Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Final Summativ Integration Answers
Uploaded by
api-314001028Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Final Summativ Integration Answers
Uploaded by
api-314001028Copyright:
Available Formats
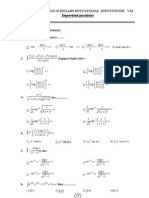
Integration exam questions
1.
METHOD 1
Region required is given by
y
(2 , 5 )
(4 , 7 )
x
( 3 , 0 )
from gdc outer intersections are at x = 3 and x = 4
Area =
4
3
(A1)(A1)
y1 y 2 dx
(M1)
= 101.75
(A3) (C6)
METHOD 2
From gdc intersections are at x = 3, x = 2, x = 4
x
Area =
2
3x 2 9 x 27 ( x 3) dx
= 101.75
x 3 (x
4
(A1)(A1)(A1)
3
3 x 2 9 x 27 ) dx
(M1)(M1)
(A1) (C6)
[6]
2.
(a)
At A, x = 0.753
(G2)
(C2)
(b)
At B, x = 2.45
(c)
Area
2.45
0.753
ydx
(G2) (C2)
= 1.78
(M1)(G1) (C2)
[6]
Chapter 14 exam revision questions
1.
(a)
y = g (x )
Q
R
P
y = f (x )
p
(A3)
Notes: Award (A1) for y = f (x), with (0, 1) shown.
Award (A1) for y = g (x), and (A1) for region A
(b)
area OPQ < area of region A < area of rectangle OSRQ
1
2 (1)(p) < area of region A < (p)(1)
p
2 < area of region A < p
2
(c)
(M1)(R1)
(A2)
(AG)
p
e p + 1 = 0 using a calculator gives
Solving the equation e
p = 0.6937 (4 decimal places)
(A2)
OR the value of p may be found as follows:
2
e p e p 1
2
2 p2
ep 1 = 0
e
2
ep
2
ep
1 1 4
2
1 5
p2
2
since e > 0
This gives p =
1 5
0.6937 (4 decimal places)
ln
e
p
(d)
x2
(A2)
ex 1
Area of region A = 0
dx
= 0.467 (using a graphic display calculator)
(M2)
(A1)
[12]
2.
The curves meet when x = 1.5247 and x = 0.74757.
x
0.74757
2
3
1.5247 1 x 2
dx
The required area =
= 1.22.
(G1)
(M1)
(G1) (C3)
[3]
3.
y = ex e
y = ln x
Curves intersect at x = 0.233
and x = 1
1
Area =
0.233
(G1)
(G1)
(ln x e x e)dx
(M1)(A1)
(G2) (C6)
= 0.201
[6]
4.
(a)
dx
1
ln 2 x 3
2x 3 2
m
0
(M1)(A1)
1 2m 3
1
1
ln
or ln 2m 3 ln 3
3
2
2
= 2
(C3)
Note: Modulus signs are not required.
(A1)
1 2m 3
ln
2
3
(b)
=1
2m 3
2m 3
3 2 , negative sign not required
2
3
3
=e ,
(M1)
2m 3
2
m
e2
3
3 = e2 1
(A1)
3
2
m = 2 (e 1) = (= 9.58)
(A1) (C3)
Note: Do not penalize if a candidate has also obtained the
incorrect value m = 12.6
[6]
7. is on the next page
3
8.
