Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Economics Lecture 3
Uploaded by
Carine Tee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageNotes for 3rd lecture, Foundation in Business, Taylor's University Lakeside Campus
Original Title
Introduction to Economics Lecture 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNotes for 3rd lecture, Foundation in Business, Taylor's University Lakeside Campus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageIntroduction To Economics Lecture 3
Uploaded by
Carine TeeNotes for 3rd lecture, Foundation in Business, Taylor's University Lakeside Campus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
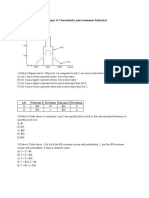
Lecture 3
A market is the institution through which buyers and sellers
interact/ engage in exchange of goods and services.
Market equilibrium is when the market is at a state of balance,
which means at one specific market price, quantity supplied equals
quantity demanded and the buyers plan matches the sellers plan.
Thersfore, there is no tendency for the price to increase or decrease.
Shortage (excess in demand) happens when consumers are willing
to buy more than producers are willing to sell. This occurs when
market price is lower than equilibrium price. Due to shortage, price
will increase. As a result, Qd decreases and Qs increases until the
original equilibrium is established. Shortage is then eliminated.
Surplus (excess in supply) happens when producers are willing to
produce more than consumers are willing to buy. This occurs when
market price is higher than equilibrium price. Price will the start to
fall due to excess supply. As price decreases, Qd increases and Qs
decreases until the original equilibrium is established. SURPLUS will
be eliminated.
*Equilibrium price and quantity will ONLY change when there is a
shift in the demand/supply curve (left or right). Otherwise, it will not
change.
Price ceiling (max price) is a regulation (imposed by the
government) that makes it illegal to charge a price higher than a
specified level, allowing consumers to purchase basic items (ie.
sugar, chicken) that were sold at a higher market price.
-price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price
-can cause shortage
Price floor (minimum price) is a regulation (imposed by the
government) that makes it illegal to trade at a price lower than a
specified level.
-set above equilibrium price
-to increase the price certain goods that are believed to be sold in
an unfair market with price that is too low (e,g, agricultural produce)
- can cause surplus
You might also like
- Price Determination & Simple ApplicationsDocument4 pagesPrice Determination & Simple ApplicationsnaiNo ratings yet
- Market Equilibrium: Research Work No. 3Document6 pagesMarket Equilibrium: Research Work No. 3Anonymous uf3lwVejINo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument16 pagesSupply and DemandMartin JanuaryNo ratings yet
- Definition of Market EquilibriumDocument7 pagesDefinition of Market EquilibriumFaye Erica HerberoNo ratings yet
- What Does Invisible Hand of The Marketplace DoDocument5 pagesWhat Does Invisible Hand of The Marketplace DoSadia RahmanNo ratings yet
- Supply and Demand: University of Cebu Lapu Lapu and MandaueDocument20 pagesSupply and Demand: University of Cebu Lapu Lapu and MandaueMeljorin LayeseNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument3 pagesDemand and SupplyShalu AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Summary MacroDocument64 pagesSummary Macrojayesh.guptaNo ratings yet
- A. The Law of Demand: Market EconomyDocument6 pagesA. The Law of Demand: Market EconomySagar KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- A. The Law of Demand: Market EconomyDocument6 pagesA. The Law of Demand: Market EconomyLeo JoyNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument16 pagesSupply and DemandRacel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics NotesDocument1 pageManagerial Economics NotesWarren Nahial ValerioNo ratings yet
- Economic Theory 1Document16 pagesEconomic Theory 1Dyepoy Figs VjoucherNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument10 pagesSupply and DemandAshikNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics 1st-QRTR PPT 4.1Document19 pagesApplied Economics 1st-QRTR PPT 4.1Agnes RamoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Analysis of CommoditiesDocument8 pagesFundamental Analysis of CommoditiesShraddha BhatNo ratings yet
- Basic Microeconomics Context Diminishing ReturnsDocument6 pagesBasic Microeconomics Context Diminishing ReturnsBryant Daniel Arguelles GacusNo ratings yet
- Market Surpluses & Market ShortagesDocument4 pagesMarket Surpluses & Market ShortagesWilfred MartinezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economic 03 enDocument38 pagesPrinciples of Economic 03 enChouiha OmarNo ratings yet
- Econ 8 Marker CWDocument1 pageEcon 8 Marker CWinaayaNo ratings yet
- Supply Analysis & Market Equilibrium: By: Aneela ChatthaDocument16 pagesSupply Analysis & Market Equilibrium: By: Aneela ChatthaShadowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Markets - AS Business StudiesDocument1 pageChapter 6: Markets - AS Business StudiesHR purposes 2006No ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Price DeterminationDocument5 pagesChapter 9-Price DeterminationBasheer KhaledNo ratings yet
- Asharab Aamir SheikhDocument7 pagesAsharab Aamir Sheikhhumair chauhdaryNo ratings yet
- Managerial Econ LessonDocument14 pagesManagerial Econ LessonKarysse Arielle Noel JalaoNo ratings yet
- Price Controls: Econ 360-002 Sonia Parsa Sparsa1@gmu - Edu G00509808 Word Count: 1540Document11 pagesPrice Controls: Econ 360-002 Sonia Parsa Sparsa1@gmu - Edu G00509808 Word Count: 1540Amir SaiedehNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - The Market System: Market Economy - Interaction Between Supply and Demand Determines What IsDocument21 pagesCH 3 - The Market System: Market Economy - Interaction Between Supply and Demand Determines What Isamer328No ratings yet
