jumper
NEBS Level 3
The two goals of the grounding system are to
compression lugs
Grounding busbar
equalize electrical potentials and to create a
Source:
Panduit
low resistance path to ground. Five basic principles are used when
damage may occur. Equip- Kits made specically for
network
designing a grounding system to accomplish these goals:
ment, racks, cabinets, lad- grounding include: grounding
1. The grounding system shall be intentional. Careful plander racks, enclosures, and jumpers, NEBS Level 3 compresning must be given to network grounding, just like any other
cable trays must be bond- sion lugs, paint-piercing hardsystem deployed in the data center. As the grounding system
ed to the grounding system. ware, grounding strips for cabinet
0605cidef2
is no more reliable than its weakest link, only high-quality
(Additional information is mounting rails, and grounding
components can be used and trained professionals must make
available in the white paper, busbars.
all connections.
Facility Considerations for
2. The grounding system shall be visually veriable. When imthe Data Center, authored by American Power Conversion,
plemented properly, you should be able to visually inspect evCisco Systems, and Panduit Corp.)
ery component of the grounding system, from the equipment,
The grounding section of TIA-942 oers guidelines that
to the rack, to the common bonding network (CBN), to the
meet the basic principles and adds additional details specic
earth. Such a system can be inspected for degradation and is
to the modern data center environment. One important issue
accessible during moves, adds, and changes (MACs), ensuris the creation of electrical continuity throughout racks and
ing long-term system reliability and scalability.
cabinets. Because most racks and cabinets are made of paint3. The grounding system shall be adequately sized. TIA-942
ed components that are bolted together, there is no guaranprovides guidelines for each component of the grounding systee that electrical continuity exists from one rack component
tem. Improper use of the guidelines can reduce network availto the next. In the data center, rack and cabinet continuity
ability and cause premature equipment failure that contributes
is important for safety; electrostatic discharge (ESD) protecto increased operating costs.
tion; and the proper grounding of switches, servers, and power
4. The grounding system shall direct damaging currents away
strips. Continuity may not exist if the installer fails to scrape
from equipment. A grounding system that complies with
paint between sections of rack or use specially designed paintTIA-942 requires each rack to bond directly to the CBN, therepiercing hardware.
by directing current away from sensitive electronics. For instance, a common error is to daisy-chain racks together.
Network grounding installation
During a surge event, the entire row of daisy-chained racks
A licensed electrician is required to bond the AC power panbecomes energized with stray current, potentially resulting in
el. Additionally, the electrician typically installs the busbar
network throughout the building. The communications
installer can complete the grounding of the busbar to the
equipment. Often, electricians are hired to build the grid of
CBN conductors under the raised access oor. Even in this
case, little thought is given to how the grounding network
bonds to the equipment.
Alarmingly, numerous data centers in operation today have
grounding busbars in place, and a grid of CBN conductors under a raised oor, but not a single rack or cabinet bonded to
the CBN. It is clear that the data center owner intended to have
grounding; however, if the racks and cabinets are not bonded to the grounding system, then there is no protection. Creating electrical continuity within racks and cabinets is best
accomplished during initial installation. This is also the best
time to create the bond from the rack to the CBN before it is
forgotten. Equipment that is installed on the racks should be
bonded at this time.
It makes sense that the contractor who installs racks, cabinets, and equipment is in the best position to create the parts
of the grounding system that go along with the installation.
Collectively, this lets you be better positioned with customers
by providing valuable information that educates data center
decision-makers on how to protect their investment.
You should include a separate line item in bid submittals for
upgrading to a TIA-942-compliant grounding system, even if
the data center has not requested such an upgrade. This inclusion lets you make a competitive bid, to engage the customer
in a conversation about TIA-942 grounding, and ultimately
to create some distance from your competition.
Common problems and solutions
Data centers often run into trouble with their grounding systems when any of the following mistakes are made:
Using the wrong type of grounding connectors. For example, connectors that use setscrews to fasten the conductor
can loosen over time, degrading the electrical bond.
Applying hardware, such as screws and washers, that are
not designed to make an electrical bond, resulting in ungrounded equipment.
Failing to create an electrical bond between the structural
components of racks and cabinets can trap currents within
sections of them, resulting in potential safety hazards, failure of ESD protection, and ungrounded equipment.
A kitted grounding system can help installers avoid the mistakes that plague data centers. Key features of a good grounding system should include:
Permanent copper compression lugs that do not loosen
over time;
Hardware, such as thread-forming screws and paint-piercing washers, and studs that cut through the durable nishes that coat data center racks and cabinets, thereby creating
a metal-to-metal connection (bond);
Components, such as hardware and jumper cables, that
are tested for their ability to create electrical bonds and
carry current.
Additionally, the kitted system should comply with TIA-942
and t any rack or cabinet that complies with the EIA-310D
standard. Everything necessary to provide a TIA-942-compliant installation should be included in the kit, such as grounding
strips, busbars, and jumpers for creating electrical continuity
throughout a rack or cabinet; antioxidant to guarantee the
long-term reliability of the electrical bonds; and instructions
that describe the proper installation techniques (helps simplify ordering of grounding components and minimizes the risk
of overlooking details).
Each component and connection in the system is critical
to creating a low-impedance grounding path. In addition to
using components that are listed by a nationally recognized
testing laboratory, such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL),
the jumper assemblies within the kits should also be listed to
UL 467 Grounding and Bonding Equipment as a means of further certifying their applicability to grounding.