You might also like
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Karnataka CET 2015 Mathematics Question PaperDocument6 pagesKarnataka CET 2015 Mathematics Question PaperjeluNo ratings yet
- SAT MATH LEVEL 2 TITLEDocument27 pagesSAT MATH LEVEL 2 TITLELeo LiuNo ratings yet
- 03 4 Numerical Integration 80-83Document3 pages03 4 Numerical Integration 80-83Shaik Afzal HussainNo ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Alevel C3C4Document59 pagesAlevel C3C4nuddin123No ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Sat PTDocument17 pagesSat PTAkmal AlfariziNo ratings yet
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Find range of values for quadratic equation less than 0Document1 pageFind range of values for quadratic equation less than 0Tanvir Al AlamNo ratings yet
- RT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A SolDocument16 pagesRT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A Solvishal110085No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- XcosxdxDocument5 pagesXcosxdxWelyab PaulaNo ratings yet
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- © Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C3 Paper JDocument2 pages© Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C3 Paper JPa GesNo ratings yet
- Best Higher Secondary School Chapter:-5: Section ADocument3 pagesBest Higher Secondary School Chapter:-5: Section Aapi-233084441No ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - 2Document22 pagesQuestion Bank - 2Sesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution Total DistributionsDocument5 pagesSolution Total Distributions8rztNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- DPP 41Document4 pagesDPP 41mmoriarity309No ratings yet
- Mathematics Integral MCQDocument11 pagesMathematics Integral MCQRaju ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Integral MCQ PDFDocument11 pagesMathematics Integral MCQ PDFBilalAzamNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations and Graphing FunctionsDocument9 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations and Graphing FunctionsNatalie Yeung100% (1)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Core Mathematics C3: GCE Examinations Advanced SubsidiaryDocument4 pagesCore Mathematics C3: GCE Examinations Advanced Subsidiarydasha962No ratings yet
- 03comp IDocument5 pages03comp Ialiscribd46No ratings yet
- Kcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Document13 pagesKcet - Mathematics - 2016: Version Code: C - 3Kamalesh ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Area PDFDocument8 pagesArea PDFNarayanan MadhavanNo ratings yet
- C3 Practice Paper A2 Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesC3 Practice Paper A2 Mark Schemebiswas_sanjay727865No ratings yet
- EAMCET 2013 Question Paper With Answer Keys and SolutionsDocument48 pagesEAMCET 2013 Question Paper With Answer Keys and SolutionsPremKumarKalikiri83% (6)
- Binomial Theorem QnsDocument5 pagesBinomial Theorem QnsamberNo ratings yet
- MCP-05!01!2011 Revision Test-2 12th SolutionDocument22 pagesMCP-05!01!2011 Revision Test-2 12th SolutionpriyankaNo ratings yet
- Ceep 2012Document27 pagesCeep 2012Edara Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Advanced Test 2 Answer Key with Detailed Solutions for Mathematics, Physics and ChemistryDocument12 pagesIIT-JEE Advanced Test 2 Answer Key with Detailed Solutions for Mathematics, Physics and ChemistryasuhassNo ratings yet
- AIEEE Minor TestsDocument65 pagesAIEEE Minor Testsprem19999No ratings yet
- BarronsCalculus-Set12 MCQDocument26 pagesBarronsCalculus-Set12 MCQPeter HyungJun Yoon0% (1)
- Math53 Exam4 05 PDFDocument1 pageMath53 Exam4 05 PDFAb YZNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper For IIT-JEE (Logarithm, Quadratic Equation and Basic Calculus)Document3 pagesPractice Paper For IIT-JEE (Logarithm, Quadratic Equation and Basic Calculus)Mahender Gujja100% (1)
- Dpp13qe ) WDocument12 pagesDpp13qe ) Wsuar90No ratings yet
- Definite Integral and AREAunder CurveDocument2 pagesDefinite Integral and AREAunder CurveVishal JalanNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument5 pagesCircleRon HartNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Mock PaperDocument25 pagesFiitjee Mock PaperShashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- © Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C3 Paper JDocument2 pages© Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C3 Paper JNashra19No ratings yet
- ALABAMA STATEWIDE MATHEMATICS CONTEST DIV III EXAMDocument6 pagesALABAMA STATEWIDE MATHEMATICS CONTEST DIV III EXAMสฮาบูดีน สาและNo ratings yet
- f5 c3 Integration NewDocument7 pagesf5 c3 Integration NewyeohsiewfongNo ratings yet
- SOLU Precalculo, 7ma Edicion - Michael SullivanDocument829 pagesSOLU Precalculo, 7ma Edicion - Michael SullivanTemistocles ZeballosNo ratings yet
- Solomon D MS - C2 EdexcelDocument4 pagesSolomon D MS - C2 EdexcelClaudiaNo ratings yet
- C2 Practice Paper A4 Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesC2 Practice Paper A4 Mark Schemeshariz500No ratings yet
- 2015 AJC Prelim Paper 1 QnsDocument7 pages2015 AJC Prelim Paper 1 QnsYing Ru ChuaNo ratings yet
- AIEEE PracticeDocument135 pagesAIEEE PracticeJoseph Viju100% (1)
- Binomial TheoremDocument8 pagesBinomial Theoremsrinu27No ratings yet
- Final Summative Assessment For IntegrationDocument6 pagesFinal Summative Assessment For Integrationapi-314001028No ratings yet
- Riemann Sums Short Answer QuestionsDocument3 pagesRiemann Sums Short Answer Questionsapi-314001028No ratings yet
- Differentiation Questions Pre Assessment Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesDifferentiation Questions Pre Assessment Mark Schemeapi-314001028No ratings yet
- Differentiation Questions Pre Assessment IntegrationDocument3 pagesDifferentiation Questions Pre Assessment Integrationapi-314001028No ratings yet
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)