Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Synopsis On OPTICAL FIBER
Uploaded by
Satya Yadav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesSynopsis on OPTICAL FIBER
Original Title
Synopsis on OPTICAL FIBER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSynopsis on OPTICAL FIBER
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesSynopsis On OPTICAL FIBER
Uploaded by
Satya YadavSynopsis on OPTICAL FIBER
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
INTRODUCTION OF OPTICAL FIBER
An optical fiber is a glass or plastic fiber
that
carries light along its length. An optical fiber is a
very thin strand of silica glass in geometry quite
like a human hair. In reality it is a very narrow ,
very long
glass
cylinder
with special character
istics. When light enters one end of the fibe r
it travels (confined within the fiber) until it
eaves the fiber at the other end.
An
optical
fiber
consists of two parts: the
core and the cladding. The core a narrow cylin
drical strand of glass and the cladding
ubular
jacket
is a t
surrounding it. The core has a
(slightly) higher refractive index than the clad
ding. Light
travelling along the coreis confin
ed by the mirror
to stay within it even when the
fiber bends around a corner. A fiber optic cable
has an additional coating around the cladding
called the jacket. The jacket usually consists
of one or more layers of polymer. Its role is
to protect the core and cladding from shocks
that might affect their optical or physical
properties. It acts as a shock absorber. Th
e jacket also provides protection from abrasi
ons, solvents and other contaminants. The
jacket does not have any optical properties that
might affect
the propagation of light within the
fiber optic cable.
ADVANTAGES OF OPTICAL FIBER :Fiber optic transmission systems a fiber optic
transmitter and
receiver, Connected by fiber optic cable offer a wide
range of
benefits not offered by traditional copper wire or
coaxial cable. These include:
1. Less Expensive
2. Thinner
3. Higher Information Carrying Capacity
4. Low Power Consumption
5. Light Weight
6. Non Flammable
7. Low Transmission Loss
8. Signal Security
9. Small Size & Weight
LIMITATIONS OF OPTICAL FIBER
1. The terminating equipment is still costly as
compared to copper wire.
2. Delicate so has to be handled carefully.
3. Communication is not totally in optical domain, so
repeated electric to optical to electrical conversion
is needed.
4.Optical amplifiers, splitters, MUX-DEMUX are still
in development stages.
5. Tapping
is
not possible. Specialized
equipment is needed to tap a fiber.
6. Optical fiber splicing is a specialized technique and
needs expertly trained manpower.
7. The splicing and testing equipments are very
expensive as compared to copper equipments.
8. Bending Cables
9.
Gamma Radiation
10. Electrical Fields
11. Sharks Eat the Cable
Applications of Optical Fiber
Cable TV,CCTV ,Optical Fiber Sensors, X-ray Imaging ,Night
Vision
You might also like
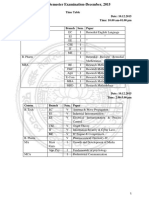
- Time Table Autumn Semester December-2015 - NewDocument14 pagesTime Table Autumn Semester December-2015 - NewSatya YadavNo ratings yet
- Routh Hurwitz AnalysisDocument29 pagesRouth Hurwitz Analysisilg1No ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Introduction To Wireless CommunicationDocument59 pagesLec 1 - Introduction To Wireless CommunicationRashidKhanNo ratings yet
- AerodynamicsDocument18 pagesAerodynamicsSatya YadavNo ratings yet
- Radar System Design (Final Version)Document108 pagesRadar System Design (Final Version)Nelapati KoteswarammaNo ratings yet
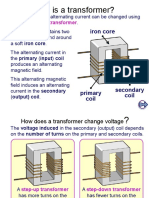
- How transformers change AC voltage levelsDocument5 pagesHow transformers change AC voltage levelsSatya Yadav100% (3)
- BTech - EC5 SyllabusDocument23 pagesBTech - EC5 SyllabusSatya YadavNo ratings yet
- Pspice TransientDocument7 pagesPspice TransientSatya YadavNo ratings yet
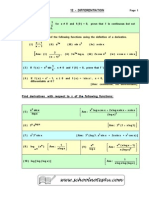
- Problems 12 - DifferentiationDocument11 pagesProblems 12 - DifferentiationNihal SinghNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Impq 11 Conic Sections Kvs PDFDocument6 pages11 Maths Impq 11 Conic Sections Kvs PDFSatya YadavNo ratings yet
- 12 2009 Sample Paper Mathematics 01 MsDocument23 pages12 2009 Sample Paper Mathematics 01 MsDalziel Saint ConceicaoNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)