Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nuclear Waste & Led Invention
Nuclear Waste & Led Invention
Uploaded by
mayuri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesThis document summarizes information about nuclear energy, waste, and LED lighting. It discusses how nuclear energy is used to produce electricity through nuclear fission in reactors. It also outlines the various impacts and classifications of nuclear waste, and methods for nuclear waste management. Case studies of the Chernobyl and Fukushima nuclear disasters are provided. Additionally, the document traces the history and advantages of LED lighting, explaining how LEDs have evolved and how widespread LED use can significantly reduce energy consumption and costs for lighting.
Original Description:
Nuclear Waste
Original Title
Nuclear Waste
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes information about nuclear energy, waste, and LED lighting. It discusses how nuclear energy is used to produce electricity through nuclear fission in reactors. It also outlines the various impacts and classifications of nuclear waste, and methods for nuclear waste management. Case studies of the Chernobyl and Fukushima nuclear disasters are provided. Additionally, the document traces the history and advantages of LED lighting, explaining how LEDs have evolved and how widespread LED use can significantly reduce energy consumption and costs for lighting.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesNuclear Waste & Led Invention
Nuclear Waste & Led Invention
Uploaded by
mayuriThis document summarizes information about nuclear energy, waste, and LED lighting. It discusses how nuclear energy is used to produce electricity through nuclear fission in reactors. It also outlines the various impacts and classifications of nuclear waste, and methods for nuclear waste management. Case studies of the Chernobyl and Fukushima nuclear disasters are provided. Additionally, the document traces the history and advantages of LED lighting, explaining how LEDs have evolved and how widespread LED use can significantly reduce energy consumption and costs for lighting.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
NUCLEAR WASTE &
LED INVENTION
Presented To:
Prof. Ishita Tanna
Presented By:
B-03 Hetal Bhatt
B-17 Chaitali Naik
B-31 Mayuri Vadher
A- Nikhil Kumbhar
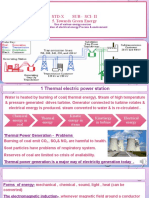
Nuclear Energy & Its Uses
Nuclear Energy is used in producing electricity.
How?
Nuclear reactor creates heat that is used to make
steam.
The steam turns a turbine connected to a
generator.
The generator then produces electricity.
Nuclear Energy Uses:
Industrial Use
Medical Use
Environmental Use
Other Uses
Nuclear Energy Process
Nuclear Waste Effects
Impact on Agriculture
Impact on Animals and Birds
Impact on Human being
Impact on Environment
Nuclear Waste Classification
The majority of power reactor wastes are classified
as:
1) Liquid radioactive wastes
2) Dry active solid wastes
3) Gases
Categories of nuclear waste
4) Very Low Level Waste
5) Low Level Waste
6) Intermediate Level Waste
7) High Level Waste
Case study- Chernobyl nuclear power plant
April 26, 1986:
Chernobyl nuclear power
plant
Operator errors cause a
reactor explosion
Explosion releases 190 tons
of radioactive gasses into
the atmosphere
Fire starts that lasts 10 days
People:
7 million lived in
contaminated areas; 3 million
were children
Wind:
Carries radiation far distances
Nuclear Waste Management
Basic steps:
Characterization
Treatment
Conditioning
Storage
Disposal
Techniques
Deep geological disposal-USA Yucca Mountain nuclear waste
repository in Nevada, Canada, Germany
Multinational repositories- Mexico, Brazil, India, China
Interim waste storage- UAE, Finland
Disposal in outer space- USA NASA
Sea disposal- Belgium, Italy
Recycling used fuel- Russia, Japan, U.K, ndia
Transmutation-Oak Ridge National Laboratory, USA
Vitrification process- India Trombey and Tarapur
Case Study: Fukushima Nuclear
Disaster
2 minutes after the earthquake the
atomic power plants Fukushima I,
Fukushima II, Onagawa and Tokai
shut down.
Destroyed the fuel tanks of the
emergency power supply.
Next day there was a huge
Hydrogen explosion in reactor block
1. To chill the reactor and to stop
the nuclear meltdown they pumped
sea water into reactor block 1
Reactor block 3 exploded on 14th
March 2011
Nuclear Plants in India
A Brief History of Lighting
2000
2009
~1990
White
LED
Lamp
Production White
High Brightness
demonstrates
LED Lamp
Red, Orange,
1970s
Incandescent
Exceeds 100 lm/W
Yellow, & Green LEDs
Sodium
First Red
Efficacy (17 lm/W) 2005
Vapor Lamp
LED
1995
White LED Lamp
High Brightness
demonstrates
Blue, Green LEDs
Fluorescent
1901
Fluorescent
Tube 1919
1879
Edison Light
Bulb
Efficacy (70 lm/W)
U.S. 223,898
Calculators and
Indicators
Monochrome
signs
Full Color Signs
Solid State Lighting
Current lighting technology is over 120
years old
LEDs began as just indicators, but are now
poised to become the most efficient light
source ever created
Basic Advantages of LED Light
LEDs arevery energy efficient
Are directional No wasted light, any
pattern possible
Have very long lifetime >50,000 hours
Start instantly nanoseconds vs. > 10 min
re-strike
Are environmentally sound no heavy
metals
Are infinitely controllable New lighting
features, power savings
Why LED Lighting?
