Professional Documents
Culture Documents
X Ray Diffraction
Uploaded by
كريم كاملOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
X Ray Diffraction
Uploaded by
كريم كاملCopyright:
Available Formats
SUCCESS MAKERS 2011
Introduction (For Reading only)
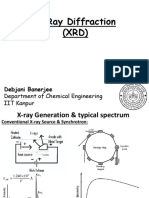
-X-rays are electromagnetic waves of very short wavelength (0.01 to 10 nm).
-They can be generated by an X-ray tube, (vacuum tube that uses a high voltage
to accelerate the electrons released by a hot cathode to a high velocity. These
electrons collide with a metal target (anode), emitting large no. of photons
which form X-rays).
X-ray Diffraction:
-Since the atomic spacing in solids is known to be very small (about 0.1 nm), so
we can use X-rays to create diffraction patterns of the atomic structure
(crystals).
-This prediction was suggested by Max von Laue in 1913 and confirmed by
subsequent experiments.
-The diffraction patterns from crystals are complex because of the three-
dimensional nature of crystal structure.
-X-ray diffraction is an extremely useful technique for showing these structures
and understanding them.
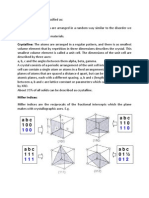
Experiment
-A collimated beam of monochromatic x-rays is incident on a crystal.
-The diffracted beams are very intense in certain directions, corresponding to
constructive interference (from waves reflected from the atoms in the crystal).
-These beams form an array of
spots known as Laue pattern.
-By analysing the positions
and intensities of these various
spots, the crystalline structure
can be deduced using
diffractometer.
Success Makers Team ©
SUCCESS MAKERS 2011
Bragg’s law
-If x-ray beam is incident on 2 atomic planes, making an angle () with one of
them, so the beam can be reflected from both the upper plane and the lower one.
-The beam reflected from the lower plane travels farther than the beam reflected
from the upper plane, because of the path difference (2d sin ) between them.
-The two beams reinforce each other (constructive interference) when this path
difference equals some integer multiple of (). (For Reading)
-This condition is known as Bragg’s law.
-For constructive interferences
2dsin θ= mλ
where m= 1, 2, 3
-This can be used to calculate the spacing (d) between atomic planes.
Success Makers Team ©
You might also like
- Chapter 3c X Ray DiffractionDocument48 pagesChapter 3c X Ray DiffractionAnup DalalNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Crystallography X-RayDocument10 pagesX-Ray Crystallography X-RayJoriel SolenonNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction Basic Concepts - DemostrationDocument21 pagesX-Ray Diffraction Basic Concepts - DemostrationAhmed MaatyNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction BriefDocument6 pagesX-Ray Diffraction BriefSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Determination of Crystal Structure and Crystallite SizeDocument17 pagesDetermination of Crystal Structure and Crystallite SizeRohit SatheshNo ratings yet
- S5) Clase 3-2 - Crystal Structures and X-RayDocument16 pagesS5) Clase 3-2 - Crystal Structures and X-RayDanielNo ratings yet
- BraggsDocument5 pagesBraggsJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- 10 X-Ray DiffractionDocument8 pages10 X-Ray DiffractionProf.Dr.Mohamed Fahmy Mohamed Hussein100% (1)
- Chapter3 X Ray Diffraction in CrystalDocument67 pagesChapter3 X Ray Diffraction in CrystalAymen AnouneeNo ratings yet
- Kimia Analisis Instrumen 2: X-Ray DiffractionDocument28 pagesKimia Analisis Instrumen 2: X-Ray Diffractionsofi salasiNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) : Ulrike TroitzschDocument38 pagesX-Ray Diffraction (XRD) : Ulrike TroitzschprianNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction 7Document11 pagesX-Ray Diffraction 7alina.tlekkabylova270202No ratings yet
- X Ray DiffractionsDocument15 pagesX Ray DiffractionsAman JhaNo ratings yet
- 8 X-Ray CrystallDocument12 pages8 X-Ray CrystallGustavo AraújoNo ratings yet
- XRD Reading Material PDFDocument69 pagesXRD Reading Material PDFMith DongreNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction Analysis Principle InsDocument57 pagesX-Ray Diffraction Analysis Principle InsPrem Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 3c X Ray DiffractionDocument48 pagesChapter 3c X Ray DiffractionmethoxyNo ratings yet
- X RayCrystallographyDocument4 pagesX RayCrystallographyHarsh 24 222No ratings yet
- PH 617 L 4 X RayDiffractionDocument67 pagesPH 617 L 4 X RayDiffractionSayantan DexNo ratings yet
- Basics of X-Ray DiffractionDocument13 pagesBasics of X-Ray Diffractionleizar_death64No ratings yet
