Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Proteins Sheets
Uploaded by
lcassidy90740 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesProteins Sheets
Uploaded by
lcassidy9074Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Proteins
“The precise folding up of @ protein into its tertiary structure
(creates a three dimensional arangement of te acive groups.
“The way each group faces wit respect othe others gives te
protein its unique chemical properties. a protein loses this
Precise structure (denaturation), itis usually unable to carry
is botogcal function. Proteins are often classifiod on tha bas
Structure (globular vs fbrous). Some of the properties used
the basis of structural classification aro culned oppost,
Primary Structure - 1° (aminoacid sequence)
Shigeo undies amino ate i gener nh patie
_ bonds to form molecules calles polypeptide chains, There are 20
Swe ines tf ante ads han be lla npser na vat
tuber oar orator. Th seaueee cles re
Drimery atuctre I's te arargement ot eacton ard
eeosongarts min arin so cma eres a ghae
‘fret opansston a pret enatcege Kon
‘Secondary Structure - 2° (a-helx or B-pleated sheet)
Dolypontdee socom flies varus wae, retamed 6 ae the
‘Secondary 2) sete Th most sornman yee of actres
‘a acaled whelk and a pleated sheet. Seconcaryeracures
fare maintained with hydrogen bands between neighboring CO.
land NH groups. H-2oncs,athoughinsiualy weak, provise
Consiecabe stergth when thee ae a larga camber of her,
‘Tha example, igi. shows the two main types oF secondary
structure. n bo the side groups [rot shown) project out
trom the aructur. Most lobule posin contain regions of«-
aloes togethor with shoots. Koratn (a fbrous prot) Ie
composed aimaat ently ofa heloos, Fboin (tk preter),
‘nator ferousrcton, almost ntl insect form.
Tertiary Structure - 3° (toiding)
Every pron has a.precse src formed by he cing of the
sncondary structure ino & complex shape cated the tertiary
‘trueture. The prot folds up because varius pons onthe
secondary sruture aie tracted 1 one anoter. The strongest
{ks ne cautes ty bonding between nachnotrg cystine amo
acti whie orm deautie Seen Other erections tat are
woven folding incuge ek onc and yrogen bonds as we
ashyerophebe reeacters.
‘Quaternary Structure - 4°
Some proteins (uch as enzymes) are complete ara funciona
wih a tora sireture only. However, mary complex protens
x38 egotepsins of poypepce chains. Tre arengement of
‘he petypepide chains nto a functional proteins termed the
_quaterary structure. Tre example (gh) stows a molecule ot
emogbbn, a enulr prken ooToosed of 4 polpenie stuns
“pos togetrer: wo genes! Bets ehams an 9 isa alpha
‘Shain Each has ahame (ion senaring) grup athe core
‘ho chain, ahien ings cxygen.Prcane canting ron peta
‘ator are eonjugeed protsina, Tho non poten pase the
rostneie group,
Denaturation of Proteins
Derturation refers 0 he loss of he twee-dmensoal sre
{ang usuly aco ebesogial uncon) ofa proton. Derauation
's often, athough not avaye, permanent. t resus trom an
_aterabon ofthe bonds thal mania Ye secondary and teraty
Suds clthe poten even thaughte sequence of amino ais
“femansuncnanged, Agen that cause denuraton ae:
*'Sirong acide and alkalis: Disrupt ionic bonde ard esl 0
naguletor of he rata Lang execaure also Breaks down
{he pmary suc cho pre.
+ Heavy metas May arp enc tends, fm stor bonds wih
‘pe caeonyl gun ol he cup, and redo prota charge.
‘The general ele isto cause tne procpiaton ofthe pci.
+ Heat and redaton(e3. UV): Cause disuption ofthe bonds
‘he pct vag incensed anergy proviso sams.
+ Detocgents and solvents: For bonds withthe non-polar
oun i he prota, thereby dung hydrogen boring.
