Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cellular Adaptation
Uploaded by
Gary JammerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cellular Adaptation
Uploaded by
Gary JammerCopyright:
Available Formats
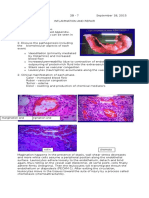
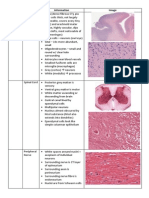
- CELLULAR ADAPTATION 1.
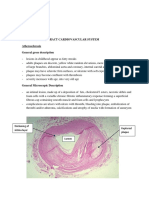
HYPERTROPHY Myocardial hypertrophy intercalated disc cytoplasm enlarged nucleus
Gross: - heart enlarged - trabecular muscles thickened - increase in weight and size Microscopic: - enlarged cytoplasm and nucleus (increase functional demand) - loss of striations - cytoplasm is bright pink & abundant - only a portion of the heart muscle, not all undergo hypertrophy
2. HYPERPLASIA Nodular hyperplasia, Prostate
fibromascular stroma prostatic nodule (of varying sizes, amorphous) lumen
fibroblast corpora amylacea (pink prostatic secretion)
pseudostratification of epithelium ?mitotic figure ?papilla ?papillary formation *common in elderly *Grossly: bossiliated, gray white, firm or rubbery in consistency, nodule protruding *Microscopically: nodules spongy in appearance *Normally lined by tall columnar cells which then transform into stratified squamous
3. ATROPHY Chronic glomerulonephritits (CGN)
lymphocytic infiltrates (violet dots) hyalinized glomeruli pink colloid substance (protein & other cell products) atropic renal tubule thickened artery
*lining of glomerulus (simple squamous) *function of glomerulus: filtration of body fluids *normally, PCT has small lumen and lined by simple cuboidal while DCT has wider lumen *more than 90% of the glomerulus in CGN is hyalinized (homgenous, glassy pink) *Chronic: lymphocytes; Acute: neutrophils *Predominant inflammatory cells: lymphocytes *Grossly: pallor, granular kidney
ATROPHY Renal Cell Carcinoma renal tubules (atropic pressure) kidney parenchyma tumor cells (clear, vacuolated cytoplasm; pyknotic) ?mitotic figure
*Grossly: huge tumor mass arises from the kidney parenchyma and well circumscribed *compression of the kidney parenchyma (medulla and cortex) - atropic pressure *malignant, there is overgrowth of tumore cells
4. METAPLASIA Chronic cervicitis with Squamous metaplasia cervix mononuclear cells fibromuscular stroma endocervical gland squamo-columnar junction
*Grossly: specimen consists of a firm, light tan, irregular tissue fragments with an aggregate diameter of 1.0cm labeled cervical tissues *exocervix lined with stratified squamous *endocervix: lined with columnar cells *metaplasia occurs in the endocervix because columnar cells are more sensitive
You might also like
- Diseases of the urinary system: kidney and bladder disordersDocument71 pagesDiseases of the urinary system: kidney and bladder disordersArsy Mira PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Pathology Lab Guidebook 2019 CH 17 Hepatobiliary SystemDocument11 pagesPathology Lab Guidebook 2019 CH 17 Hepatobiliary System6460801016No ratings yet
- Annalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.Document88 pagesAnnalyn S. Da-Anoy, M.D., R.M.T.api-25914483No ratings yet
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocument28 pagesChronic Pyelonephritisarun j.rNo ratings yet
- Kardiovaskular Anatomi Laboratorium Universitas Pembangunan Nasional JakartaDocument37 pagesKardiovaskular Anatomi Laboratorium Universitas Pembangunan Nasional Jakartainas khoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- Tumor Pada Ginjal: Dr.H.Delyuzar, M.Ked (Pa), Sppa (K)Document134 pagesTumor Pada Ginjal: Dr.H.Delyuzar, M.Ked (Pa), Sppa (K)Dony DamaraNo ratings yet
- Margination and Adhesion Margination and AdhesionDocument3 pagesMargination and Adhesion Margination and AdhesionKat JolejoleNo ratings yet
- Renal PathologyDocument119 pagesRenal PathologyEmmanuel God's willNo ratings yet
- Merging Result MergedDocument35 pagesMerging Result MergedEdmarie GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Guide to the Hepatobiliary System and Liver DiseaseDocument29 pagesGuide to the Hepatobiliary System and Liver DiseaseRahulNo ratings yet
- Pathology Seminar Review (Semester 1)Document26 pagesPathology Seminar Review (Semester 1)Lin AdutNo ratings yet
- Vascular Histology 1Document62 pagesVascular Histology 1Selim sarıgülNo ratings yet
- PECOMADocument25 pagesPECOMAAnan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Ug Practical SlideDocument18 pagesUg Practical SlideKNo ratings yet
- Neoplasms of Renal System: Dr. Mohamed Iqbal MusaniDocument24 pagesNeoplasms of Renal System: Dr. Mohamed Iqbal MusanihashridzNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PathologyDocument35 pagesCardiovascular Pathologyzeroun2480% (5)
- Bladder and Testis. PicDocument87 pagesBladder and Testis. PicDr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiNo ratings yet
