Professional Documents
Culture Documents
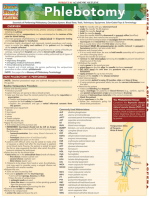
VENIPUNCTURE
Uploaded by
Sakeena Chanel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views2 pagesThis document discusses various methods for obtaining blood samples and performing common blood tests. It describes techniques such as syringe, serum separation, and whole blood collection tubes. Skin puncture and capillary blood tests are outlined, including typical collection sites. Common blood tests are summarized, such as hematocrit, hemoglobin, blood glucose, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Normal ranges are provided for many of the tests.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various methods for obtaining blood samples and performing common blood tests. It describes techniques such as syringe, serum separation, and whole blood collection tubes. Skin puncture and capillary blood tests are outlined, including typical collection sites. Common blood tests are summarized, such as hematocrit, hemoglobin, blood glucose, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Normal ranges are provided for many of the tests.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views2 pagesVENIPUNCTURE
Uploaded by
Sakeena ChanelThis document discusses various methods for obtaining blood samples and performing common blood tests. It describes techniques such as syringe, serum separation, and whole blood collection tubes. Skin puncture and capillary blood tests are outlined, including typical collection sites. Common blood tests are summarized, such as hematocrit, hemoglobin, blood glucose, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Normal ranges are provided for many of the tests.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
VENIPUNCTURE (cont’d)
Syringe Method or Butterfly
1. Used for difficult draws, small veins or small amount of blood is necessary.
2. Requires a 2 to 30cc syringe
(10-20cc) and 19-23 gauge needle
3. Speciman tube is filled quickly
Serum Only Test
1. Requires that whole blood speciman be allowed to clot and then centrifued to obtain
serum and use serum separator tube
a. Tubes with no additives must be allowed to sit vertically 20 to 30 min to allow
clotting
Whole Blood
1. To obtain plasma, tubes with anticoagulant are needed
2. Gently rotate tube with additive in a figure 8 motion immediately to mix anticoagulant.
Skin Puncture and Capillary Blood Test
1. Explain Procedure
Capillary: Minute blood vessel that convey blood from arterioles to venules
2. Capillary Blood
a. Found under the surface of the skin
b. Most practical sites to obtain blood are:
1. Ring or Great finger
2. Ear lobe
3. In infants: great toe or heel
4. Keep log of information
a. Date
b. Patient name
c. Test performed
d. Results of test
e. Your initials
Hematocrit (Hct)
1. Screening test to determine anemia or polycythemia
a. Anemia: condition which there is a lack of circulating red blood cells
2. Polycythemia: excessive number of RBCs
Microhematocrit Capillary Tube
1. Used (contains Heparin)
2. Use clay to seal one end
3. Centrifual action separates RBC from serum
4. Hematocrit is expressed as the % of packed RBCs in the total volume of blood
a. Normal range for male adults: 40-54%
b. Normal range for female 37-47%
Hemoglobin (Hgb)
1. A protein found in RBCs that transport the molecules of O2 in the blood
a. Normal range male is 14-18g/100cc of blood
b. Normal range for female is 12-16g/100cc of blood
Blood Glucose Screening
1. May use reagent strip
2. Most reliable is glucometer
3. Normal fasting blood sugar (FBS) range is 80-120mg/100cc of blood
