Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Heat Stroke
Uploaded by
Farr Krizha Tangkusan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
183 views1 pageHeat stroke (Homeo module, 2015)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHeat stroke (Homeo module, 2015)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
183 views1 pagePathophysiology of Heat Stroke
Uploaded by
Farr Krizha TangkusanHeat stroke (Homeo module, 2015)
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
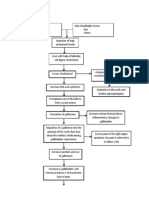
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF HEAT STROKE
(Correlated with laboratory findings)
Heat exposure
(greater heat production, less heat loss)
Increased core body temperature
Increased metabolism
Stimulate central thermo stat at preoptic
nucleus in anterior hypthalamus
hypoglycemia
Sends efferent signals via
autonomic venous system
Systemic vasoconstrition
Trigger cutaneous vasodilation and
diaphoresis (facilitate heat loss)
Involuntary muscle cramps
Excessive sweating
Exacerbate hyperthermia
Dehydration
rhabdomyolysis
Fluid and electrolyte imbalance
Destruction of myoglobin
Decreased circulating blood vol
Ca binds to
damaged muscles
Decreased renal perfusion
Fe released
hypocalcemia
Free radical formation
Decreased GFR
Increased hemolysis
Highly concentrated urine
hematuria
Dark-colored (tea-colored) urine
hyperchloremia
Body thinks there is presence
of pathogens thus releases
cytokines
hypernatremia
Increased
BUN
Hemoconcentration
(Increased RBC,
Increased Hct)
Damages kidneys
Increased WBC
Proteinuria
Smoky-urine
@farr_awaaaay
You might also like
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Renal Concept MapDocument8 pagesRenal Concept MapXtine CajiNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding Issues: Lactation Physiology, Deficits, Cracked Nipples, Mastitis & MoreDocument20 pagesBreastfeeding Issues: Lactation Physiology, Deficits, Cracked Nipples, Mastitis & Moremarina_shawky100% (1)
- Adult HealthDocument28 pagesAdult HealthL1NEDS DNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisKush KhannaNo ratings yet
- BioethicsCasesEEI 316232215 PDFDocument38 pagesBioethicsCasesEEI 316232215 PDFAman UllahNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors: CholelithiasisDocument10 pagesRisk Factors: CholelithiasisRoyster CabralNo ratings yet
- Presentation PathophysiologyDocument11 pagesPresentation PathophysiologyJade DeopidoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions CHFDocument3 pagesNursing Interventions CHFbanyenye25100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide to Urinalysis Screening and InterpretationDocument9 pagesPractical Guide to Urinalysis Screening and InterpretationyuppierajNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument34 pagesSexually Transmitted InfectionsMariana Creciun100% (1)
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument9 pagesUlcerative Colitiskint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document7 pagesExperiment 7kimber_gado100% (2)
- GIT DiSEASES Dumping SyndromeDocument3 pagesGIT DiSEASES Dumping SyndromeLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Oxytocin (Pitocin) : Slide 1Document16 pagesOxytocin (Pitocin) : Slide 1Kalesha JonesNo ratings yet
- What Is Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument3 pagesWhat Is Peptic Ulcer DiseaseKarl Angelo SimbajonNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Git Function 2Document35 pagesAlterations in Git Function 2Lloyd The UnicornNo ratings yet
- GASTRO TESTSDocument24 pagesGASTRO TESTSMicah EllaNo ratings yet
- Narratives Case NotesDocument4 pagesNarratives Case NotesKnigh RiderNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoshua DavantesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Ureteral CalculiDocument14 pagesPathophysiology of Ureteral CalculiEdmel Pamplona DuquesaNo ratings yet
- MicrocephalyDocument4 pagesMicrocephalykurei_bluflamedNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid Benefits, Uses, Side EffectsDocument3 pagesFolic Acid Benefits, Uses, Side EffectsDadybooboo2013No ratings yet
- PUCAN, Julienne BSN III-D - SGD - HYPO&HYPERCHLOREMIADocument10 pagesPUCAN, Julienne BSN III-D - SGD - HYPO&HYPERCHLOREMIAJulienne PucanNo ratings yet
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria Case StudyDocument87 pagesParoxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria Case Studyrachael100% (4)
- Professional AdjustmentDocument22 pagesProfessional AdjustmentArgee Alonsabe100% (1)
- Availability: Classifications: Antihistamine Antipruritic Pregnancy Category: CDocument4 pagesAvailability: Classifications: Antihistamine Antipruritic Pregnancy Category: CCay SevillaNo ratings yet
- CarboplatinDocument10 pagesCarboplatinapi-273179395No ratings yet
- Relationship Between CKD Stage and Pulmonary Edema on Chest X-RayDocument6 pagesRelationship Between CKD Stage and Pulmonary Edema on Chest X-RayAnnisa RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Importance of Honesty in MedicineDocument3 pagesImportance of Honesty in MedicineSuiweng WongNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology FinalDocument2 pagesPathophysiology FinallarissedeleonNo ratings yet