- Applied Eco - PPT Module 3Document25 pagesApplied Eco - PPT Module 3Bernardita Sison-CruzNo ratings yet
- Market EquilibriumDocument11 pagesMarket EquilibriumClaudine SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Basic Analysis of Demand and SupplyDocument15 pagesBasic Analysis of Demand and SupplyAmphion VinceNo ratings yet
- How Demand and Supply Determine Market Price: PDF (55K) Agri-News This WeekDocument6 pagesHow Demand and Supply Determine Market Price: PDF (55K) Agri-News This WeekMonika KshNo ratings yet
- Sept Monthly Test EcoDocument3 pagesSept Monthly Test EcoWai HponeNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics READING WEEK 2Document3 pagesApplied Economics READING WEEK 2jeanaguilos2023No ratings yet
- How Demand Market Price Jan12 2015Document5 pagesHow Demand Market Price Jan12 2015nivetithaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Part 3Document16 pagesMicroeconomics Part 3YzappleNo ratings yet
- Political Examen 3-5Document5 pagesPolitical Examen 3-5Felicitas MNo ratings yet
- Ba 200Document3 pagesBa 200Maricon Santos MonisNo ratings yet
- Demand and SupplyDocument29 pagesDemand and SupplyJenina Lee PacisNo ratings yet
- Demand, Supply and Producer's Surplus of Agri-Commodities: Nature and Determinants of Demand and Supply of Farm Products Demand & SupplyDocument8 pagesDemand, Supply and Producer's Surplus of Agri-Commodities: Nature and Determinants of Demand and Supply of Farm Products Demand & SupplyMamta VermaNo ratings yet
- Market EquilibriumDocument2 pagesMarket EquilibriumMuhammad ButtNo ratings yet
- Maximum Price (AS Economics)Document2 pagesMaximum Price (AS Economics)Muhammad ButtNo ratings yet
- Supply, Demand and The Market ProcessDocument7 pagesSupply, Demand and The Market ProcessAris GueseNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of SupplyDocument5 pagesBasic Elements of SupplysabaahatNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of SupplyDocument5 pagesBasic Elements of SupplysabaahatNo ratings yet
- Applied Econ FinalsDocument5 pagesApplied Econ FinalsKrysha FloresNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium: Summary and Introduction To EquilibriumDocument17 pagesEquilibrium: Summary and Introduction To EquilibriumUmer EhsanNo ratings yet
- Economics For Managers GTU MBA Sem 1 Chapter 4Document24 pagesEconomics For Managers GTU MBA Sem 1 Chapter 4Rushabh VoraNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument11 pagesEconomics41Sudipta BeraNo ratings yet
- Lec 7 Determination of Market PriceDocument13 pagesLec 7 Determination of Market PriceNEERAJA UNNINo ratings yet
- CH 4 Supply DemandDocument39 pagesCH 4 Supply DemandMohamedAhmedNo ratings yet
- ECO162 - Market Equilibrium and Government InterventionDocument41 pagesECO162 - Market Equilibrium and Government InterventionPixie Hollow100% (1)
- Law of Supply and DemandDocument49 pagesLaw of Supply and DemandArvi Kyle Grospe PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Government InterventionDocument8 pagesGovernment Interventionjamilhasan8No ratings yet
- Market Equilibrium & ApplicationsDocument22 pagesMarket Equilibrium & ApplicationsAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- Health Economics SupplyDocument7 pagesHealth Economics SupplyPao C EspiNo ratings yet
- Economic Report Price Celing Price FloorDocument15 pagesEconomic Report Price Celing Price Floor2023-25 SOURABH PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document1 pagePaper 1aryan mehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Man Econ.Document1 pageChapter Two Man Econ.tjcute125No ratings yet
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- MCQ Risk and Consumer BehaviourDocument4 pagesMCQ Risk and Consumer BehaviourCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- Class Activity - UncertaintyDocument3 pagesClass Activity - UncertaintyCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - UncertaintyDocument3 pagesTutorial 4 - UncertaintyCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Exercises - Practise More!Document2 pagesTutorial Exercises - Practise More!Carine TeeNo ratings yet
- Examples On GEDocument7 pagesExamples On GECarine TeeNo ratings yet
- Financial Economics - Extra PracticeDocument2 pagesFinancial Economics - Extra PracticeCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- FE - Tutorial 5 - General EquilibriumDocument6 pagesFE - Tutorial 5 - General EquilibriumCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- Wealth Management Tutorial SolutionDocument3 pagesWealth Management Tutorial SolutionCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument27 pagesRisk ManagementCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- Risk Management: Topic 11: National and International Regulatory Framework (Basel 1,2 and 3)Document50 pagesRisk Management: Topic 11: National and International Regulatory Framework (Basel 1,2 and 3)Carine TeeNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Individual AssignmentDocument24 pagesDerivatives Individual AssignmentCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- FE - Tutorial 1Document2 pagesFE - Tutorial 1Carine TeeNo ratings yet
- Carine FYP From GoogleDocument42 pagesCarine FYP From GoogleCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Panel Data: Slides by Niels-Hugo Blunch Washington and Lee UniversityDocument18 pagesExperimental and Panel Data: Slides by Niels-Hugo Blunch Washington and Lee UniversityCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- Portfolio MGT - Group AssignmentDocument28 pagesPortfolio MGT - Group AssignmentCarine Tee100% (2)
- Economics Lecture 1Document2 pagesEconomics Lecture 1Carine TeeNo ratings yet
- EO Lecture 5 March 2018 (Ratnes Rasiah)Document37 pagesEO Lecture 5 March 2018 (Ratnes Rasiah)Carine TeeNo ratings yet
- Written ReportDocument19 pagesWritten ReportCarine TeeNo ratings yet
- ISB CheatSheetDocument12 pagesISB CheatSheetCarine Tee100% (1)
- ISB CheatSheetDocument12 pagesISB CheatSheetCarine Tee100% (1)