Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Redox Potentials
Uploaded by
koronakis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views1 pageOriginal Title
redox potentials
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views1 pageRedox Potentials
Uploaded by
koronakisCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
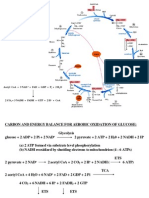
Table 1: Two-Electron Reduction Potentials
Redox Couple (2-electron reductions) E°'/mV
at 25°C
Reference
Xanthine/hypoxanthine, H+ -371 13, 14
Uric acid/xanthine, H+ -360 13
DTTox (cyclic disulfide), 2H+/DTT (Dithiotreitol) -317a 15
NAD+, H+/NADH -316 16, 13
NADP+, H+/NADPH -315 16, 11
Lipoic acid, 2H+/Dihydrolipoic acid -290 11, 17
GSSG, 2H+/2GSH (Glutathione) -240 18, 19
Cys-S-S-Cys, 2H+/2Cys-SH (Cystiene) -230 11, 20
TrxSS, 2H+/Trx(SH2) (Thioredoxin) -240b 18
GrxSS, 2H+/Grx(SH2) (Glutaredoxin) -218 18
FMN, 2H+/FMNH2 -219 21
FAD, 2H+/FADH2 -219 21
Riboflavin, 2H+/Leuco-riboflavin -200 13, 12
Acetaldehyde, 2H+/ethanol -197 13
Pyruvate, 2H+/lactate -183 11
Oxaloacetate, 2H+/malate -166 22
Methylene blue, 2H+/Leuco-methylene blue +11 11, 12
Dehydroascorbate, H+/Ascorbate +54 23
Ubiquinone (CoQ),2H+/ubihydroquinone (CoQH2) +84 24
O2, 2H+/ H2O2 + 300 7
NO3
-/NO2
- +421 25
H2O2, 2H+/2H2O +1320
You might also like
- TCA III Summary - PPSXDocument7 pagesTCA III Summary - PPSXBio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Activating Reagents 2. Depressants 3. Others (They Modify: PH, Coagulation, Redox, Rheology, Etc.)Document13 pagesActivating Reagents 2. Depressants 3. Others (They Modify: PH, Coagulation, Redox, Rheology, Etc.)ksteyonNo ratings yet
- Krapcho Dealkoxycarbonylation - Tet Lett - 1973Document4 pagesKrapcho Dealkoxycarbonylation - Tet Lett - 1973badarmunir941No ratings yet
- Diagram Proses Fischer tropsDocument2 pagesDiagram Proses Fischer tropsAgrivina Abel NoviraNo ratings yet
- Serie 1 - Ex5Document5 pagesSerie 1 - Ex5Karfala KandeNo ratings yet
- Electrocatalytic effect of underpotential Tl, Pb and Bi monolayers on redox reactionsDocument13 pagesElectrocatalytic effect of underpotential Tl, Pb and Bi monolayers on redox reactionsDonaldo HerreraNo ratings yet
- ChelationDocument12 pagesChelationAvinash PatilNo ratings yet
- Solubilities of L-Glutamic Acid, 3-NitrobenzoicDocument10 pagesSolubilities of L-Glutamic Acid, 3-NitrobenzoicNilgün Gülen TarganNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsNo ratings yet
- 10 1002@047084289X rn00544 PDFDocument9 pages10 1002@047084289X rn00544 PDFWalid Ebid ElgammalNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Cisplatin Hydrolytes with GlutathioneDocument6 pagesReactions of Cisplatin Hydrolytes with GlutathioneAnonymous ZY43E2DTNo ratings yet
- The Biocatalyzed Stereoselective Preparation of Polycyclic CyanohydrinsDocument7 pagesThe Biocatalyzed Stereoselective Preparation of Polycyclic CyanohydrinsDaigo G MamaniNo ratings yet
- Terpenes Importance General Structure and Biosynthesis PDFDocument9 pagesTerpenes Importance General Structure and Biosynthesis PDFAlejandra AvilaNo ratings yet
- Dimedone + AldehydeDocument5 pagesDimedone + AldehydemeeraanushaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Topics and Energy CarriersDocument37 pagesLecture 2 Topics and Energy CarriersKay156065No ratings yet
- La302484x Si 001Document10 pagesLa302484x Si 001physi CHeMNo ratings yet
- 161 BMF 38 Homohopanes and Gammaceranes v1Document4 pages161 BMF 38 Homohopanes and Gammaceranes v1Abdourahamane Ibrahim Ari MaïnaNo ratings yet
- 6 Metabolism 2014-2015Document33 pages6 Metabolism 2014-2015Chui WaiNo ratings yet
- O C SPA S A S: Rganic Hemistry Kill UmmaryDocument6 pagesO C SPA S A S: Rganic Hemistry Kill Ummaryhasan_j688675No ratings yet
- Molecules 02 00007Document4 pagesMolecules 02 00007Félix Álvarez de BroglieNo ratings yet
- Iron Oxide Catalyst Rapidly Reduces Sulfur-Containing Aromatic Nitro CompoundsDocument3 pagesIron Oxide Catalyst Rapidly Reduces Sulfur-Containing Aromatic Nitro CompoundsUdai PratapsinghNo ratings yet
