Professional Documents
Culture Documents
59 Hyper Spec
59 Hyper Spec
Uploaded by
aqzeeshan78Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
59 Hyper Spec
59 Hyper Spec
Uploaded by
aqzeeshan78Copyright:
Available Formats
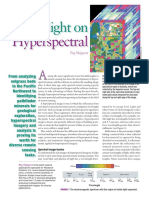
Hyperspectral Analysis Process
Hyperspectral remote sensors collect images simultaneously in many narrow,
contiguous wavelength bands. The prototype Hyperspectral Analysis process
in TNTmips V5.90 provides the specialized, interactive analysis tools that are
required to fully exploit the spectral range and spectral resolution provided by
hyperspectral datasets. The process allows you to work with two different types
of objects: hyperspectral images and spectral libraries. A hyperspectral image
consists of a set of raster bands in a Project File, along with associated wave-
length information for each band. You can select and view spectra for image
cells and save them in a spectral library. The saved image spectra can then be
used to map similar materials throughout the image. You can also work with
libraries of field and laboratory spectra and use selected spectra to identify
matching materials in the image. The U.S. Geological Survey’s standard spec-
tral library (containing laboratory spectra for nearly 500 minerals) is included
as a starting point for material identification.
Hyperspectral Analysis Workflow
Available Methods:
Nominal Calibration
Convert radiance values to
• Minimum Offset • Equal Area Normalization
RGB display of three bands from a hyperspectral image of
Cuprite, Nevada, acquired by NASA’s AVIRIS instrument apparent reflectance • Dark Field Offset • Log Residuals
(Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer). When you • Flat Field Calibration
open a hyperspectral image for analysis, the process
automatically selects a set of three bands with low, medium,
and high wavelength for an RGB display. You can also use
the Layer Controls to add any single band or RGB
combination of bands to the display. Remove Continuum
Extract Image Spectra Remove the spectral
View spectral plots, specify envelope (continuum) from
a spectral range to work in, the spectra to build a library
Available Methods: Spectrum Matching save spectra in library of “continuum-removed”
• Spectral Angle Mapper Search USGS spectral absorption features
library for matching
• Band Mapping laboratory spectra
Available Methods:
Spectral Classification
Classify image cells using
• Spectral Angle Mapper
Spectral Plot • Cross Correlation
1.0 selected laboratory spectra or
extracted image spectra • Linear Unmixing
0.75
• Matched Filtering
0.50
0.25
0.0
2.05 2.11 2.17 2.23 2.29 2.35 2.41
Wavelength (micrometers)
Image spectrum extracted from area
dominated by the alteration mineral alunite.
Matching laboratory spectrum for alunite found
by the Spectral Angle matching procedure.
Classification results for selected mineral spectra overlaid on a single
grayscale image band. Each color identifies cells that match a specific laboratory
mineral spectrum within an adjustable tolerance level. Red = K-alunite, cyan = Na-
alunite, yellow = kaolinite, blue = chalcedony, green = calcite. Alunite, kaolinite, and
chalcedony (opal) are hydrothermal alteration products commonly associated with gold and
other precious metal deposits. The illustration shows separate color-mapped classification
results for each mineral using the Cross Correlation method.