- TextOfBioethics PDFDocument228 pagesTextOfBioethics PDFNgoc HoangNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of NeonatesDocument17 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of NeonatesYu ShiNo ratings yet
- Improving a Family's Sleeping Habits Through EducationDocument10 pagesImproving a Family's Sleeping Habits Through EducationtaniaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Joint Disease Study GuideDocument18 pagesRheumatic Joint Disease Study Guidechalinsammy1No ratings yet
- Concept Map of CKD Gastrointestinal SymptomsDocument4 pagesConcept Map of CKD Gastrointestinal SymptomsWendy Escalante0% (1)
- Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesReflection PapershanoiapowelllNo ratings yet
- Rinary Ract Nfections: Classification Pathophysiology Risk Factors Clinical Manifestation DiagnosticsDocument27 pagesRinary Ract Nfections: Classification Pathophysiology Risk Factors Clinical Manifestation DiagnosticsDARYmagpantayNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT Chapter 11 Promoting Fetal and Maternal HealthDocument7 pagesHANDOUT Chapter 11 Promoting Fetal and Maternal HealthClouiseNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Perioperative CareDocument8 pagesOptimizing Perioperative CareJan Crizza Dale R. FrancoNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Litiasis EctomyDocument23 pagesCholecystitis Litiasis EctomyTimothy WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Managing Nause and Vomiting-Crit-Care-Nurse-2003-Garrett-31-50 PDFDocument22 pagesManaging Nause and Vomiting-Crit-Care-Nurse-2003-Garrett-31-50 PDFpmuftiaNo ratings yet
- Types of ShocksDocument33 pagesTypes of Shocksmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- SDL - 4.pdf AnotherDocument3 pagesSDL - 4.pdf AnotherJose Troy NgoaNo ratings yet
- Nur 1210 Pedia Concept Module 4B Alterations With Infectious, Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseDocument19 pagesNur 1210 Pedia Concept Module 4B Alterations With Infectious, Inflammatory and Immunologic ResponseweissNo ratings yet
- NCM104b BSN220 Mobility NursingDocument9 pagesNCM104b BSN220 Mobility NursingChristian Apelo SerquillosNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument9 pagesPathophysiologySuzette PipoNo ratings yet
- Module V ActDocument3 pagesModule V ActQueencess hayoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic management of bleomycinDocument1 pagePharmacologic management of bleomycinKim ApuradoNo ratings yet
- Care For Patients With Alteration in Perception and CoordinationDocument12 pagesCare For Patients With Alteration in Perception and Coordinationevlujtrep9690100% (1)
- CiprobayDocument2 pagesCiprobayianecunar100% (1)
- Case Study 101: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm With Acute Kidney InjuryDocument8 pagesCase Study 101: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm With Acute Kidney InjuryPatricia Ann Nicole ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management Pancreatic CancerDocument2 pagesNursing Management Pancreatic CancerKit NameKo100% (2)
- Fever, Hyperthermia, HypothermiaDocument34 pagesFever, Hyperthermia, HypothermiaAli AsadullahNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- ICS - 1st LeDocument4 pagesICS - 1st LeAbigail Mayled LausNo ratings yet
- 2011 Adult Periodic Health Exam GuidelinesDocument5 pages2011 Adult Periodic Health Exam GuidelinesEndrik SyNo ratings yet
- ComMed Attendance FormDocument1 pageComMed Attendance FormFarr Krizha TangkusanNo ratings yet
- Im History PeDocument4 pagesIm History PeFarr Krizha TangkusanNo ratings yet
- Psych HX & MsedocxDocument7 pagesPsych HX & MsedocxFarr Krizha TangkusanNo ratings yet
- Menstruation and Other Cyclical PhenomenaDocument4 pagesMenstruation and Other Cyclical PhenomenaFarr Krizha TangkusanNo ratings yet
- WHO 2015 - Mal TX Guidelines - 9789241549127 - Eng PDFDocument318 pagesWHO 2015 - Mal TX Guidelines - 9789241549127 - Eng PDFDody ChandraNo ratings yet
- MGMR2015 MedGrooveGUIDELINES PDFDocument4 pagesMGMR2015 MedGrooveGUIDELINES PDFFarr Krizha TangkusanNo ratings yet
- Medrhythmia Guidelines: A. QualificationsDocument4 pagesMedrhythmia Guidelines: A. QualificationsFarr Krizha TangkusanNo ratings yet
- HX PE TemplateDocument2 pagesHX PE TemplateFarr Krizha TangkusanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AGE With DHNDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGE With DHNFarr Krizha Tangkusan50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of CholeraDocument1 pagePathophysiology of CholeraFarr Krizha Tangkusan67% (3)
- Blood ChemistryDocument1 pageBlood ChemistryFarr Krizha TangkusanNo ratings yet
- History of ComputerDocument30 pagesHistory of ComputerFarr Krizha TangkusanNo ratings yet
- IMCI - Chart BookletDocument39 pagesIMCI - Chart BookletJason MirasolNo ratings yet
- 624692Document7 pages624692Farr Krizha TangkusanNo ratings yet