- New Schiff Bases Derived From 3,4-Diamino-1h-1,2,4-Triazole-5 (4h) - Thione - Synthesis and Characterization (#1016611) - 2053858Document17 pagesNew Schiff Bases Derived From 3,4-Diamino-1h-1,2,4-Triazole-5 (4h) - Thione - Synthesis and Characterization (#1016611) - 2053858منى غانم ضاحي الحديديNo ratings yet
- 05 Worksheet 1 (Genchem) RelelevoDocument1 page05 Worksheet 1 (Genchem) Relelevocessarine relevoNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of 3-sulfonyloxypyridines: Oxidative ring expansion of α-furylsulfonamides and N→O sulfonyl transferDocument5 pagesSynthesis of 3-sulfonyloxypyridines: Oxidative ring expansion of α-furylsulfonamides and N→O sulfonyl transferlapsNo ratings yet
- Camphorsultam CleavageDocument3 pagesCamphorsultam Cleavageleda_prandiNo ratings yet
- Reagent Group Out Group in Remark: Key For ConversionsDocument2 pagesReagent Group Out Group in Remark: Key For ConversionsChetan KumarNo ratings yet
- Departm T of Textile Industries, National Taipei Institute of Twhnology, Taipei, Taiwan (Received 18 April 1994 Aceqted 3 June 1994)Document10 pagesDepartm T of Textile Industries, National Taipei Institute of Twhnology, Taipei, Taiwan (Received 18 April 1994 Aceqted 3 June 1994)Manthan JainNo ratings yet
- Potential - PH (Pourbaix) DiagramsDocument14 pagesPotential - PH (Pourbaix) DiagramsedwinNo ratings yet
- Angew. Chem - Int. Ed., 2022, 61, 2021135 (Oxazaborolidine + Synthons) SIDocument140 pagesAngew. Chem - Int. Ed., 2022, 61, 2021135 (Oxazaborolidine + Synthons) SIludoNo ratings yet
- Psyc EqnsDocument3 pagesPsyc Eqnsbblackwood3No ratings yet
- Enzymatic Assay of GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE (EC 1.11.1.9) PrincipleDocument4 pagesEnzymatic Assay of GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE (EC 1.11.1.9) PrincipleVempati Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Iron DiagramDocument14 pagesIron DiagramGrace DuongNo ratings yet
- Synthesis, Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Some Novel Acridine DerivativesDocument11 pagesSynthesis, Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Some Novel Acridine DerivativesPratiwi Rukmana NasutionNo ratings yet
- Caso SteviaDocument5 pagesCaso SteviaLambert TitoNo ratings yet
- 2 Triazine ChemistryDocument21 pages2 Triazine ChemistryyuregomesNo ratings yet
- Competitive Hydrodesulfurization Of 4,6-Dimethyldibenzothiophene, Hydrodenitrogenation Of 2-Methylpyridine, And Hydrogenation Of Naphthalene Over Sulfided Nimo/Γ -Al ODocument10 pagesCompetitive Hydrodesulfurization Of 4,6-Dimethyldibenzothiophene, Hydrodenitrogenation Of 2-Methylpyridine, And Hydrogenation Of Naphthalene Over Sulfided Nimo/Γ -Al Oioanaandra5690No ratings yet
- ZZZ (0) Modified Trichothecenes (XXXX 325)Document24 pagesZZZ (0) Modified Trichothecenes (XXXX 325)amaroluisNo ratings yet
- Tautomerization of Adenine Facilitated by Water: Computational Study of MicrosolvationDocument6 pagesTautomerization of Adenine Facilitated by Water: Computational Study of MicrosolvationvalentinaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Monosubstituted Succinic Acids From Tert-ButylsuccinateDocument3 pagesSynthesis of Monosubstituted Succinic Acids From Tert-ButylsuccinateJerzy JaniczekNo ratings yet
- CITRIC ACID CYCLE OVERVIEW (All Carried Out in Mitochondrial Matrix)Document19 pagesCITRIC ACID CYCLE OVERVIEW (All Carried Out in Mitochondrial Matrix)Kenshin Himura BahtosaiNo ratings yet
- Crystal - Res.ku - Edu Taksnotes Biol 638 Notes CHP 16Document19 pagesCrystal - Res.ku - Edu Taksnotes Biol 638 Notes CHP 16shahjafferNo ratings yet
- Diastereoselectivity of The Horner Wittig Reaction in The Synthesis of Beta Hydroxy Phosphine OxidesDocument24 pagesDiastereoselectivity of The Horner Wittig Reaction in The Synthesis of Beta Hydroxy Phosphine OxidesWill HoddsNo ratings yet
