Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Gdjdjyt
Uploaded by
Novita Sari DewiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Gdjdjyt
Uploaded by
Novita Sari DewiCopyright:
Available Formats
or fosphenytoin (20 mg/kg) (Class I, Level of Evidence B; Figure 3).
An alternative to
phenytoin infusion is levetiracetam (500 mg q12h, adjusted for renal insufficiency). Side
effects of phenytin infusions include rash, hypotension, arrhythmias, and severe
hypocalcemia for the phosphenytoin presentation. Patients with ICH may benefit from
prophylactic anti-epileptic drug therapy, but no randomized trial has addressed the efficacy of
this approach. The American Heart Association Guidelines have recommended anti-epileptic
medication for up to one month, after which therapy should be discontinued in the absence of
seizures. This recommendation is supported by the results of a recent study that showed that
the risk of early seizures was reduced by prophylactic antiepileptic drug therapy [95]. The 30day risk for convulsive seizures after ICH is approximately 8%, and the risk of overt status
epilepticus is 1% to 2%. Lobar location and small hematomas are independent predictors of
early seizures.
The argument for prophylactic anticonvulsant therapy in stuporous or comatose ICH patients
is bolstered by the fact that continuous electroencephalogram monitoring demonstrates
electrographic seizure activity in approximately 25% of these patients, despite prophylactic
anti-epileptic drug therapy. The risk of late seizures or epilepsy among
survivors of ICH is 5% to 27%.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- DDDD DDDD DDDD DDDD DDocument1 pageDDDD DDDD DDDD DDDD DNovita Sari DewiNo ratings yet
- OA JenniferDocument27 pagesOA JenniferNovita Sari DewiNo ratings yet
- E EeeeeeeeeeeeDocument1 pageE EeeeeeeeeeeeNovita Sari DewiNo ratings yet
- A AaaaaaaaaaDocument1 pageA AaaaaaaaaaNovita Sari DewiNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument1 pageDaftar PustakaNovita Sari DewiNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument1 pageDaftar PustakaNovita Sari DewiNo ratings yet
- Ca ColonDocument72 pagesCa ColonTeofilus KristiantoNo ratings yet
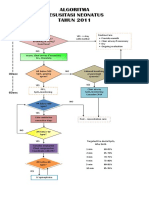
- ALGORITMA Resus NeonatusDocument1 pageALGORITMA Resus NeonatusNovita Sari DewiNo ratings yet
- Cover Jilid 1Document1 pageCover Jilid 1Syahputra Parlindungan RajagukgukNo ratings yet
- 05 PDFDocument17 pages05 PDFNovita Sari DewiNo ratings yet
- ALGORITMA Resus NeonatusDocument1 pageALGORITMA Resus NeonatusNovita Sari DewiNo ratings yet
- Morpot 11 Agustus 2015 Kelompok 1Document11 pagesMorpot 11 Agustus 2015 Kelompok 1Novita Sari DewiNo ratings yet