100% found this document useful (1 vote)
19K views4 pagesGland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Nature
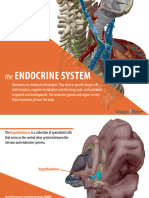
This document summarizes the major endocrine glands and their hormones, target tissues, and actions. The hypothalamus releases hormones that stimulate or inhibit the adenohypophysis. The neurohypophysis secretes antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin which target the kidneys and uterus/mammary glands. The adenohypophysis releases hormones like growth hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, and gonadotropins which target various tissues. Other glands secrete hormones like insulin, glucagon, cortisol, estrogen and thyroid hormones which regulate processes in multiple organs.
Uploaded by
rnalfasCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
19K views4 pagesGland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Nature
This document summarizes the major endocrine glands and their hormones, target tissues, and actions. The hypothalamus releases hormones that stimulate or inhibit the adenohypophysis. The neurohypophysis secretes antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin which target the kidneys and uterus/mammary glands. The adenohypophysis releases hormones like growth hormone, thyroid stimulating hormone, and gonadotropins which target various tissues. Other glands secrete hormones like insulin, glucagon, cortisol, estrogen and thyroid hormones which regulate processes in multiple organs.
Uploaded by
rnalfasCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Hormones and Their Functions