The widespread use of LEDs over the next
10 years can:
Save energy (Good)
Save money
Help protect the environment (Green)
LED lighting can reduce electricity needs
for lighting by more than 60%
You might also like
- Nuclearenergy 1 210115153034Document29 pagesNuclearenergy 1 210115153034gaviNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy 2018Document35 pagesNuclear Energy 2018Nivi MiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear EnergyDocument60 pagesNuclear EnergyArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Environmentalsciencemodule2notes 140206195027 Phpapp01Document41 pagesEnvironmentalsciencemodule2notes 140206195027 Phpapp01api-296317938No ratings yet
- Chernobyl An OverviewDocument28 pagesChernobyl An OverviewFOOTBALL AND MOVIES ZONENo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactor: Submitted By: Ranjodh Singh 1180070117 RD4701B61Document17 pagesNuclear Reactor: Submitted By: Ranjodh Singh 1180070117 RD4701B61Kaleem ShiekhNo ratings yet
- Deadliest Nuclear Disasters: by Shreyas Parwar and Sudarshan N NDocument24 pagesDeadliest Nuclear Disasters: by Shreyas Parwar and Sudarshan N NSudarshan NavaleNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument14 pagesUntitled PresentationDarrion MoreauNo ratings yet
- TAUFIA ALIYAR - Attachment: PDF: WW - Lev.1 - No.1Document7 pagesTAUFIA ALIYAR - Attachment: PDF: WW - Lev.1 - No.1TAUFIA ALIYARNo ratings yet
- Energy and Society: Prof. Amit Lath Rutgers, The State University of New JerseyDocument30 pagesEnergy and Society: Prof. Amit Lath Rutgers, The State University of New Jerseyfaisal yousafNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: Shantanu Paul Student ID: S201604047 BuetDocument10 pagesNuclear Energy: Shantanu Paul Student ID: S201604047 BuetShantanu PaulNo ratings yet
- Nuclear EnergyDocument37 pagesNuclear EnergyAkash Prajapati100% (1)
- Power PlantsDocument12 pagesPower PlantsLinda Leon TomaNo ratings yet
- Itroduction To Nuclear ChemistryDocument19 pagesItroduction To Nuclear ChemistryNickNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerDocument3 pagesNuclear PowerChristian Bartl - bartlweb.netNo ratings yet
- What Is Nuclear Power?: - It Is Simply Electricity Made FromDocument15 pagesWhat Is Nuclear Power?: - It Is Simply Electricity Made FromG.DheerkaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper KoDocument7 pagesReaction Paper KoJerenmie De Jesus ChuaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fact Sheet 3aDocument1 pageNuclear Fact Sheet 3aDilip YadavNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Accidents and HolocaustDocument19 pagesNuclear Accidents and HolocaustSurendra RanwaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Vs Fossil FuelsDocument10 pagesNuclear Power Vs Fossil FuelsAYALEYDENNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PresentationDocument16 pagesNuclear Power Presentationdinesh1625No ratings yet
- Hazards of Nuclear PollutionDocument18 pagesHazards of Nuclear PollutionSanktifierNo ratings yet
- Week8 1Document53 pagesWeek8 1Belmonte, Jhon Romel C.No ratings yet
- Recommended Books:: Introduction To Types of Renewable Energy, Fuel Cell and Heat Pump SystemsDocument37 pagesRecommended Books:: Introduction To Types of Renewable Energy, Fuel Cell and Heat Pump SystemsTahaMustahsanNo ratings yet
- An All-Embracing Review of Solar Energy: Centre For Development of Advanced Computing, Mohali, Punjab, IndiaDocument4 pagesAn All-Embracing Review of Solar Energy: Centre For Development of Advanced Computing, Mohali, Punjab, IndiaDodi Rmpuna BoangmanaluNo ratings yet
- Research QuestionDocument4 pagesResearch QuestionBehrouz AlipourNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: Boon or BaneDocument18 pagesNuclear Energy: Boon or BaneMuzamil MohamedNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV Nuclear Power PlantDocument54 pagesUNIT IV Nuclear Power Plantsai venkatsharmaNo ratings yet
- NUCLEAR POWER PLANT PresentationDocument39 pagesNUCLEAR POWER PLANT PresentationAmol ToraneNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: A Basic Overview By: Mark Dalski, Tom Child, Colt Lorson, and Chris MounseyDocument11 pagesNuclear Energy: A Basic Overview By: Mark Dalski, Tom Child, Colt Lorson, and Chris Mounseyhelperforeu100% (1)