+
‘Amino seid
sequence
2 y
Foarogen
ons
‘Trees! sbape 8
ystogen bonds septa
‘Alpha (a) helix or frpleated sheet
3
louie
bre
Polypeptide chain
a
- Beato:
spa cen
Hemoglobin molecule —intemaitin exh
otypepieencises en te
Sonar oresrate gue
Hemoglobin's Chemical Formula
CC scsy H sais O are N ray S Fe,
‘cotiagen consists of twee nea!
pelypeptidee wound around each
‘ther 6 form ate" Evry tie
‘amine eld mean peypartt
falyeine (Gly) malecule. whe
I} eeogen borg ccc hek
‘ree sand logtner
Bovine insu is relatively smal rosin consisting ot
‘wo polypepide chars anv chin ania cha). These
‘wc chains are hed ogenr by csi ridge Sabie
rsgnooring cystine (Cys) molecules
* Sretly explain how proteins are involved inthe following functional roles:
{@) Structural issues of the body:
(©) Reguiating body processes:
(6) Contractile elements:
{@) Immunological response to pathogens:
{(¢) Tansporting molecules within colls and in the bloodstream:
(9) Catalyzing metabolic reactions in cals:
Explain haw denaturation destrays protein function:
& |S. Describe one structural ference between globular and fibrous proteins:
“4 Determine the total number of amino acids inthe « and 6 chains ofthe insulin molecule illustrated above:
Patan Ra
Amino Acids
‘Amino acids are the basic units from which proteins are amino acids) trom their det. Al ther amino acide ca
made, Plants can manufacture all the amino acids they constructed from these essential amino acids. The oro="
require from simpler molecules, but animals must obtain @ which the diferent amino acids are linked together to ©
certain number of ready-made amino acids (called essential proteins is controlled by genes on the chromosomes.
Properties of Amino Acids TRE pep cn rm
Tivee examples of amine aces wih gee amos
citerent chevicelproperies ave shown Gat fameesocteate alia Propory i
rm win helt specie Fr groups
farina Te F groups can have qu
Aveo eremcal roperte
Cysteine Lysine ‘Aspartic acid
“The ater of amino actsina pot
|s ected by he oer of
rucooiesn ONA and mRNA.
Peptide bonds lnk amino eds
{get in ong pore eaes
povpootde hans 200 moy fom |
parterall ofa prota,
‘The amine aide aro inked together by peptide bonde to form eng
chain of upto several hunared amino acids (caled sokypopts chins).
‘These chains may bo functional unis (complete by themsehves) or they
‘may need tobe jones to other polpeptise chains before they can cay
‘out heeft, Inhumans, nt al amino acids can be manuiactured
by our body en must be ten in wih our cat eight n adults). These
{ara the essontial amino acid’ (ndcated bythe symbol @ onthe ah
“T Dasorbe the biological functions of amino acids:
2. Desorite what makes each of the 20 amino acids unique:
‘3. Name the type of bond that links amino acids together:
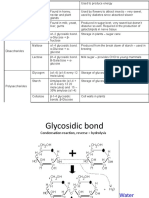
Condensation and Hydrolysis Reactions
2 acid can combine to form opto chain in what is a
2. eondeneationrsacion Pete ane canbe broken Hy ee o
by hydrolysis ts smols amie acs SN-G-c: IN-C-c%
2 amino pa Lee
ane Amino seid Amino acia
A
Hydrolysis reaction
When 8 alpepie ie pit
5 became procoes of
Algcaten, 2 water molocula
provides a rydrogen ane a
cron croup
ig
Ho
Dipeptige
“ater Pepto ter
Dipeptice
‘Describe the process that determines the sequence in which amino acids are liked together to form polypeptide chains:
Explain what is moant by essential amino acids:
‘Deserve briefly the process of the condensation reaction for amino acids:
DDesoribe briefly the proness ofthe hydralysis reaction for amino acs:
8 Name the optical isomeric form that occurs in nearly all amino acids in ving things:
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument7 pagesAmino Acids and Proteinslcassidy9074No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates PPDocument11 pagesCarbohydrates PPlcassidy9074No ratings yet
- Enzyme ExperimentsDocument9 pagesEnzyme ExperimentssummerfordmNo ratings yet
- Properties of EnzymesDocument7 pagesProperties of Enzymeslcassidy9074No ratings yet