Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy of Head and Neck
Anatomy of Head and Neck
Uploaded by
Youssef Salah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views61 pagesThe document discusses the anatomy and functions of the trigeminal and maxillary nerves. The trigeminal nerve has three divisions that transmit sensation from the head, face, and mouth. It also carries motor fibers to chewing muscles. The maxillary nerve transmits sensory fibers from parts of the face and nasal cavity. It contains postganglionic parasympathetic fibers that innervate lacrimal, nasal, and palatine glands. The maxillary nerve originates in the trigeminal ganglion and divides into branches that supply regions of the face, nose, palate, and upper teeth.
Original Description:
Original Title
Anatomy
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the anatomy and functions of the trigeminal and maxillary nerves. The trigeminal nerve has three divisions that transmit sensation from the head, face, and mouth. It also carries motor fibers to chewing muscles. The maxillary nerve transmits sensory fibers from parts of the face and nasal cavity. It contains postganglionic parasympathetic fibers that innervate lacrimal, nasal, and palatine glands. The maxillary nerve originates in the trigeminal ganglion and divides into branches that supply regions of the face, nose, palate, and upper teeth.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views61 pagesAnatomy of Head and Neck
Anatomy of Head and Neck
Uploaded by
Youssef SalahThe document discusses the anatomy and functions of the trigeminal and maxillary nerves. The trigeminal nerve has three divisions that transmit sensation from the head, face, and mouth. It also carries motor fibers to chewing muscles. The maxillary nerve transmits sensory fibers from parts of the face and nasal cavity. It contains postganglionic parasympathetic fibers that innervate lacrimal, nasal, and palatine glands. The maxillary nerve originates in the trigeminal ganglion and divides into branches that supply regions of the face, nose, palate, and upper teeth.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 61
ANATOMY OF HEAD AND NECK
Dr. Khaled Hassan
Lecturer of Oral Surgery
MIU
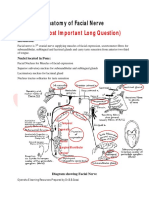
THE TRIGEMINAL NERVE (V)
7.1 Functions
The trigeminal nerve transmits sensation from the skin of
the anterior part of the head, the oral and nasal cavities, the teeth
and the meninges. It has three divisions (ophthalmic, maxillary and
mandibular) subsequently treated as separate nerves. Its mandibular
division also carries motor fibres to muscles used in chewing.
7.2 Attachment, course, divisions (Fig. 7.1)
• Attached to lateral aspect of pons, near middle cerebellar
peduncle.
• Passes below tentorium cerebelli, to middle cranial fossa.
• Trigeminal (sensory) ganglion in depression on temporal bone.
• Splits into ophthalmic (Va), maxillary (Vb) and mandibular (Vc).
7.3 Trigeminal ganglion
• It contains cell bodies of primary sensory neurons in all three
divisions of trigeminal nerve, except those of proprioceptive
neurons (see Chapter 4).
• It is partially surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid in recess of subarachnoid
space: trigeminal, or Meckel’s, cave.
THE MAXILLARY NERVE (Vb)
9.1 Functions
The maxillary nerve transmits sensory fibres from
the skin of the face between the palpebral fissure and the
mouth, from the nasal cavity and sinuses, and from the maxillary
teeth.
At its origin it contains only sensory fibres. Some of its branches
transmit postganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the pterygopalatine
ganglion which pass to the lacrimal, nasal and palatine
glands (see Section 17.3), and others convey taste (visceral sensory)
fibres from the palate to the nucleus of the solitary tract (see
Section 17.4).
9.2 Origin, course and branches (Fig. 9.1)
• originates from trigeminal ganglion in middle cranial fossa;
• passes in lower part of lateral wall of cavernous sinus;
• meningeal branch (middle cranial fossa – sensory);
• foramen rotundum, to;
• pterygopalatine fossa which divides into main branches, infraorbital
and zygomatic, and gives other branches to nose, palate and
upper teeth.