MicroImages, Inc. l 201 North 8th Street l Lincoln, Nebraska l 68508-1347 l USA
Voice (402)477-9554 l FAX (402)477-9559 l email info@microimages.com l Web www.microimages.com
You might also like
- Radiance MPDocument123 pagesRadiance MPvsinisa1No ratings yet
- Bio 5LA Lab Manual Fall 2013Document73 pagesBio 5LA Lab Manual Fall 2013oxnerdki50% (2)
- Hyperspectral ImagingDocument10 pagesHyperspectral Imagingsamirsamira928No ratings yet
- Journal 2Document11 pagesJournal 2suryabmepco23No ratings yet
- Hyperspectral ImagingDocument24 pagesHyperspectral Imagingjwt9478No ratings yet
- Measurements Chapter 15: Lecture 2. in Situ (Field/lab) Re EctanceDocument37 pagesMeasurements Chapter 15: Lecture 2. in Situ (Field/lab) Re EctancealphasisNo ratings yet
- Hyper Spectral Rob I LaDocument25 pagesHyper Spectral Rob I Lasamirsamira928No ratings yet
- CHE-816 Mol Nanotech - 18 - Characterization Techniques - 3Document10 pagesCHE-816 Mol Nanotech - 18 - Characterization Techniques - 3Rabia KhanNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Hyperspectral ImagesDocument40 pagesAnalyzing Hyperspectral ImagesAndreea CameliaNo ratings yet
- Hyperspectral Imaging: Techniques, Issues, and Applications: Antony Lam Human-Machine Interaction Systems EngineeringDocument54 pagesHyperspectral Imaging: Techniques, Issues, and Applications: Antony Lam Human-Machine Interaction Systems EngineeringYessica RosasNo ratings yet
- Classification of Pavia University Hyperspectral Image Using Gabor and SVM ClassifierDocument7 pagesClassification of Pavia University Hyperspectral Image Using Gabor and SVM Classifiersuryabmepco23No ratings yet
- FINAL Paper Hyper Neural DER FinalDocument35 pagesFINAL Paper Hyper Neural DER FinalDaniel RagonaNo ratings yet
- Spotlight On Hyperspectral. 201 - Shippert P - PDFDocument5 pagesSpotlight On Hyperspectral. 201 - Shippert P - PDFRoman Ignacio Escobar PizarroNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopic Ellipsometry: University of Texas at El Paso Lynn Santiago Dr. Elizabeth Gardner Chem 5369Document24 pagesSpectroscopic Ellipsometry: University of Texas at El Paso Lynn Santiago Dr. Elizabeth Gardner Chem 5369Ali KamaliNo ratings yet
- FLUOSOLID - Catelli Et Al 2017Document10 pagesFLUOSOLID - Catelli Et Al 2017christophel canalNo ratings yet
- Why Use Hyperspectral ImageryDocument3 pagesWhy Use Hyperspectral ImageryAndreea CameliaNo ratings yet
- CCFS PaskalevaDocument12 pagesCCFS PaskalevaJohn Michael ApacibleNo ratings yet
- Fast Multispectral Imaging by Spatial Pixel-Binning and Spectral UnmixingDocument7 pagesFast Multispectral Imaging by Spatial Pixel-Binning and Spectral UnmixingRaj VelNo ratings yet
- Avantes Raman Bundles: Avaraman: Raw MaterialsDocument2 pagesAvantes Raman Bundles: Avaraman: Raw MaterialsJorge Luis VazquezNo ratings yet
- Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data Analysis and Future ChallengesDocument31 pagesHyperspectral Remote Sensing Data Analysis and Future ChallengesAdduru U G SankararaoNo ratings yet
- Eds Brochure X Ray SpecDocument8 pagesEds Brochure X Ray SpecdocamityadavNo ratings yet
- Multispectral Interlaced Sparse SamplingDocument19 pagesMultispectral Interlaced Sparse SamplingRaushan Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Classification of Hyperspectral ImagesDocument64 pagesClassification of Hyperspectral Imagesuser5 sonkiyaNo ratings yet
- LabChart Spike HistogramDocument2 pagesLabChart Spike HistogrammanuelNo ratings yet
- Diffusereflectance Technique For Infraredanalysisof UrinarycalculiDocument4 pagesDiffusereflectance Technique For Infraredanalysisof UrinarycalculiAnurak OnnnoomNo ratings yet
- Image Segmentation Gabor CinC 1998Document5 pagesImage Segmentation Gabor CinC 1998Faris KamaaluddinNo ratings yet
- Ctalogo de AADocument8 pagesCtalogo de AAFernando MarcosNo ratings yet
- Orbis BrochureDocument8 pagesOrbis BrochureAnugerah Prima Era GlobalindoNo ratings yet
