Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antenna
Uploaded by
Sumit ShakyaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antenna
Uploaded by
Sumit ShakyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Antenna Theory
By
Mattias Hellgren
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Contents
• Radio Frequency
• Antenna Basics
• Different type of Antennas
• VSWR & Bandwith
• Decibel
• dBi vs dBd
• Directivity
• Gain
• Radiation Parameters
• Anechoic Chamber
• How do we evaluate/design a antenna
• in RF perspective?
• TEMS
• GPS
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Radio Frequency
RF and Wavelength
Radio Frequency (RF) is a term that refers to an alternating current having
characteristics such that, if the current is input to an antenna, an
electromagnetic field is generated.
The RF-field has a wavelength that is inversely proportional to the frequency
Wavelength ( lamda ) = 299 792 458 / f
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Antenna Basics
What’s an antenna?
Antenna : transitional structure between a wave, in free-space
and a guiding device.
• Part of the transmitting/receiving system which is designed to
radiate or receive electromagnetic waves
• Most antennas are resonant devices, which operates
over a relative narrow frequency band
• Has to be tuned to the same frequency as the radio system
which it is connected to operates in
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Different types of antennas
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Antenna Basics
Impedance
Impedance (Z) : a vector consisting of resistance and reactance
Impedance: Z = R + jX
Resistance: R
Inductive: + jXL
Capacitive: - jXC
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Antenna Basics
Impedance
Antennna impedance
ZA = (RL+Rr) + jXA
RL = Dielectric and conducting losses in antenna and tranmission line
Rr = Radiation resistance for the antenna
For an efficient transfer of energy, the impedance of the source,
the antenna and transmission line connecting the source to the
antenna must be the same. Traditionally they are designed for
50 Ohms impedance.
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
VSWR
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
Antenna
Uforward + UReflected Transmitted wave
VSWR=
Uforward - UReflected
ZA+ j
VSWR = 1:1 = >100% transmitted
VSWR = 2:1 => 89% transmitted
ZC Reflected wave
Transmission line Forward wave
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
VSWR and BW
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio and Bandwidth
VSWR
fU - fL
BW = X 100%
fC
2
fC= Center frequency
fL= Lower frequency
fU= Upper frequency
1
fC Frequency
fL BW fU
Bandwith: the range of frequencies with acceptable antenna performance
measured by one or more of the preformance parameters e.g. VSWR
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Decibel (dB)
What’s decibel dB?
Logarithmic expression of the ratio between two signal powers,
voltages or current levels. Power amplitude difference in decibels,
symbolized SdBP is :
SdBP= 10 log (P1 / P2 )
For voltages or currents, one uses 20 log X
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
dBi vs dBd
2.15dBi = 0dBd
Decibel relative an isotropic antenna, dBi
Gain of an antenna relative an isotropic radiator.
An isotropic radiator is theoretical ideal, radiates equally in all directions
Decibel relative a dipole antenna, dBd
Gain of an antenna system relative a half-wave dipole
G[dBi] = G[dBd] + 2.15
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Antenna Directivity
Directivity (D)
The ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction from the
antenna to the radiation intensity averaged over all directions
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Antenna Gain
Gain (G)
Directivity multiplied with the efficiency of the antenna
U 4ðU
GA = De0 = e0 = e0
U0 Prad
GA = Gain of antenna
E0 = Total efficiency
D = Directivity
U = Radiation intensity (W/unit solid angle)
U0 = Radiation intensity of a isotropic source (W/unit solid angle)
Prad = Total radiated power (W)
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Radiation Parameters
Radiation Pattern measurement
Graphical representation of the field magnitude
at a fixed distance from an antenna as a function of direction
i.e. angular variation of the test antennas radiation.
Gain measurement
Absolute measurement that gives the angular variation of the
test antenna’s radiation. Needed to fully characterize the radiation
properties of the test antenna.
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Radiation Parameters
Polarization
Defined as the polarization of the electromagnetic wave
radiated by the antenna along a vector originating the
antenna along the primary direction of propagation.
The direction of the oscillating electrical field vector
i.e. orientation of the E-filed.
Four basic types of polarization
Vertical-, horizontal-linear polarization and Left-hand elliptical,
Right-hand elliptical polarization.
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
Radiation Parameters
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
How do we evaluate/design a antenna
in RF perspective?
• Network Analyzer
Input impedance
S-parameters
Transmission measurements
• Antenna Range
Radiation pattern
Gain
Polarization
• Simulation Tools
IE3D
HFSS
• Live Measurement Systems
TEMS
GPS dual reciver
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
TEMS
TEst Mobile System
• Tems is a tool for verification and planning of cellular system
• It is a ”live” test system, two mobile phones and a laptop is combined
• The system monitors and saves/log the signaling between Mobile phone
and Base station
Antenna testing using TEMS
• MS1 used with a reference antenna e.g. ¼-wave antenna mounted
on the middle of the roof
• MS2 connected to the test antenna
• A call is set up between the Mobile phone’s during the test
• Several test routs is driven to monitor different RF-conditions
• Evaluation is performed comparing the two Mobile phone’s using a Smarteq
developed program
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
TEMS
TEst Mobile System
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
TEMS
External antenna vs. Mobile in talk position
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
GPS, Global Positioning System
Do you know??
know??
• You need Three satellites to get a position fix
• You need Four satellites to get the Clock/Time
• The satellite signals gets weaker further to the north, the satellite
”turn back” at 55 degrees north
• The GPS signals are very weak, -112dBm, a comunication system
in the vicinity of the GPS system could cause it to fail,(GSM +33dBm)
• One orbit around the earth takes 11 hours and 57,97 minutes
• Smarteq GPS antennas are design/tested to work togheter with other
communication systems
• Smarteq GPS antennas are tested to work mounted at an angel
of 45 degrees
2001-11-18 Mattias Hellgren
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- AntennaDocument29 pagesAntennaVijay VermaNo ratings yet
- Sterlite Adsl Profile ConfigDocument8 pagesSterlite Adsl Profile ConfigVijay VermaNo ratings yet
- What Does The Celltool - MBX Program Do?Document1 pageWhat Does The Celltool - MBX Program Do?Vijay VermaNo ratings yet
- ReasoningDocument14 pagesReasoningVijay VermaNo ratings yet
- UserManual TSMWDocument94 pagesUserManual TSMWVijay VermaNo ratings yet
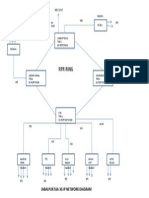
- RPR Ring: Jabalpur Ssa 3G Ip Network DiagramDocument1 pageRPR Ring: Jabalpur Ssa 3G Ip Network DiagramVijay VermaNo ratings yet
- 04-6224-301 Alcatel - Lucent 9312 Compact Smart Installation GuideDocument10 pages04-6224-301 Alcatel - Lucent 9312 Compact Smart Installation GuideVijay Verma100% (1)
- BTS Terminal User GuideDocument168 pagesBTS Terminal User GuideVijay VermaNo ratings yet
- AntennaDocument12 pagesAntennaVijay VermaNo ratings yet