Professional Documents
Culture Documents
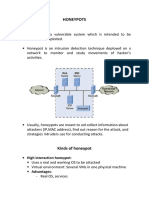
Honeypots Are Closely Monitored Network Decoys
Uploaded by
Akram Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageHoneyd is a virtual honeypot daemon that simulates virtual computer systems at the network level to appear as unallocated network addresses, fooling network fingerprinting tools. It simulates the networking stacks of different operating systems and can provide services for many virtual systems. Honeyd also supports virtual routing topologies to create large virtual networks that include characteristics like latency and packet loss.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHoneyd is a virtual honeypot daemon that simulates virtual computer systems at the network level to appear as unallocated network addresses, fooling network fingerprinting tools. It simulates the networking stacks of different operating systems and can provide services for many virtual systems. Honeyd also supports virtual routing topologies to create large virtual networks that include characteristics like latency and packet loss.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageHoneypots Are Closely Monitored Network Decoys
Uploaded by
Akram KhanHoneyd is a virtual honeypot daemon that simulates virtual computer systems at the network level to appear as unallocated network addresses, fooling network fingerprinting tools. It simulates the networking stacks of different operating systems and can provide services for many virtual systems. Honeyd also supports virtual routing topologies to create large virtual networks that include characteristics like latency and packet loss.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Honeyd: A Virtual Honeypot Daemon
(Extended Abstract)
Honeypots are closely monitored network decoys
serving several purposes: they can distract adversaries
from more valuable machines on a network, they can
provide early warning about new attack and exploitation
trends and they allow in-depth examination of
adversaries during and after exploitation of a honeypot.
Deploying physical honeypots is often time intensive
and expensive as different operating systems require
specialized hardware and every honeypot requires
its own physical system. This paper presents Honeyd, a
framework for virtual honeypots, that simulates virtual
computer systems at the network level. The simulated
computer systems appear to run on unallocated network
addresses. To fool network fingerprinting tools, Honeyd
simulates the networking stack of different operating
systems and can provide arbitrary services for an
arbitrary number of virtual systems. Furthermore, the
system supports virtual routing topologies that allow the
creation of large virtual networks including characteristics
like latency and packet loss. We discuss Honeyd’s
design and implementation.
1
You might also like
- Hacking and Networking ComponentsDocument14 pagesHacking and Networking ComponentsKhawaja SabbaqNo ratings yet
- Hacking Module 07Document46 pagesHacking Module 07Jitendra Kumar Dash100% (2)
- Hackers Tools 1 - 2Document6 pagesHackers Tools 1 - 2nanangn007No ratings yet
- IT Data Security: Assignment-1Document12 pagesIT Data Security: Assignment-1ManthanNo ratings yet
- What Is A Honeypot?Document8 pagesWhat Is A Honeypot?Anup SahuNo ratings yet
- Glossary of 100 Networking Terms You Must KnowDocument4 pagesGlossary of 100 Networking Terms You Must KnowMartinho ReisNo ratings yet
- A Virtual Honeypot FrameworkDocument15 pagesA Virtual Honeypot FrameworkЮля ПеревознюкNo ratings yet
- S 0104 Virtual HoneypotDocument7 pagesS 0104 Virtual HoneypotRaheem ShaikNo ratings yet
- Honeynets: Implementation and Testing of A Honeynet To Verify A Network's Security ConditionDocument20 pagesHoneynets: Implementation and Testing of A Honeynet To Verify A Network's Security ConditionajisaiNo ratings yet
- Network Forensic Based On Honeynet: Deepali Kansal, Navdeep Singh SethiDocument4 pagesNetwork Forensic Based On Honeynet: Deepali Kansal, Navdeep Singh SethiIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- CEH ToolsDocument7 pagesCEH ToolsLordWaderNo ratings yet
- Honey PotsDocument5 pagesHoney PotsAreefNo ratings yet
- CEH Pentesting Tools: SniffersDocument5 pagesCEH Pentesting Tools: SniffersDamianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 VMDocument13 pagesLecture 1 VMAzkahViqarNo ratings yet
- VirtualisationDocument6 pagesVirtualisationMelroyNo ratings yet
- ServerDocument65 pagesServerKuhiuhyrfNo ratings yet
- Tanuj Seminar ReportDocument23 pagesTanuj Seminar Reporttanuj kumarNo ratings yet
- Honeypots: Malware Class Presentation Xiang Yin, Zhanxiang Huang, Nguyet Nguyen November 2 2004Document72 pagesHoneypots: Malware Class Presentation Xiang Yin, Zhanxiang Huang, Nguyet Nguyen November 2 2004LissyVargheseNo ratings yet