You might also like
- Anatomy of The Facial NerveDocument75 pagesAnatomy of The Facial NerveRao Rizwan Shakoor67% (3)
- Facial Nerve & Trigeminal NerveDocument25 pagesFacial Nerve & Trigeminal NerveRafiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument7 pagesCranial NerveshamnahrjunaidNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve: Navigation SearchDocument6 pagesFacial Nerve: Navigation SearchKanika VarmaNo ratings yet
- Nerves of The Face and MouthDocument48 pagesNerves of The Face and Mouthshabs_1No ratings yet
- LADocument93 pagesLAkaedeamira_113974100% (2)
- Adekunle Seminar in Cranial NervDocument34 pagesAdekunle Seminar in Cranial NervBamgbose OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- NervesDocument16 pagesNervesDerahNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve 2Document87 pagesFacial Nerve 2bhavyaNo ratings yet
- 2 M 22. V VII IX Cranial NervesDocument14 pages2 M 22. V VII IX Cranial NervesHellNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument23 pagesTrigeminal NerveLilly PaulNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument92 pagesTrigeminal Nervemounika33% (3)
- 2d Facial Nerve-Dr GosaiDocument6 pages2d Facial Nerve-Dr GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- The Trigeminal and Facial NervesDocument7 pagesThe Trigeminal and Facial NervesJose CastroNo ratings yet
- The Trigeminal and Facial NervesDocument7 pagesThe Trigeminal and Facial NervesJose CastroNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument76 pagesTrigeminal Nerveanhca4519No ratings yet
- Cranial and Peripheral Nerves - MartinDocument108 pagesCranial and Peripheral Nerves - MartinTherese Jane Tirador100% (1)
- Trigeminal Nerve VDocument4 pagesTrigeminal Nerve Vm1m2mNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument5 pagesTrigeminal NervermarawanNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument29 pagesCranial NervesMadalina DutanNo ratings yet
- The Facial Nerve (CN VII) - Course - Functions - TeachMeAnatomyDocument1 pageThe Facial Nerve (CN VII) - Course - Functions - TeachMeAnatomyYomna NimerNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiDocument76 pagesTrigeminal Nerve: Dr.B.B.GosaiAlexAlxNo ratings yet
- The Trigeminal NerveDocument83 pagesThe Trigeminal NerveRicha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument12 pagesTrigeminal NerveTabata SantanaNo ratings yet
- Nervio Trigemino Articulo 2019Document8 pagesNervio Trigemino Articulo 2019Wendy Alejandra NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy AssignmentDocument10 pagesAnatomy AssignmentObansa JohnNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument65 pagesCranial NervesatefmaboodNo ratings yet
- GA&E 10 - Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesGA&E 10 - Peripheral Nervous SystemSu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument126 pagesTrigeminal NerveAsha Praveena100% (4)
- Nervo FacialeDocument15 pagesNervo FacialeAndrea PescosolidoNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves 2010Document25 pagesCranial Nerves 2010Rosa hcNo ratings yet
- Os 3Document11 pagesOs 3مرتضى محمد فاضل جرجوكNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervsDocument14 pagesCranial NervsluckyNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve Anatomy & Course in Middle EAR: Done by Thasni T U Roll No 102 Vignesh Sunil Roll No 105 7 SEMDocument60 pagesFacial Nerve Anatomy & Course in Middle EAR: Done by Thasni T U Roll No 102 Vignesh Sunil Roll No 105 7 SEM102 .Thasni T.U . 6th sem100% (1)
- Facial NerveDocument4 pagesFacial NerveAppas SahaNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of The Cranial Nerves Vii-XiiDocument38 pagesThe Anatomy of The Cranial Nerves Vii-Xiiabdul azizNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Trigeminal NerveDocument48 pagesAnatomy of Trigeminal NerveNicky RomeoNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves V, Vii, Viii, Ix, X, Xi, Xii: DR Nan Ommar FMHS, UnimasDocument32 pagesCranial Nerves V, Vii, Viii, Ix, X, Xi, Xii: DR Nan Ommar FMHS, UnimasMerriNo ratings yet
- Embryology-Development of Central Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesEmbryology-Development of Central Nervous Systemtenshi315No ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument54 pagesCranial NervesFatima Kh SalahNo ratings yet
- Brain StemDocument6 pagesBrain StemOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- By: Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & DR - Sanaa AlshaarawiDocument24 pagesBy: Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & DR - Sanaa AlshaarawiRakesh Kumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- 1 My Trigeminal NerveDocument23 pages1 My Trigeminal NerveDan 04No ratings yet
- Pares 2Document50 pagesPares 2api-3701995No ratings yet
- Saraf Kranial: (Neuroanatomi, Somatic)Document7 pagesSaraf Kranial: (Neuroanatomi, Somatic)Fitri SukmawatiNo ratings yet
- List of Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesList of Cranial NervesEunice A. EdaniolNo ratings yet
- Guide To Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesGuide To Cranial NervesmuhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- Human Function AnatomyDocument8 pagesHuman Function AnatomyaishbiyaNo ratings yet
- 3.trigeminal NerveDocument81 pages3.trigeminal NerverajaniNo ratings yet
- L18 Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesL18 Cranial NervesmoshlingmomoNo ratings yet
- Olfactory Nerve (2024)Document40 pagesOlfactory Nerve (2024)doctormdali7889No ratings yet
- אני משתף איתך את 'OMF injuries (traumas) answers'Document119 pagesאני משתף איתך את 'OMF injuries (traumas) answers'Shany SchwarzwaldNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument82 pagesOral Cavitydavid100% (1)
- The BrainDocument31 pagesThe BrainHusseinNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaDocument62 pagesAnatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaIin Widya Sari SiregarNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V) : Presented By: Hamza Yousaf Usaid Yousaf Amna Khalil Maha Aziz Rimsha AkramDocument30 pagesTrigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V) : Presented By: Hamza Yousaf Usaid Yousaf Amna Khalil Maha Aziz Rimsha AkramHamza YousafNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Summary PDFDocument9 pagesCranial Nerves Summary PDFMudassar SattarNo ratings yet
- 56 Cranial Nerves, OverviewDocument4 pages56 Cranial Nerves, OverviewVicenteFavianCovarrubiasAlcayagaNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument2 pagesTrigeminal NerveVanshika JainNo ratings yet
- Neuromodulation in Headache and Facial Pain Management: Principles, Rationale and Clinical DataFrom EverandNeuromodulation in Headache and Facial Pain Management: Principles, Rationale and Clinical DataGiorgio LambruNo ratings yet