a. Fasting means nothing to eat or drink for 8-12 hours
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
1. Known as ESR, Sed rate, SR
2. Blood test that tests the rate at which RBCs settle in a particular calibrated tube, within a
given amount of time; usually 1 hour
3. Determines the degree of inflammation in the body
4. Used in the diagnosis and evaluation of respiratory tract diseases, cancer, arthritis
5. Whole blood is required
6. Normal rate RBCs fall is 1mm/5min
7. Females are higher than males, especially during menstruation and pregnancy
You might also like
- BLOOD SPECIMEN CollectionDocument12 pagesBLOOD SPECIMEN CollectionJohn Henry G. Gabriel IV100% (11)
- Practical Haematology GazaDocument86 pagesPractical Haematology GazaTophe DiqiNo ratings yet
- Hematology NotesdocxDocument11 pagesHematology NotesdocxdmclmllNo ratings yet
- Blood CollectionDocument42 pagesBlood CollectionArslan Arshad100% (1)
- Hem Lab Microhematocrit F15Document10 pagesHem Lab Microhematocrit F15Joan Christie WijayaNo ratings yet
- Tom Rockmore - Hegel's Circular EpistemologyDocument213 pagesTom Rockmore - Hegel's Circular Epistemologyluiz100% (1)
- Intro To HematologyDocument9 pagesIntro To HematologyDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Hematology 2 LaboratoryDocument11 pagesHematology 2 LaboratoryChristine BadilloNo ratings yet
- Hematocrit (HCT) (Packed Cell Volume PCV) : Objectives: ToDocument19 pagesHematocrit (HCT) (Packed Cell Volume PCV) : Objectives: ToRamadan PhysiologyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical HematologyDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Clinical HematologyBishoy GalalNo ratings yet
- Hematocrit Lab Test MaelDocument2 pagesHematocrit Lab Test MaelMuhamad NaemNo ratings yet
- F&E, Oxygenation - PreTestDocument9 pagesF&E, Oxygenation - PreTestToni Marie Buenconsejo PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Norman K. Denzin - The Cinematic Society - The Voyeur's Gaze (1995) PDFDocument584 pagesNorman K. Denzin - The Cinematic Society - The Voyeur's Gaze (1995) PDFjuan guerra0% (1)
- Clotting TimeDocument26 pagesClotting TimeMalliga SundareshanNo ratings yet
- PCV and EsrDocument40 pagesPCV and EsrArslan Arshad100% (2)
- Lesson Plan - Sight Word ObservationDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - Sight Word Observationapi-253277023No ratings yet
- GTAG-14 Edited With Ad 05-20-20101 PDFDocument32 pagesGTAG-14 Edited With Ad 05-20-20101 PDFpiornelNo ratings yet
- Hematology NotesDocument17 pagesHematology NotesEly Sibayan100% (2)
- Sketch NotesDocument32 pagesSketch NotesFilipe Rovarotto100% (8)
- Abg AnalysisDocument9 pagesAbg AnalysisLakshmi RjNo ratings yet
- Revised LabDocument18 pagesRevised LabAbu AyemanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Ordinal NumbersDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Ordinal Numbersapi-329663096No ratings yet
- Blood Investigations: Dr. Maulika PatelDocument21 pagesBlood Investigations: Dr. Maulika Patelpatrikmodi100% (1)
- Post Lab 01-09Document7 pagesPost Lab 01-09Patrick ParconNo ratings yet
- Hematology Sop (Revise 2023)Document8 pagesHematology Sop (Revise 2023)Jeffrey GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Technical College of Applied Sciences Medical Laboratory Science First Stage - Second Semester Lab Technic ReportDocument9 pagesTechnical College of Applied Sciences Medical Laboratory Science First Stage - Second Semester Lab Technic ReportELYANNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Hematocrit DeterminationDocument7 pagesExercise 5 Hematocrit DeterminationJam RamosNo ratings yet