- Adenosine Triphosphate - WikipediaDocument65 pagesAdenosine Triphosphate - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Chem 340 Exam FormulasDocument4 pagesChem 340 Exam FormulasZevano C. SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Palladium Nanoparticles in Carbon Thin Film Lined SBA-15 Nanoreactors EfficientDocument6 pagesPalladium Nanoparticles in Carbon Thin Film Lined SBA-15 Nanoreactors EfficientDana MateiNo ratings yet
- Aldehid Dan KetonDocument5 pagesAldehid Dan KetonVicha FatanahNo ratings yet
- Verne89 - Template For Biochemical Pathways - BWDocument1 pageVerne89 - Template For Biochemical Pathways - BWhediyeNo ratings yet
- DFT Study On Mechanism of The Classical Biginelli ReactionDocument4 pagesDFT Study On Mechanism of The Classical Biginelli ReactionDuvan CastañedaNo ratings yet
- 2006 Claver1Document7 pages2006 Claver1Quimico271No ratings yet
- UV/Vis Spectrophotometer ManualDocument273 pagesUV/Vis Spectrophotometer ManualJungmin KimNo ratings yet
- 738616703organic ConversionDocument8 pages738616703organic ConversionSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- 10 3390@antiox8120589Document17 pages10 3390@antiox8120589Durga Prasad KalamNo ratings yet
- A. EMP Pathways/Glycolysis: Steps Reactants Products Enzyme Type of ReactionDocument2 pagesA. EMP Pathways/Glycolysis: Steps Reactants Products Enzyme Type of ReactionAsh YehiaNo ratings yet
- Suspect Screening Analysis in House Dust From Belgium Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Prioritization List and Newly Identified ChemicalsDocument20 pagesSuspect Screening Analysis in House Dust From Belgium Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Prioritization List and Newly Identified ChemicalspedroNo ratings yet
- Buffer solution explainedDocument27 pagesBuffer solution explainedSohel AnsariNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis-Gluconeogenesis-Pentose Phosphate-Krebs Cycle Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezDocument4 pagesGlycolysis-Gluconeogenesis-Pentose Phosphate-Krebs Cycle Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezCristhian LozanoNo ratings yet
- Tips For ConversionDocument2 pagesTips For ConversionPratham ZalaNo ratings yet
- Gas Hydrates 1: Fundamentals, Characterization and ModelingFrom EverandGas Hydrates 1: Fundamentals, Characterization and ModelingDaniel BrosetaNo ratings yet
- Accuracy Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageAccuracy Cheat Sheet PDFValter SchuelerNo ratings yet
- Tape MeasureDocument2 pagesTape MeasureMatthew PageNo ratings yet
- Idimerize ™ Inducible Heterodimer System User Manual: Clontech Laboratories, IncDocument16 pagesIdimerize ™ Inducible Heterodimer System User Manual: Clontech Laboratories, InckoronakisNo ratings yet
- In-Plate Dynamic Light Scattering, Uv and White Light ImagerDocument2 pagesIn-Plate Dynamic Light Scattering, Uv and White Light ImagerkoronakisNo ratings yet
- Spicy SpinachDocument1 pageSpicy SpinachkoronakisNo ratings yet
- ProtocolDocument2 pagesProtocolkoronakisNo ratings yet
- Drawing WashingDocument42 pagesDrawing WashingkoronakisNo ratings yet
- Reviving Interest in Tempera Painting TechniquesDocument59 pagesReviving Interest in Tempera Painting TechniquesAnamaria Durval da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Spicy SpinachDocument1 pageSpicy SpinachkoronakisNo ratings yet
- Planes of The Head FrontDocument1 pagePlanes of The Head FrontkoronakisNo ratings yet
- Drawing WashingDocument42 pagesDrawing WashingkoronakisNo ratings yet
- Blue-Hue Scattering Turbid Medium EffectDocument5 pagesBlue-Hue Scattering Turbid Medium EffectkoronakisNo ratings yet
- Prawn Phad ThaiDocument1 pagePrawn Phad ThaikoronakisNo ratings yet
- Extra Measurements From Left To RightDocument1 pageExtra Measurements From Left To RightkoronakisNo ratings yet
- Dss Igg XlinkDocument2 pagesDss Igg XlinkkoronakisNo ratings yet
- Addendum Colour ChartDocument1 pageAddendum Colour ChartkoronakisNo ratings yet
- Playing With Period Pigments2Document8 pagesPlaying With Period Pigments2koronakisNo ratings yet
- Dss Igg XlinkDocument2 pagesDss Igg XlinkkoronakisNo ratings yet