- KPD 3016: Pengajaran Teknologi Dan Penaksiran 1 Kumpulan A: Tugasan 3Document11 pagesKPD 3016: Pengajaran Teknologi Dan Penaksiran 1 Kumpulan A: Tugasan 3SMAF3016No ratings yet
- E&E 18ME751 3rd IA Important Questions With AnswersDocument9 pagesE&E 18ME751 3rd IA Important Questions With AnswerslakshmishashreyasknNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactorDocument33 pagesNuclear ReactorHaren SinghNo ratings yet
- Fuel and Energy Utilization Ece4433: Segi UniversityDocument14 pagesFuel and Energy Utilization Ece4433: Segi Universityrock balboa100% (1)
- Physical Science G11 Week 14 ModuleDocument4 pagesPhysical Science G11 Week 14 ModuleShannenNo ratings yet
- Non-Conventional Sources of EnergyDocument30 pagesNon-Conventional Sources of EnergyNamhaa SharmaNo ratings yet
- Non Conventional Energy SourcesDocument26 pagesNon Conventional Energy SourcesNiladri Paul0% (1)
- STD-X Sub - Sci-Ii 5. Towards Green EnergyDocument8 pagesSTD-X Sub - Sci-Ii 5. Towards Green EnergySagar WaghmareNo ratings yet
- Unit VI. Fossil Fuels and Nuclear EnergyDocument70 pagesUnit VI. Fossil Fuels and Nuclear EnergyPatricia Sofia DizonNo ratings yet
- (Energy Resources) A Bednego Aryee Aaryee@ryerson - Ca Ryerson UniversityDocument66 pages(Energy Resources) A Bednego Aryee Aaryee@ryerson - Ca Ryerson UniversityIman MustafaNo ratings yet
- TME 223 - Module 6 - 2020 - 2021Document48 pagesTME 223 - Module 6 - 2020 - 2021Skill ShareNo ratings yet
- Solar Photovoltaic: Fundamental, Technology and ApplicationsDocument25 pagesSolar Photovoltaic: Fundamental, Technology and ApplicationsAnil SinghNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant ProtestsDocument24 pagesNuclear Power Plant ProtestsDhruv SinghviNo ratings yet
- Nces Module 1&2Document113 pagesNces Module 1&2Naveen S BasandiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry NotesDocument13 pagesNuclear Chemistry Notesapi-369706779No ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument74 pagesRadioactivitykevin mosesNo ratings yet
- Dialog InggrisDocument7 pagesDialog Inggrisridhoazhari303No ratings yet
- Ce-105 II Evs Energy 1Document41 pagesCe-105 II Evs Energy 1akashNo ratings yet
- Reactor PresantationDocument18 pagesReactor Presantationapi-347038029No ratings yet
- Energy Types and UsesDocument15 pagesEnergy Types and UsesGeorges HachemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Energy, SustainabilityDocument89 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Energy, SustainabilityHui QingNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy and EnvironmentDocument24 pagesRenewable Energy and EnvironmentDouaa ElatifiNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Energy Sources: Energy Source Can Be Divided Into 3-TypesDocument17 pagesUNIT-1 Energy Sources: Energy Source Can Be Divided Into 3-TypesSuprava GhoshPaulNo ratings yet
- Assistant Professor Organic Chemistry Division, SAS, VIT University, Vellore - 14Document33 pagesAssistant Professor Organic Chemistry Division, SAS, VIT University, Vellore - 14RiajiminNo ratings yet
- Olatunde J Aladesote Ryan Carter, and Petronella James-OkekeDocument7 pagesOlatunde J Aladesote Ryan Carter, and Petronella James-OkekeSharen ArdyanaNo ratings yet
- Uranium: The Myth of Clean Air - CO2 Production in The Nuclear Fuel CycleDocument41 pagesUranium: The Myth of Clean Air - CO2 Production in The Nuclear Fuel CycleRapheal RapsangNo ratings yet
- Chem 111 - Week 4Document16 pagesChem 111 - Week 4Reyy ArbolerasNo ratings yet
- LecPPT1 - Nuclear Engineering BasicsDocument41 pagesLecPPT1 - Nuclear Engineering BasicsVishal MeenaNo ratings yet
- Devastating Nuclear Accidents throughout History: Causes and Results - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksFrom EverandDevastating Nuclear Accidents throughout History: Causes and Results - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Mayuri VadherDocument12 pagesPresented By: Mayuri VadhermayuriNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Mayuri VadherDocument13 pagesPresented By: Mayuri VadhermayuriNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Mayuri VadherDocument14 pagesPresented By:: Mayuri VadhermayuriNo ratings yet
- An Autobiography or The Story of Experiments With Truth: M.K.GandhiDocument8 pagesAn Autobiography or The Story of Experiments With Truth: M.K.GandhimayuriNo ratings yet