- THYROID PATHOLOGY KEY POINTSDocument39 pagesTHYROID PATHOLOGY KEY POINTSPriiya AshiwiniNo ratings yet
- Renal Cancers - Shalom - 2Document30 pagesRenal Cancers - Shalom - 2Bryan FjbNo ratings yet
- 3 - Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Diseases 2.4 (2024)Document60 pages3 - Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Diseases 2.4 (2024)R. nounNo ratings yet
- 3rd Stage Liver Diseases (2) - HMUDocument31 pages3rd Stage Liver Diseases (2) - HMUjwan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Male Genital System Pathology OverviewDocument12 pagesMale Genital System Pathology OverviewStephanie NuñezNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument90 pagesBone Marrow ExaminationRuxandra MesarosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 (Renal Tumors)Document15 pagesLecture 9 (Renal Tumors)Logyn SamNo ratings yet
- ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS WITH ABSCESS: KIDNEY INFECTIONDocument14 pagesACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS WITH ABSCESS: KIDNEY INFECTIONIC BNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Anatomy GuideDocument61 pagesCirculatory Anatomy GuideEshtiey_MegaNo ratings yet
- Histology UnkownsDocument11 pagesHistology UnkownsBec Jeans100% (2)
- Glioma Types and GradesDocument176 pagesGlioma Types and GradesHikari AoiNo ratings yet
- Breast CytologyDocument34 pagesBreast Cytologypooo800% (1)
- Donor Liver and Kidney Frozen Section Evaluation CriteriaDocument7 pagesDonor Liver and Kidney Frozen Section Evaluation CriteriaJose SirittNo ratings yet
- Solid and Cystic Lesion of PancreasDocument27 pagesSolid and Cystic Lesion of PancreasRabina PantaNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Cell InjuryDocument42 pagesPraktikum Cell InjurySharmadave SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Brain and Body Pathology SlidesDocument20 pagesBrain and Body Pathology SlidesMrgNo ratings yet
- Autopsy Reveals Cardiomegaly, Emphysema, CirrhosisDocument5 pagesAutopsy Reveals Cardiomegaly, Emphysema, CirrhosisInukaicchi TakumichiNo ratings yet
- Spleen PowerpointDocument30 pagesSpleen PowerpointZakira Alberto100% (1)
- Liver, Mammary, Zymbal's Gland & Kidney Lesion CriteriaDocument17 pagesLiver, Mammary, Zymbal's Gland & Kidney Lesion CriteriaRavishankar NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Urinary SystemDocument29 pagesDiseases of Urinary SystemHassan.shehri100% (9)
- Pathology Slides 1Document28 pagesPathology Slides 1SydNo ratings yet
- SECTION 6: Spleen: and OverviewDocument38 pagesSECTION 6: Spleen: and Overviewtudoranluciana1No ratings yet
- The Liver: Dr. I Made Naris Pujawan, M.Biomed, SP - PADocument19 pagesThe Liver: Dr. I Made Naris Pujawan, M.Biomed, SP - PAAnonymous D29e00No ratings yet
- Connective Tissue TumorsDocument60 pagesConnective Tissue TumorsRahul Nagda67% (3)
- WBC Slide Diagnosis GuideDocument5 pagesWBC Slide Diagnosis GuideCenonina Paola TapiaNo ratings yet
- Gross SpecimensDocument16 pagesGross SpecimensRavi RagavendarNo ratings yet
- Glandular Cells & Benign Disorders The Uterine CervixDocument41 pagesGlandular Cells & Benign Disorders The Uterine CervixSara VinamdNo ratings yet
- Soft Tumour TissueDocument43 pagesSoft Tumour TissueAakhyaaNo ratings yet
- Review Paper: I. Explain Briefly The Following TermDocument6 pagesReview Paper: I. Explain Briefly The Following Termapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Endo ImagingDocument4 pagesEndo ImagingRachel BarrosNo ratings yet
- Tumours of KidneyDocument39 pagesTumours of KidneyjabirNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Ang, Karl Justin L., Mti University of Santo Tomas 4D-MTDocument44 pagesHematology: Ang, Karl Justin L., Mti University of Santo Tomas 4D-MTKarl J. AngNo ratings yet
- Renal Tumors Classification GuideDocument38 pagesRenal Tumors Classification GuideMim Rashed0% (1)
- DI Abdomen P 674 737 PART 2 SEC 3Document64 pagesDI Abdomen P 674 737 PART 2 SEC 3tudoranluciana1No ratings yet
- NEUROPATHOLOGYDocument28 pagesNEUROPATHOLOGYPratama SutardiNo ratings yet
- Salivary gland cytology guideDocument30 pagesSalivary gland cytology guidePatrick BayuNo ratings yet
- Solid Renal Mass: Hisham Alkhatib, M.DDocument49 pagesSolid Renal Mass: Hisham Alkhatib, M.DMinaz PatelNo ratings yet
- Lymph Node cytologyDocument55 pagesLymph Node cytologyBoy blueNo ratings yet
- Practical 4 Cardivascular and Hepatobiliary SystemDocument9 pagesPractical 4 Cardivascular and Hepatobiliary SystemchinNo ratings yet
- Childhood TumoursDocument23 pagesChildhood Tumoursarun j.rNo ratings yet
- CNS TumorDocument32 pagesCNS TumorBbem ooNo ratings yet
- Skin PathologyDocument55 pagesSkin PathologyJhost Clinton PurbaNo ratings yet