- Important Key NotesDocument5 pagesImportant Key NotesLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Lab ReviewerDocument3 pagesLab Reviewerryana cabreraNo ratings yet
- Blood Testing: Laboratory ExerciseDocument6 pagesBlood Testing: Laboratory ExerciseDaniela AmorimNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis Practical Work GuidelineDocument6 pagesHemostasis Practical Work Guidelinemutiara hnryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HematologyDocument67 pagesIntroduction To HematologyMera MendozaNo ratings yet
- MICROHEMATOCRITDocument19 pagesMICROHEMATOCRITNico LokoNo ratings yet
- Istinye University Medical Faculty Physiology Lab Notes Blood Sampling Capillary Blood SamplingDocument7 pagesIstinye University Medical Faculty Physiology Lab Notes Blood Sampling Capillary Blood Samplingazouz jaboobiNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of TrypanosomiasisDocument82 pagesDiagnosis of TrypanosomiasisDrVijayata Choudhary100% (1)
- Lec 2 Biochemistry PracDocument17 pagesLec 2 Biochemistry PracMarwan A.GhafoorNo ratings yet
- Clinical Haematology Lab. 1: Practical PhysiologyDocument31 pagesClinical Haematology Lab. 1: Practical PhysiologyHameed SabahNo ratings yet
- Specimen CollectionDocument60 pagesSpecimen Collectionmyla adapNo ratings yet
- Capillary Fragility (Resistance) Test:: Assays For Primary HaemostasisDocument18 pagesCapillary Fragility (Resistance) Test:: Assays For Primary HaemostasisJohn Fritz Gerald BascoNo ratings yet
- WameedMUCLecture 2021 9260965Document5 pagesWameedMUCLecture 2021 9260965Mubarak Abubakar yaroNo ratings yet
- HCT HGB EsrDocument6 pagesHCT HGB EsrIrachel ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Principle Behind Special Collection Procedures, Special Supplies or EquipmentDocument50 pagesPrinciple Behind Special Collection Procedures, Special Supplies or EquipmentSofia JuliaNo ratings yet
- PLT MeasurementsDocument6 pagesPLT MeasurementsAudreySlitNo ratings yet
- Estimation of PCV by Wintrobe MethodDocument18 pagesEstimation of PCV by Wintrobe Methodjyoti singhNo ratings yet
- Packed Cell Volume (PCV)Document24 pagesPacked Cell Volume (PCV)Eyasu demsewNo ratings yet
- Packed Cell VolumeDocument5 pagesPacked Cell VolumeMotasem Sirag Mohmmed othmanNo ratings yet
- MT Activity 1Document18 pagesMT Activity 1Luigie TorresNo ratings yet
- Technical ProcedureDocument142 pagesTechnical Procedureflavianamcl2012No ratings yet
- Hema I Chapter 10 - PCVDocument24 pagesHema I Chapter 10 - PCVchris andrieNo ratings yet
- Lab #1 (Phlebotomy)Document24 pagesLab #1 (Phlebotomy)Neda'a GhNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Q&ADocument3 pagesBlood Transfusion Q&APratheebaNo ratings yet
- Chap 11 SummDocument12 pagesChap 11 SummMark GuinobanNo ratings yet
- Collection of Blood Sample From Experimental AnimalsDocument12 pagesCollection of Blood Sample From Experimental AnimalslovehopeNo ratings yet
- Blood Smear and PCVDocument10 pagesBlood Smear and PCVغالب الموسويNo ratings yet
- Physiology 1 Practical Notebook Submitted To: Dr. Aniza Ishaque Submitted By: Momina Nadeem Rimsha Zareen Abdullah Najam Aman SarfrazDocument18 pagesPhysiology 1 Practical Notebook Submitted To: Dr. Aniza Ishaque Submitted By: Momina Nadeem Rimsha Zareen Abdullah Najam Aman SarfrazMaryam ShahzadiNo ratings yet
- 2HKWZ4PJPDocument10 pages2HKWZ4PJPMizahNo ratings yet
- Pathology Notes HemalathaDocument117 pagesPathology Notes HemalathapriyagerardNo ratings yet
- HEMA LAB5 ESR & StainingDocument4 pagesHEMA LAB5 ESR & StainingSareene Joyce PepitoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-12-29 at 8.13.14 AMDocument28 pagesScreenshot 2022-12-29 at 8.13.14 AMRaza StylinsonNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping PDFDocument23 pagesBlood Grouping PDFMaxamed Cali AtomNo ratings yet