Ideally, components that make up the grounding kits are
tested to determine their ability to function during realworld conditions, such as earthquakes, lightning strikes, and
AC power faults. Telcordia Technologies NEBS Level 3 test
of power connectors simulates response to these events and
other scenarios that are likely in the data center environment.
(For more information, see The Electrical Distributor, January
2004, Minimize Service Interruptions. www.tedmag.com).
NEBS Level 3 is the most stringent test available to the industry, and power connectors that meet NEBS Level 3 should be
specied for data centers at every tier level.
Business booster
Network grounding provides a win-win opportunity for you,
and for data center managers. If you, as a contractor, understand the value of a well-designed system, you can provide expert consultative services and enhance your positioning as a
valuable partner.
To avoid the problems that are common in network grounding systems, you should implement only engineered solutions
that comply with accepted industry standards, such as TIA-942
and NEBS Level 3. And following proper network grounding
practices will provide your customers with the highest level
of network grounding capability.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- 20sep16 Anna Von Reitz The Truth Has Come Out Finally and ConclusivelyDocument6 pages20sep16 Anna Von Reitz The Truth Has Come Out Finally and ConclusivelyNadah8100% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
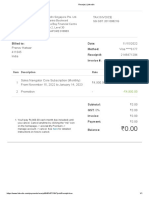
- Receipt - LinkedInDocument1 pageReceipt - LinkedInpratikraje.shinde11No ratings yet
- List of Investment Banks in United Arab Emirates & Doha QatarDocument8 pagesList of Investment Banks in United Arab Emirates & Doha QatarNandan SapaleNo ratings yet
- Taxation 01Document17 pagesTaxation 01Julius Lester Abiera0% (1)
- Job Description: To Be The Preferred Provider of Contract Mining ServiceDocument8 pagesJob Description: To Be The Preferred Provider of Contract Mining Servicepamungkas23No ratings yet
- Commercial Law - Study GuideDocument147 pagesCommercial Law - Study Guidecybawolf0180% (5)
- United States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitDocument31 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Petty Cash Fund Policy - EcaDocument4 pagesPetty Cash Fund Policy - EcaTelle SirchNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet and Income StatementDocument7 pagesBalance Sheet and Income StatementAlexNo ratings yet
- Answer: Problem 10-4: Requirement ADocument17 pagesAnswer: Problem 10-4: Requirement APatricia Nicole BarriosNo ratings yet
- Esubalew TakeleDocument65 pagesEsubalew TakeleMinaw BelayNo ratings yet
- DR - Ritu Sapra - Distributions To ShareholdersDocument34 pagesDR - Ritu Sapra - Distributions To ShareholdersAdil AliNo ratings yet
- ECON1132 Midterm2 2013springDocument4 pagesECON1132 Midterm2 2013springexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2lordaiztrandNo ratings yet
- Puneet ResumeDocument3 pagesPuneet Resumeapi-457888955No ratings yet
- Quiz I - Engg 404 2022Document5 pagesQuiz I - Engg 404 2022JAN JERICHO MENTOYNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On The Downfall of Kingfisher Airlines: Review ArticleDocument4 pagesA Case Study On The Downfall of Kingfisher Airlines: Review ArticleDeepak NNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - International Investment and Financing DecisionDocument22 pagesLecture 9 - International Investment and Financing DecisionAlice LowNo ratings yet
- Cash & Non-Cash Items - Kuya Joseph's BlogDocument9 pagesCash & Non-Cash Items - Kuya Joseph's BlogRedNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Assignment: Participants Name: Zeeshan Hussain Haris Ali Adil Farooq Fahad AnjumDocument4 pagesCorporate Finance Assignment: Participants Name: Zeeshan Hussain Haris Ali Adil Farooq Fahad AnjumDN OtakuNo ratings yet
- Money and Credit: Study of Ancient Indian Coins, The Research Institute of Ancient Scientific Studies, New-DelhiDocument23 pagesMoney and Credit: Study of Ancient Indian Coins, The Research Institute of Ancient Scientific Studies, New-DelhiDharmendra PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 3.management Accounting Vs Financial AccountingDocument9 pages3.management Accounting Vs Financial AccountingsjugliNo ratings yet
- REVIEW AND PRACTICE Chapter 8 Accounting For ReceivablesDocument3 pagesREVIEW AND PRACTICE Chapter 8 Accounting For Receivablesukandi rukmanaNo ratings yet
- PrenticeHall Finance SeriesDocument4 pagesPrenticeHall Finance SeriesYo_amaranthNo ratings yet
- Donald Trump - WikipediaDocument79 pagesDonald Trump - WikipediaImperiumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Adjustments, Financial Statements, and Financial ResultsDocument36 pagesChapter 4: Adjustments, Financial Statements, and Financial ResultsBarry PatnettNo ratings yet
- A Level Essay Questions by Topics (1998-2012) : Microeconomics Topic 1 Central Economics Problems and Resource AllocationDocument11 pagesA Level Essay Questions by Topics (1998-2012) : Microeconomics Topic 1 Central Economics Problems and Resource AllocationToh Qin KaneNo ratings yet
- Senior Financial Analyst in Washington DC VA Resume Joseph TrammDocument2 pagesSenior Financial Analyst in Washington DC VA Resume Joseph TrammJosephTrammNo ratings yet
- Financial Eduation and Investment Awareness-22Document6 pagesFinancial Eduation and Investment Awareness-22Vinay Gowda D M100% (1)