- FTIR: Introdution and Application To ForensicsDocument23 pagesFTIR: Introdution and Application To ForensicsLJ GicoleNo ratings yet
- Full Document - Hyperspectral PDFDocument96 pagesFull Document - Hyperspectral PDFJayaprabha ManiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument43 pagesCell Structure and FunctionzoeakatNo ratings yet
- Spectral Imaging Revised RemovedDocument6 pagesSpectral Imaging Revised RemovedSilence is BetterNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Spectramax 190 Microplate Reader VWR InternationalDocument4 pagesDokumen - Tips - Spectramax 190 Microplate Reader VWR InternationalDavid MartinzNo ratings yet
- RS 401 Lecture 9Document21 pagesRS 401 Lecture 9Jacques AdjoyiNo ratings yet
- Axis Supra Brochure 1697534772937Document8 pagesAxis Supra Brochure 1697534772937prathompoom.newyawongNo ratings yet
- Similarity-Based Unsupervised Band Selection For Hyperspectral Image AnalysisDocument6 pagesSimilarity-Based Unsupervised Band Selection For Hyperspectral Image AnalysisRicardo FNo ratings yet
- A New Data Analysis Strategy in LIBS ImagingDocument8 pagesA New Data Analysis Strategy in LIBS ImagingJavi Moros PortolésNo ratings yet
- Engineering Applications of Arti Ficial IntelligenceDocument10 pagesEngineering Applications of Arti Ficial IntelligenceVũ Tâm MinhNo ratings yet
- Engineering Applications of Arti Ficial IntelligenceDocument10 pagesEngineering Applications of Arti Ficial IntelligenceVũ Tâm MinhNo ratings yet
- L Principles MicrosDocument60 pagesL Principles MicrosRasul AmirovNo ratings yet
- Tescan Magna Brochure Uhr SemDocument8 pagesTescan Magna Brochure Uhr SemJulio CasalloNo ratings yet
- 80005323enDocument2 pages80005323enNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 3036 JungDocument6 pages3036 JungPriyanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance (Qa) Procedures For Software: Evaluation of An Adc Quality SystemDocument7 pagesQuality Assurance (Qa) Procedures For Software: Evaluation of An Adc Quality SystemdawadhaliNo ratings yet
- Spectrometer With A Two Layer Biparted Ten Dichroic Mirror ArrayDocument10 pagesSpectrometer With A Two Layer Biparted Ten Dichroic Mirror ArrayAhmed M. NawarNo ratings yet
- Parametric Imaging of Specular Reflections and Diffuse Scattering of Tissue From Multi-Directional Ultrasound Echo Signal DataDocument4 pagesParametric Imaging of Specular Reflections and Diffuse Scattering of Tissue From Multi-Directional Ultrasound Echo Signal Data3532929121No ratings yet
- Multivariate Methods For Analysis of Environmental Reference Materials Using Laser-Induced Breakdown SpectrosDocument7 pagesMultivariate Methods For Analysis of Environmental Reference Materials Using Laser-Induced Breakdown SpectrosOnime No IchinoseNo ratings yet
- This Version May No Longer Be AccessibleDocument14 pagesThis Version May No Longer Be AccessibleVũ Tâm MinhNo ratings yet
- Sawyer 2017 J. Opt. 19 045301Document11 pagesSawyer 2017 J. Opt. 19 045301李宗憲No ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption. Redefined. Contraa 800Document5 pagesAtomic Absorption. Redefined. Contraa 800Bùi An VinhNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy: Theory and PrinciplesDocument28 pagesFourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy: Theory and PrinciplesmaopacificNo ratings yet
- Optical Microscopy IntroductionDocument42 pagesOptical Microscopy IntroductionHuda AmirNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology-Chapter 2Document81 pagesNanotechnology-Chapter 2tarunNo ratings yet
- Witec Alpha 300R MicroscopeDocument8 pagesWitec Alpha 300R MicroscopeDileep RautNo ratings yet
- GEO424 Lect09 Spec & Bands PDFDocument19 pagesGEO424 Lect09 Spec & Bands PDFAires Rafael Rutherford AiresNo ratings yet
- Aq6375 Optical Spectrum Analyzer For Long Wavelength Band: MORI Tohru ISHIHARA Gentarou KANEKO Tsutomu HORIGUCHI AtsushiDocument4 pagesAq6375 Optical Spectrum Analyzer For Long Wavelength Band: MORI Tohru ISHIHARA Gentarou KANEKO Tsutomu HORIGUCHI AtsushiGhallab AlsadehNo ratings yet