- Physiology Practical For 1st Year Institute Pharmacy StudentsDocument14 pagesPhysiology Practical For 1st Year Institute Pharmacy StudentsSnipper HunterNo ratings yet
- CP BookDocument99 pagesCP BookKeerthy VasanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Platelets: Hematology 2-LaboratortyDocument37 pagesOverview of Platelets: Hematology 2-LaboratortyMiggy PascualNo ratings yet
- Clotting Time PDFDocument17 pagesClotting Time PDFKhaled ZatariNo ratings yet
- Hema I Chapter 12 - ESRDocument29 pagesHema I Chapter 12 - ESRdileca1448No ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument2 pagesSeptic Shockمحمد زينNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Part III - UpdatedDocument38 pagesModule 2 - Part III - UpdatedDhriti NayyarNo ratings yet
- How To Connect To iSCSI Targets On QNAP NAS Using MPIO On Windows 2008Document30 pagesHow To Connect To iSCSI Targets On QNAP NAS Using MPIO On Windows 2008Jazz OberoiNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Bank For Advanced Accounting 1 E by Bline 382235889 Test Bank Bank For Advanced Accounting 1 E by BlineDocument31 pagesTest Bank Bank For Advanced Accounting 1 E by Bline 382235889 Test Bank Bank For Advanced Accounting 1 E by BlineDe GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/iesDocument1 pageDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Learning Competency/iesErma JalemNo ratings yet
- TRUMPF Marking Laser BrochureDocument48 pagesTRUMPF Marking Laser BrochureKKM SBNo ratings yet
- Lecture Planner - Chemistry - MANZIL For JEE 2024Document1 pageLecture Planner - Chemistry - MANZIL For JEE 2024Rishi NairNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Design: Figure 1. Architecture Diagram For Greykite Library's Main Forecasting Algorithm, SilverkiteDocument3 pagesAlgorithm Design: Figure 1. Architecture Diagram For Greykite Library's Main Forecasting Algorithm, Silverkitesiper34606No ratings yet
- Alfa Laval Aalborg Os Tci Marine BoilerDocument2 pagesAlfa Laval Aalborg Os Tci Marine Boilera.lobanov2020No ratings yet
- Thermal ComfortDocument50 pagesThermal ComfortSSNo ratings yet
- The Senior High School in The Phillipines: The Way To The WorldDocument5 pagesThe Senior High School in The Phillipines: The Way To The WorldRodel Ramos DaquioagNo ratings yet
- TuberkulosisDocument285 pagesTuberkulosisTeuku M. FebriansyahNo ratings yet
- TML IML DefinitionDocument2 pagesTML IML DefinitionFicticious UserNo ratings yet
- HTML Editor 8Document13 pagesHTML Editor 8Guru PrasadNo ratings yet
- Soal PTS Vii BigDocument6 pagesSoal PTS Vii Bigdimas awe100% (1)
- PCNSE DemoDocument11 pagesPCNSE DemodezaxxlNo ratings yet
- Project in Precal: Mary Joyce MolinesDocument11 pagesProject in Precal: Mary Joyce MolinesJaja KeykNo ratings yet
- CN Blue Love Rigt Lyrics (Romanized)Document3 pagesCN Blue Love Rigt Lyrics (Romanized)Dhika Halet NinridarNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire OriginalDocument6 pagesQuestionnaire OriginalJAGATHESANNo ratings yet
- Croda Smarter Polymers Guide Sep 2019Document20 pagesCroda Smarter Polymers Guide Sep 2019Keith Tamura100% (1)
- თინათინ ზურაბიშვილი, თვისებრივი მეთოდებიDocument111 pagesთინათინ ზურაბიშვილი, თვისებრივი მეთოდებიNino LomaiaNo ratings yet
- ISA Guidelines PPF 1Document19 pagesISA Guidelines PPF 1Vasu DevanNo ratings yet
- UVEX - Helmets & Eyewear 2009Document19 pagesUVEX - Helmets & Eyewear 2009Ivica1977No ratings yet
- Lay Planning TypesDocument1 pageLay Planning TypesGaurav Shakya100% (1)