- Honeypots Seminar1 CollegeDocument7 pagesHoneypots Seminar1 CollegeJoseph John GabrielNo ratings yet
- Ad HocNetworksDocument26 pagesAd HocNetworkskarthickamsecNo ratings yet
- Welcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Document5 pagesWelcome To International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDNo ratings yet
- 01 Cloud Computing Background Distributed SystemsDocument36 pages01 Cloud Computing Background Distributed SystemsKashfi ShormitaNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument8 pagesUnit Ivenkata rama krishna rao junnuNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument30 pagesComputer Networkthilakraja2000No ratings yet
- Distributed Operating SystemDocument24 pagesDistributed Operating Systembubun_metal100% (1)
- CS02DOS Unit 1UNit - 1 IntroductionDocument6 pagesCS02DOS Unit 1UNit - 1 IntroductionSalar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Words EnglishDocument4 pagesWords EnglishSantiago Garzón RamírezNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System in Software Defined Networks Using Machine Learning ApproachDocument8 pagesIntrusion Detection System in Software Defined Networks Using Machine Learning ApproachIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Distributed SystemDocument162 pagesDistributed SystemBiki JhaNo ratings yet
- Ngajar - 5 Virtual MachineDocument13 pagesNgajar - 5 Virtual MachineReza NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Devices Used in Each Layer of TCPDocument10 pagesDevices Used in Each Layer of TCPMD. TasneemNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CloudDocument102 pagesUnit 1 CloudChetha SpNo ratings yet
- Oral UpdateDocument10 pagesOral UpdateAditya KokateNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Network and Internet (MT-L)Document30 pages2.1 Network and Internet (MT-L)muhammad hussainNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Network and Internet (MT-L)Document30 pages2.1 Network and Internet (MT-L)muhammad hussainNo ratings yet
- Architecture of Distributed SystemsDocument22 pagesArchitecture of Distributed SystemsNisha JosephNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesInterview QuestionsishwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Internet and NetworkingDocument4 pagesChapter - 2 Internet and NetworkingbaljitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Grid Computing ,: Networked ComputersDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Grid Computing ,: Networked Computersdevendra250788No ratings yet
- Honeynet Height Interactive Tool Sebek3 Detecting Techniques-FormtedDocument19 pagesHoneynet Height Interactive Tool Sebek3 Detecting Techniques-FormtedMohammed_Almeh_3588No ratings yet
- 1 Eecs 2009 28Document46 pages1 Eecs 2009 28hussain9haider-1No ratings yet
- Experiment No.5 - Cyber SecurityDocument10 pagesExperiment No.5 - Cyber SecurityNIRANJAN KALENo ratings yet
- SupresoresDocument5 pagesSupresoresÁngelLópezNo ratings yet
- Notes 2.1 - Networks (Part 1)Document11 pagesNotes 2.1 - Networks (Part 1)dragongskdbsNo ratings yet
- Honeypot-A Secure Network SystemDocument5 pagesHoneypot-A Secure Network SystemJohnBusigo MendeNo ratings yet
- Study - Data Center, Docker Container and Fortigate Network FinaDocument8 pagesStudy - Data Center, Docker Container and Fortigate Network Finanaimur821No ratings yet
- Csc322 Assignment 1csc322Document3 pagesCsc322 Assignment 1csc322Anabia JanetNo ratings yet
- Coc 3 EditedDocument186 pagesCoc 3 EditedYuri AngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 PDCDocument51 pagesChapter 01 PDCAnver ArshadNo ratings yet
- Remote DesktopDocument5 pagesRemote Desktopsetiyawanmuktiwijaya160902No ratings yet
- Solution To Black Hole AttackDocument26 pagesSolution To Black Hole AttackNaresh KNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Peer-To-Peer SquirrelDocument28 pagesUnit 3 Peer-To-Peer SquirrelSwapnil ShindeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Distributed Systems and Characterisation: Valerie G. SilverioDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Distributed Systems and Characterisation: Valerie G. Silveriovalerie51420004776No ratings yet
- NEWHONEYPOTDocument7 pagesNEWHONEYPOTvickyNo ratings yet
- Name The Device and Tell On What Area This Device Usually UseDocument18 pagesName The Device and Tell On What Area This Device Usually UseRowena Mae N. LangonesNo ratings yet
- Part 2Document37 pagesPart 2Salih AkadarNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument9 pagesFinal Projectapi-522484422No ratings yet
- Networking Hardware IGCSE CIE Computer Science Free Material For o LevelDocument12 pagesNetworking Hardware IGCSE CIE Computer Science Free Material For o Levelamartya k singhNo ratings yet