- Pycon 2019 PDFDocument38 pagesPycon 2019 PDFWilliam Gómez OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Principle of CBCTDocument77 pagesPrinciple of CBCTSagar Adhikari100% (5)
- Krauss 2010-LC-high Resolution MS in Environmental Analysis - From Target Screening To The Identification of UnknownsDocument9 pagesKrauss 2010-LC-high Resolution MS in Environmental Analysis - From Target Screening To The Identification of UnknownsyenNo ratings yet
- Spectrochemical Analysis Using Infrared Multichannel DetectorsFrom EverandSpectrochemical Analysis Using Infrared Multichannel DetectorsNo ratings yet
- Color LectureDocument124 pagesColor LectureSiamese buckaroo100% (1)
- Evaluating The Relationship Between Tooth Color and Enamel Thickness, Using Twin Flash Photography, Cross-Polarization Photography, and SpectrophotometerDocument11 pagesEvaluating The Relationship Between Tooth Color and Enamel Thickness, Using Twin Flash Photography, Cross-Polarization Photography, and Spectrophotometer陳奕禎No ratings yet
- Beam Splitter Tutorial ZemaxDocument12 pagesBeam Splitter Tutorial ZemaxprajneshNo ratings yet
- Intel Qx3 Activity BookDocument16 pagesIntel Qx3 Activity BookBeenish MirzaNo ratings yet
- Auto TaksDocument1 pageAuto Taksapi-263686066No ratings yet
- Week11 - The MicroscopeDocument31 pagesWeek11 - The MicroscopeJr BalagtasNo ratings yet
- LED LightDocument22 pagesLED LightsultanprinceNo ratings yet
- Calibration Kit Fulldome 1118Document1 pageCalibration Kit Fulldome 1118BoanergeNo ratings yet
- Photo TechniqueDocument52 pagesPhoto Techniquetuah81No ratings yet
- QA Harian, Mingguan Dan Bulanan Untuk CT ScanDocument19 pagesQA Harian, Mingguan Dan Bulanan Untuk CT ScanSelly OktaviantiNo ratings yet
- OptoelectronicDevices S16Document17 pagesOptoelectronicDevices S16puceiroaleNo ratings yet
- Reporting in Science About Curved MirrorsDocument26 pagesReporting in Science About Curved Mirrorsadrian pabyNo ratings yet
- CR vs. DDRDocument13 pagesCR vs. DDRshaunmeroNo ratings yet
- DLP IN SCIENCE 7 (Demo)Document11 pagesDLP IN SCIENCE 7 (Demo)Kristel Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Dubois Sunscreen DocumentDocument4 pagesDubois Sunscreen Documentneha sahuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MorelSophieDocument9 pagesTutorial MorelSophieLuong Van DungNo ratings yet
- Geometric Unsharpness: RadiographyDocument3 pagesGeometric Unsharpness: RadiographykingstonNo ratings yet
- ICLC Mod7 EnglishDocument476 pagesICLC Mod7 EnglishShifan Abdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- Photography Club Mid Year Accomplishment ReportDocument3 pagesPhotography Club Mid Year Accomplishment ReportJennifer MartinNo ratings yet
- X Ray PDFDocument15 pagesX Ray PDF1985kr100% (1)
- Project OSCAR: Total Internal ReflectionDocument8 pagesProject OSCAR: Total Internal ReflectionHARSHIT shuklaNo ratings yet
- Test10th (Life Process and Reflection and Refraction)Document4 pagesTest10th (Life Process and Reflection and Refraction)Hanshu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopic Characterization of Indian Standard Sand: G. Anbalagan, A. R. Prabakaran, S. GunasekaranDocument9 pagesSpectroscopic Characterization of Indian Standard Sand: G. Anbalagan, A. R. Prabakaran, S. GunasekaranAliFriendNo ratings yet
- PW 2023 NeetDocument5 pagesPW 2023 NeetvisvanthNo ratings yet
- Exercises Week 5: Fiber Communication: Fig 1: 2x2 Optical Coupler Used As MultiplexerDocument4 pagesExercises Week 5: Fiber Communication: Fig 1: 2x2 Optical Coupler Used As MultiplexerJeff GanterNo ratings yet
- Atomic Scattering Factors 1Document14 pagesAtomic Scattering Factors 1Soumajit DasNo ratings yet
- Physics 43 HW # 8 Chapter 40 ProblemsDocument3 pagesPhysics 43 HW # 8 Chapter 40 ProblemsJose AguilarNo ratings yet