- Interference of Light & It's Applications (Interferometry)Document24 pagesInterference of Light & It's Applications (Interferometry)Pranav Marathe100% (11)
- Lec 5Document14 pagesLec 5Floyd AbianNo ratings yet
- 8 XRDDocument14 pages8 XRDWahyu Eko PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Principle and Application of X Ray DiffractometerDocument39 pagesLecture 1 Principle and Application of X Ray DiffractometerVadivelanNo ratings yet
- Reference Book: Elements of X-Ray DiffractionDocument14 pagesReference Book: Elements of X-Ray Diffractiondtu epNo ratings yet
- XrayDocument39 pagesXraysusanta kumar sahuNo ratings yet
- MS&E 11 Raja Muhammad Usama Muhammad Asim Harris Hassan Usman Ahmed SiddiquiDocument28 pagesMS&E 11 Raja Muhammad Usama Muhammad Asim Harris Hassan Usman Ahmed SiddiquiShahZaib AnwarNo ratings yet
- Diffraction by Crystal LatticeDocument19 pagesDiffraction by Crystal LatticeGülşah BÜYÜKNo ratings yet
- X-Ray DiffractionDocument6 pagesX-Ray DiffractionAhmed Al-AwamiNo ratings yet
- XRD PPT Part 2Document39 pagesXRD PPT Part 2BME62Thejeswar SeggamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document75 pagesChapter 2蘇翊愷No ratings yet
- MSE8013 Chapter02 Wave Diffraction and The Reciprocal LatticeDocument61 pagesMSE8013 Chapter02 Wave Diffraction and The Reciprocal LatticeJie GanNo ratings yet
- Lec8 Xray-DTA (Compatibility Mode)Document98 pagesLec8 Xray-DTA (Compatibility Mode)Chandima WickramasingheNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Structure Unfolding TechniquesDocument29 pagesUnit 4 Structure Unfolding TechniquesvijayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3c X Ray DiffractionDocument51 pagesChapter 3c X Ray DiffractionDeependra Kumar Ban100% (1)
- Chapter 3c X Ray DiffractionDocument51 pagesChapter 3c X Ray Diffractionkaushaltrivedi46No ratings yet
- HAFTA XRD-1-dönüştürüldüDocument26 pagesHAFTA XRD-1-dönüştürüldüKatrina Ranee RamosNo ratings yet
- MS&E 11 Raja Muhammad Usama Muhammad Asim Harris Hassan Usman Ahmed SiddiquiDocument28 pagesMS&E 11 Raja Muhammad Usama Muhammad Asim Harris Hassan Usman Ahmed SiddiquiShahZaib AnwarNo ratings yet
- XDR1Document83 pagesXDR1zeyadwaeli500No ratings yet
- X-ray Diffraction:: X-rays are electromagnetic waves (λ = 0.1 - 100 Å)Document6 pagesX-ray Diffraction:: X-rays are electromagnetic waves (λ = 0.1 - 100 Å)Miles NsgNo ratings yet
- X Ray DiffractionDocument13 pagesX Ray DiffractionMahmoud HawaryNo ratings yet
- XRD (X - Ray Diffraction)Document7 pagesXRD (X - Ray Diffraction)summi64No ratings yet
- Lecture 02 ADocument68 pagesLecture 02 AHữu Nam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Laser-Trapped Mirrors in SpaceDocument25 pagesLaser-Trapped Mirrors in SpaceClifford StoneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3c X Ray DiffractionDocument40 pagesChapter 3c X Ray DiffractiondhandametNo ratings yet
- XRD Kuliah Anorganik AdvanceDocument31 pagesXRD Kuliah Anorganik AdvanceMulyaNo ratings yet
- Bragg'S Law, and Diffractometer: by Ayesha SiddiqaDocument11 pagesBragg'S Law, and Diffractometer: by Ayesha SiddiqaAyesha SiddiqaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry A Molecular Approach Canadian 1st Edition Tro Solutions ManualDocument38 pagesChemistry A Molecular Approach Canadian 1st Edition Tro Solutions Manualfoliosemyophanr2cl100% (16)
- Chemistry A Molecular Approach Canadian 1st Edition Tro Solutions ManualDocument38 pagesChemistry A Molecular Approach Canadian 1st Edition Tro Solutions Manualsiliquavexinglygmnfo100% (13)
- Ebook Chemistry A Molecular Approach Canadian 1St Edition Tro Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument56 pagesEbook Chemistry A Molecular Approach Canadian 1St Edition Tro Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtranhhanr87100% (14)
- X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) PDFDocument44 pagesX-Ray Diffraction (XRD) PDFMohamad AlamehNo ratings yet
- Interaction Between A Surface Acoustic Wave and Adsorbed AtomsDocument10 pagesInteraction Between A Surface Acoustic Wave and Adsorbed AtomsmubarakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document23 pagesChapter 3POURNIMA kengaleNo ratings yet
- Study Material of Class 12 Physics 2023-24-65-99Document35 pagesStudy Material of Class 12 Physics 2023-24-65-99budgies2005No ratings yet
- 1 XRDDocument44 pages1 XRDMaheep upadhyayNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)Document31 pagesX-Ray Diffraction (XRD)Yulianto NugrohoNo ratings yet
- X - Ray Diffraction (XRD)Document26 pagesX - Ray Diffraction (XRD)Ajith KumarNo ratings yet